Quantum random number generator for source-independent high-dimensional time encoding
A quantum random number, source-independent high-dimensional technology, applied in the field of quantum communication, can solve the problem that the output rate is not very high, and achieve the effect of improving the output rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
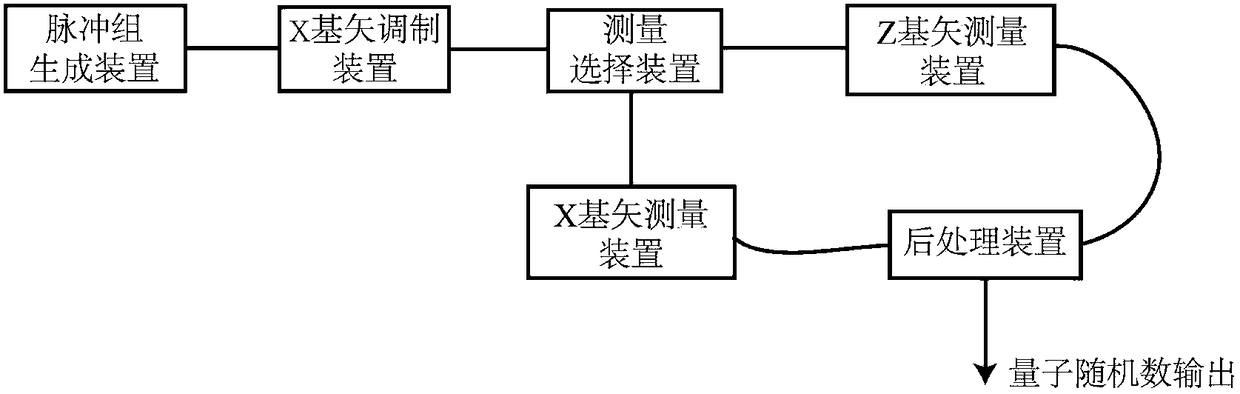
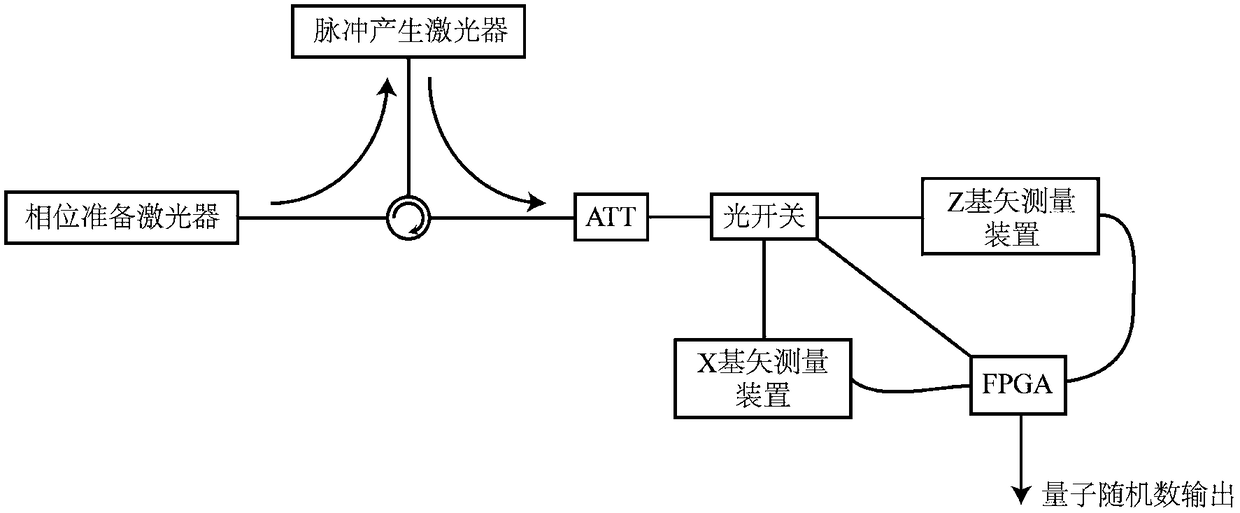
[0075] see image 3 , a source-independent high-dimensional time-coded quantum random number generator in this embodiment includes a sending module and a receiving module that match each other. The sending module includes phase preparation laser, pulse generating laser, fiber circulator and attenuator (ATT); the receiving module includes optical switch, X base vector measuring device, Z base vector measuring device and post-processing device (FPGA).
[0076] Taking encoding dimension 4 as an example, the working process of the quantum random number generator in this embodiment includes:
[0077] 1. The phase preparation laser generates long pulses and injects pulses into the fiber circulator to generate lasers;
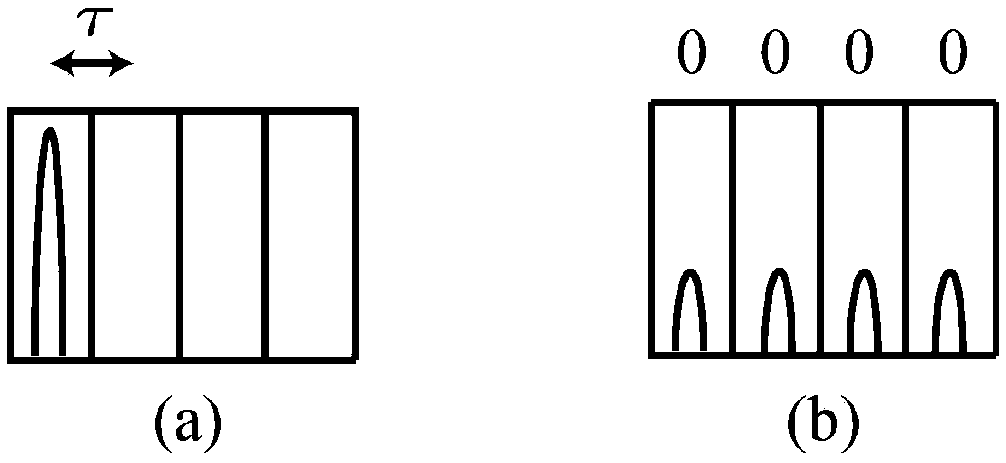
[0078] Prepare the internal modulation method of the laser driving voltage by adjusting the phase (see below for details), and modulate the pulse group to a certain eigenstate |f of the X basis vector i >, the value is selected in advance, and each pulse group is mo...
Embodiment 2
[0097] see Figure 9 , in this embodiment, an unbalanced beam splitter (BS) is used for passive measurement; the transmittance and reflectivity of the BS are the same as the probability of the Z-based vector modulation and the X-based vector modulation; the BS divides the incident pulse component beam into two The transmitted pulse group enters the Z-based vector measuring device and the reflected pulse group enters the X-based vector measuring device. Due to the passive measurement, there is no need for additional random numbers to select the measurement device and the specific beam splitting ratio is given by parameter optimization. The rest of the devices and steps of this embodiment are the same as in Embodiment 1, so they will not be described in detail.
Embodiment 3
[0099] see Figure 10 , in the sending module of the present embodiment, the continuous laser light emitted by the laser is modulated by an intensity modulator (IM) to output a short pulse sequence; four consecutive short pulses in the pulse sequence form a pulse group, and the phase modulator (PM) will Each pulse group is modulated to a preselected eigenstate of an X basis vector. The remaining devices and steps of this embodiment are the same as those of Embodiment 1, so they will not be described in detail.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com