High-level transmission method and device used in base station and UE (User Equipment)
A technology of serial number and bit group, applied in the direction of transmission modification based on link quality, adjustment of transmission mode, transmission system, etc., can solve problems such as packet loss and inability to correctly interpret the serial number of protocol data packets.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
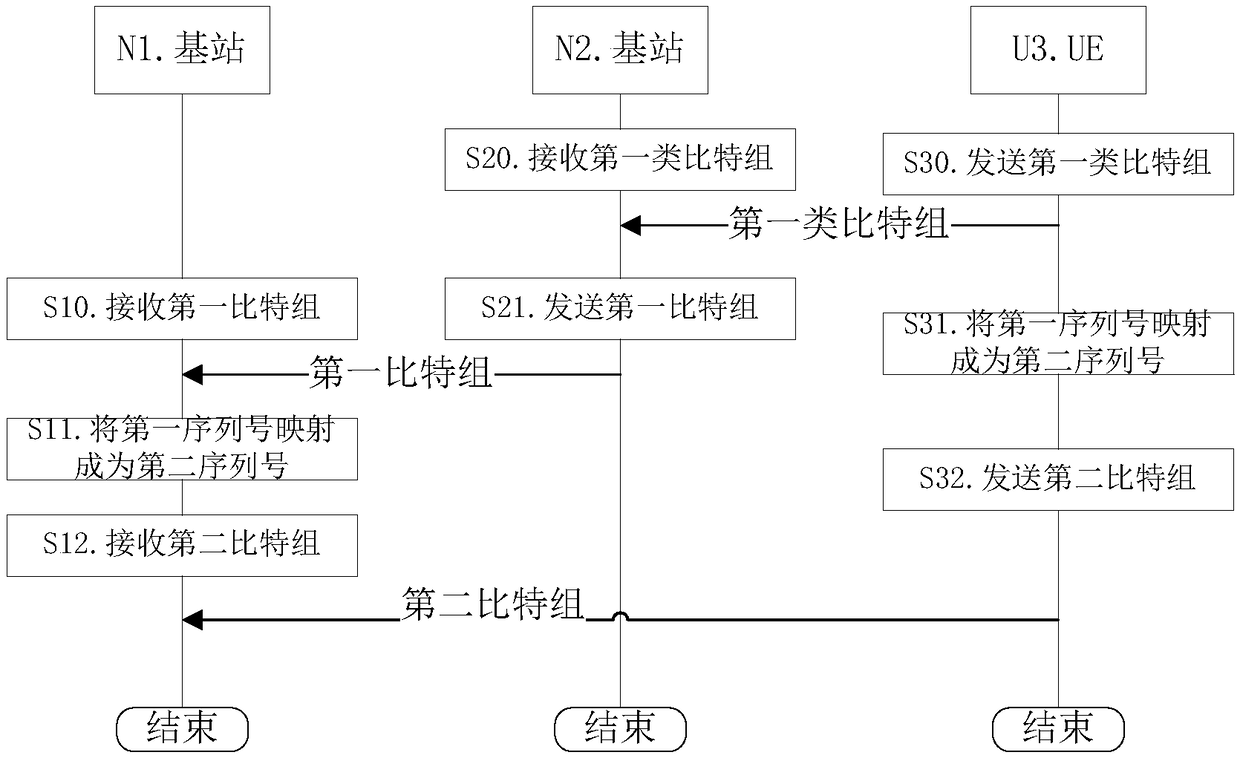
[0275] Embodiment 1 illustrates a flow chart of a transmission initiated by the first node, as shown in the attached figure 1 shown. attached figure 1 In , the base station N1 and the base station N2 are the maintenance base stations of the serving cell of the user equipment UE U3. figure 1 Describe the scenario of uplink transmission.
[0276] for base station N1 , the first bit group is received in step S10, the first sequence number is mapped to the second sequence number in step S11, and the second bit group is received in step S12. The first bit group includes {the first serial number, the first bit sequence}. The second bit group includes {the second sequence number, the first bit sequence}.
