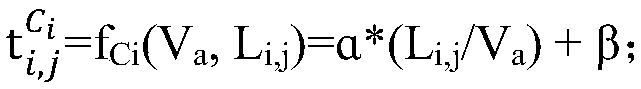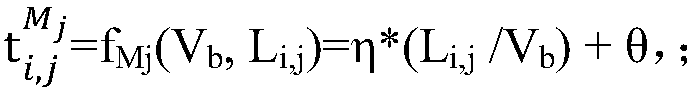Space-time correlation target re-identification method and system
A spatiotemporal correlation and re-identification technology, applied in the field of target re-identification, can solve the problems of not considering the real-time motion state of the target, staying in the drawing of GIS maps, and the phase and time of the target movement trajectory being out of synchronization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments. The following examples will help those skilled in the art to further understand the present invention, but do not limit the present invention in any form. It should be noted that those skilled in the art can make several modifications and improvements without departing from the concept of the present invention. These all belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
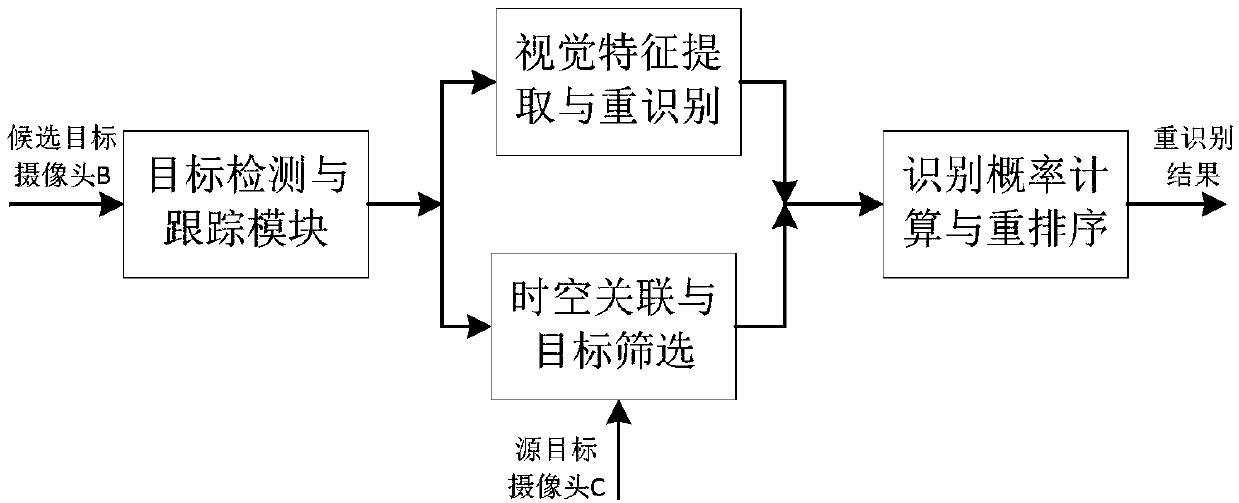
[0042] The present invention combines the pixel motion rate of the target in the video data to estimate the probability distribution of the duration of the target crossing two adjacent cameras with a certain distance in each segment of video data; The target is screened and pre-processed to filter out candidate targets that exceed the reasonable spanning time interval, reducing the probability of similar targets being mistakenly matched as tracking targets.
[0043] Specifically, in the embodiment...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com