Method for recovering valuable metals from positive electrode material of waste lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery and positive electrode material technology, applied in the field of recycling valuable metals, can solve the problems of large environmental risks, solid waste water, large consumption of acid and alkali, etc., achieve high industrial application prospects, reduce recycling costs, and high recovery rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] A kind of method of the present invention reclaims valuable metal from waste lithium ion battery anode material lithium cobalt oxide, comprises the following steps:
[0047] (1) Discharge the lithium cobaltate lithium-ion waste battery with 100g / L salt water; disassemble and remove the metal casing (or soft case), and separate the positive electrode sheet, negative electrode sheet, diaphragm, and electrolyte; the obtained positive electrode sheet Carry out crushing and sieving to separate aluminum foil and positive electrode material.
[0048] (2) Separate the positive electrode material and ammonium bisulfate according to n((NH 4 ) HSO 4 ) / n(Co+2Li)=1.1 (molar ratio) and mixed in a tube furnace, the temperature of the calcination is 500° C., and the calcination time is 1 h.
[0049] (3) Crush the obtained roasted material, use pure water (or tap water) to prepare the slurry according to the liquid-solid ratio of 3:1ml / g, and stir and leaching for 30 minutes in a wate...
Embodiment 2
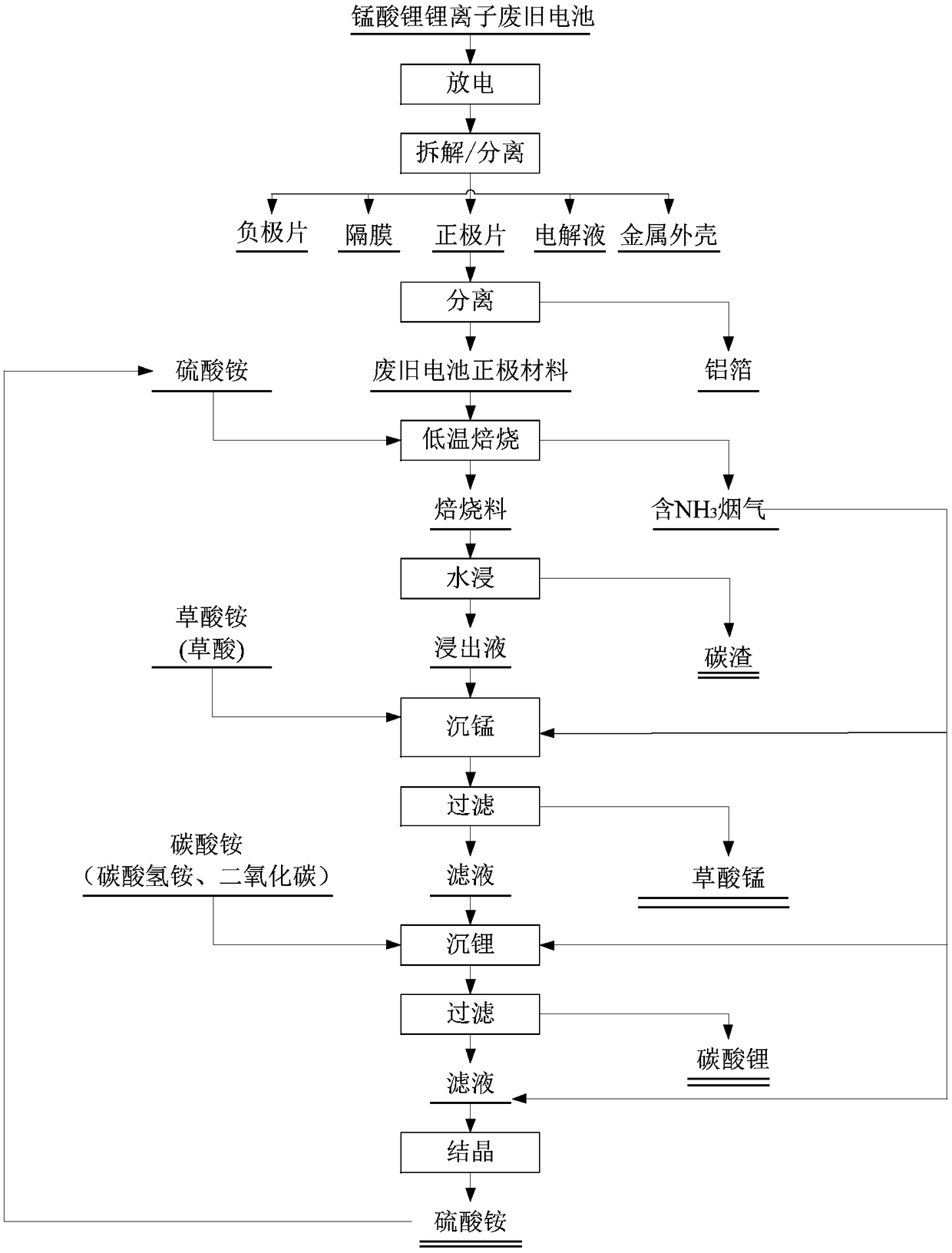
[0055] A method of reclaiming valuable metals from waste lithium ion battery cathode material lithium manganate of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0056] (1) Use 100g / L salt water to discharge lithium manganate lithium-ion waste batteries; disassemble and remove the metal casing (or soft case), and separate the positive electrode sheet, negative electrode sheet, diaphragm, and electrolyte; the obtained positive electrode sheet Crushing and sieving are carried out to separate aluminum foil and positive electrode material.