[0277] for base station N2 , receiving the first type of bit group in step S20, and sending the first bit group in step S21. The first type of bit group includes {the first type of serial number, and the bit sequence associated with the first type of serial number}. The f...
Embodiment 2
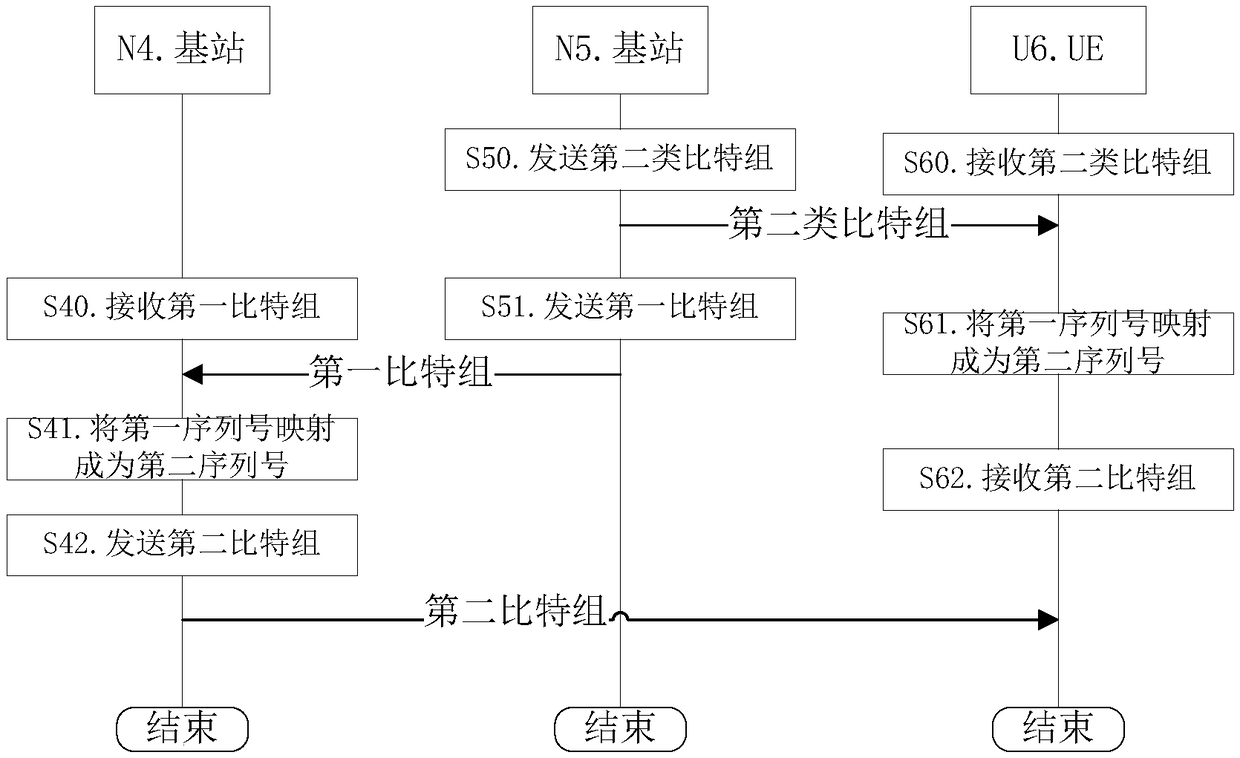
[0325] Embodiment 2 illustrates another flow chart of the transmission initiated by the first node, as shown in the attached figure 2 shown. attached figure 2 In , the base station N4 and the base station N5 are the maintenance base stations of the serving cell of the user equipment UE U6. figure 2 Describe the scenario of downlink transmission.
[0326] for base station N4 , the first bit group is received in step S40, the first sequence number is mapped to the second sequence number in step S41, and the second bit group is sent in step S42. The first bit group includes {the first serial number, the first bit sequence}. The second bit group includes {the second sequence number, the first bit sequence}.
[0327] for Base station N5 , the second type of bit group is sent in step S50, and the first bit group is sent in step S51. The first bit group includes {the first serial number, the first bit sequence}. The second-type bit group includes {second-type serial numb...
