Process method for producing high-tin-lead-calcium alloy by using waste lead-acid battery waste lead grid
A technology of waste lead-acid batteries and a process method, which is applied in the field of comprehensive recycling of waste lead-acid batteries, can solve the problems of inability to utilize metal tin in waste lead-acid grids, achieve good reaction effects, simple process, and reduce production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
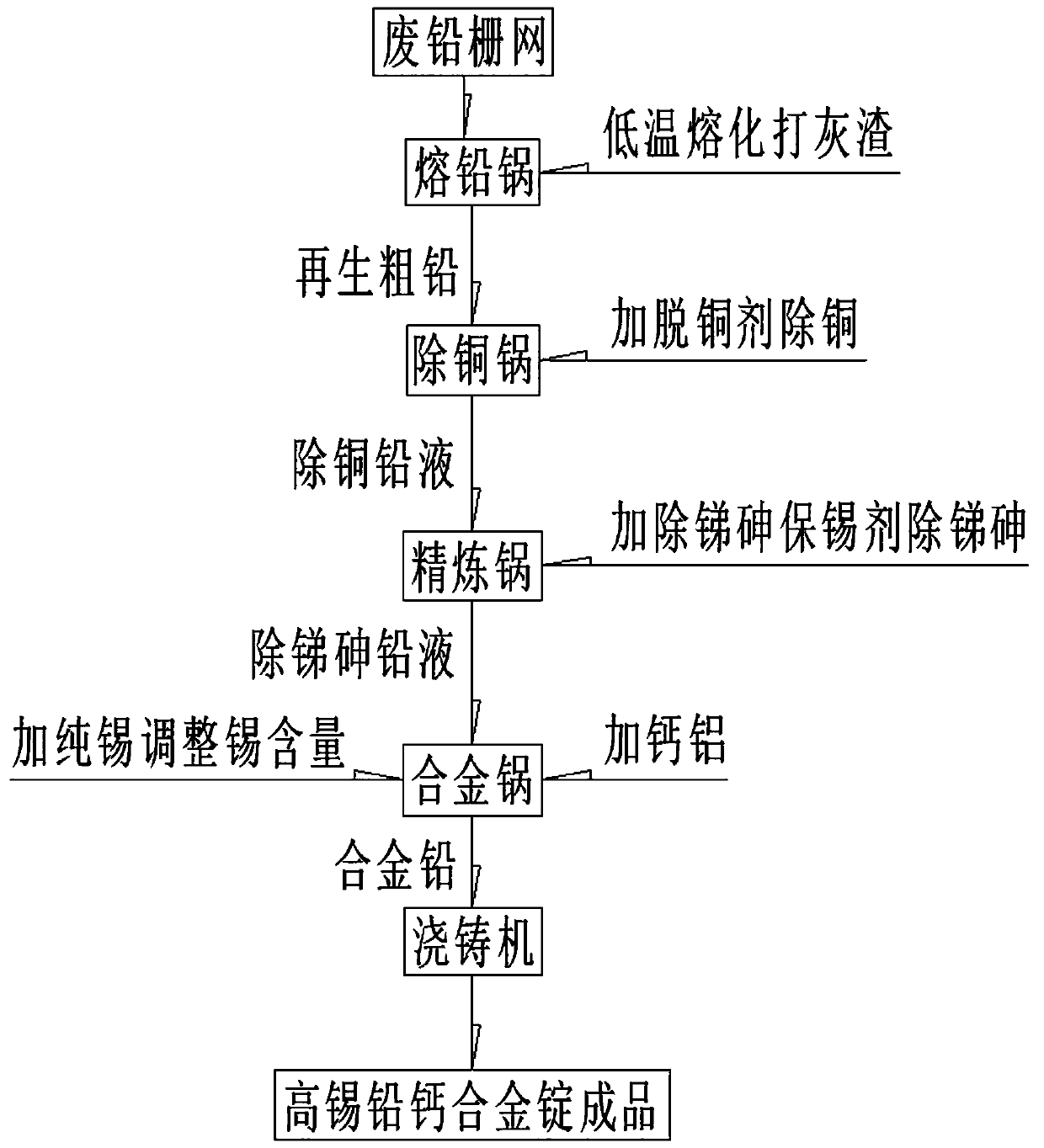
[0034] Example 1: The waste lead grid is melted in the melting pot at 410±20°C, and the lead liquid is pumped into the copper removal pot with a lead pump after the ash is removed, and the sampling spectrum is analyzed. The composition: Sb 0.132%, As 0.0051%, Sn 0.71 %, Cu 0.013%, Bi 0.0031%, Ag0.00062%, Pb balance; heating up to 490±20°C, adding pyrite powder to remove copper, sampling direct reading spectral analysis, the composition is as follows: Sb 0.130%, As 0.0051 %, Sn 0.70%, Cu 0.0005%, Bi 0.0031%, Ag 0.00062%, Pb balance.
[0035] After the ash and slag are crushed, the copper and lead liquid is pumped into the refining pot with a lead pump.
[0036] Raise the temperature of the copper and lead removal solution in the refining pot to 580±20°C, calculate the amount of antimony, arsenic and tin retention agent based on 1.1 times the total amount of antimony and arsenic, turn on the mixer, stir the lead solution to generate a vortex, and input the speed so that it does ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: The waste lead grid is melted in the melting pot at 370±20°C, after the ash is removed, the lead liquid is pumped into the copper removal pot with a lead pump, and the sampling spectrum is analyzed. The composition: Sb 0.08%, As 0.009%, Sn 0.61 %, Cu 0.013%, Bi 0.004%, Ag0.00078%, Pb balance; cool down to 360±20°C, add red phosphorus to remove copper, sample direct reading spectrum analysis, the composition is as follows: Sb0.081%, As 0.0081%, Sn 0.592%, Cu 0.0004%, Bi 0.004%, Ag 0.00078%, Pb balance.
[0040] After the ash and slag are crushed, the copper and lead liquid is pumped into the refining pot with a lead pump.
[0041] Raise the temperature of the copper and lead removal liquid in the refining pot to 570±20°C, calculate the amount of antimony, arsenic and tin retention agent used as 1.5 times the total amount of antimony and arsenic, turn on the mixer, stir the lead liquid to generate a vortex, and input the speed so as not to affect the vortex Th...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3: The waste lead grid is melted at 430±20°C in the melting pot, and after the ash is removed, the lead liquid is pumped into the copper removal pot with a lead pump, and the sampling spectrum is analyzed. The composition: Sb 0.07%, As 0.01%, Sn 0.45 %, Cu 0.014%, Bi 0.004%, Ag0.0008%, Pb balance; heating up to 480±20°C, adding pyrite powder to remove copper, sampling direct reading spectrum analysis, the composition is as follows: Sb 0.069%, As 0.0091 %, Sn 0.45%, Cu 0.00046%, Bi 0.004%, Ag 0.00079%, Pb balance.
[0045] After the ash and slag are crushed, the copper and lead liquid is pumped into the refining pot with a lead pump.
[0046] Raise the temperature of the copper and lead removal solution in the refining pot to 580±20°C, calculate the amount of antimony, arsenic and tin retention agent used as 1.4 times the total amount of antimony and arsenic, turn on the mixer, stir the lead solution to generate a vortex, and input the speed so as not to affect t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com