[0057] (2) The obtained positive electrode material is mixed with ammonium bisulfate according to n((NH 4 ) HSO 4 ) / n(Mn+2Li)=1.2, and roasted in a tube furnace, the temperature of the roasting is 500° C., and the roasting time is 1 h.
[0058] (3) Crush the obtained roasted material, use pure water (or tap water) to prepare the slurry according to the liquid-solid ratio of 3:1ml / g, and stir and leaching for 30 minutes in a water bat...
Embodiment 3
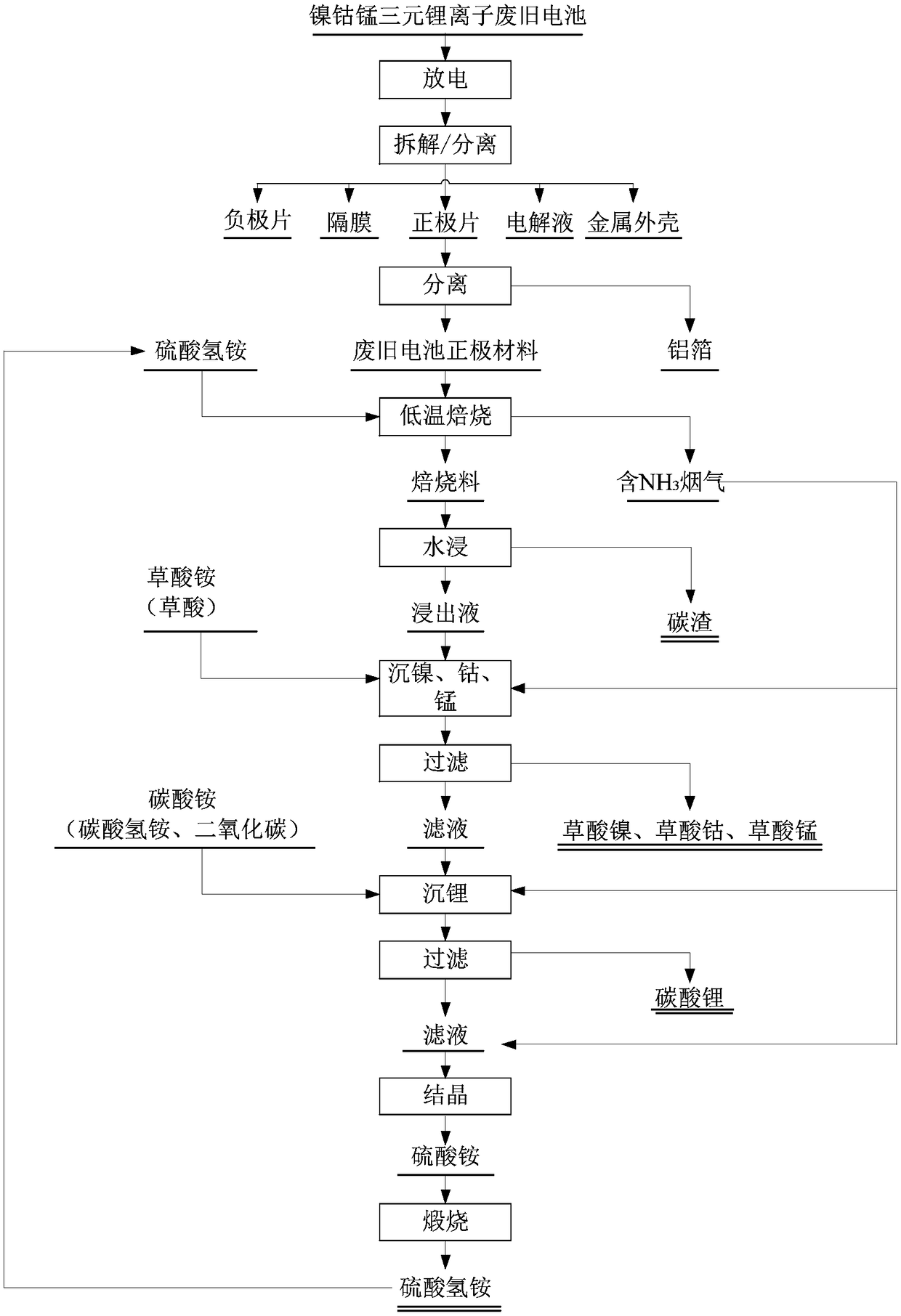
[0063] A method for recovering valuable metals from the ternary material of the positive electrode material of the waste lithium-ion battery according to the present invention, the process flow chart is as follows figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0064] (1) Discharge the waste nickel-cobalt-manganese ternary lithium-ion battery with 100g / L salt water, disassemble and remove the metal casing (or soft casing), and separate the positive electrode sheet, negative electrode sheet, diaphragm, and electrolyte. The obtained positive electrode sheet is crushed, and the aluminum foil and the positive electrode material are screened out.
[0065] (2) The obtained positive electrode material is mixed with ammonium bisulfate according to n((NH 4 ) HSO 4 ) / n(Ni+Co+Mn+2Li)=1.3, and roasted in a tube furnace, the temperature of the roasting is 550° C., and the roasting time is 2 hours.
[0066] (3) Crush the obtained roasted material, use pure water (or tap water) to prepar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com