Embodiment 3
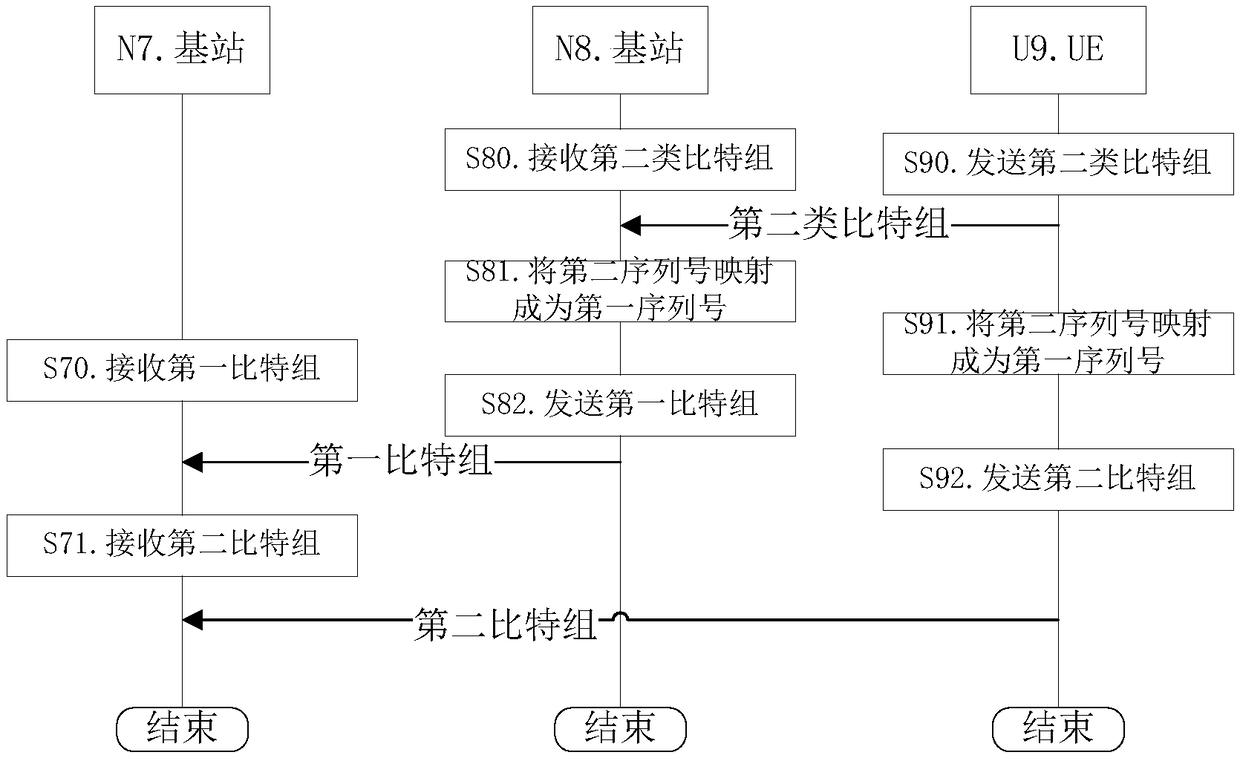
[0379] Embodiment 3 illustrates a flow chart of the transmission initiated by the second node, as shown in the attached image 3 shown. attached image 3 In , the base station N7 and the base station N8 are the maintenance base stations of the serving cell of the user equipment UE U9. image 3 Describe the scenario of uplink transmission.
[0380] for base station N7 , the first bit group is received in step S70, and the second bit group is received in step S71. The first bit group includes {the first serial number, the first bit sequence}. The second bit group includes {the second sequence number, the first bit sequence}.
[0381] for base station N8 , in step S80 the second type of bit group is received, in step S81 the second sequence number is mapped to the first sequence number, in step S82 the first bit group is sent. The second-type bit group includes {second-type serial number, bit sequence associated with the second-type serial number}. The first bit group i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com