Preparation of zero-valent iron supported MC (mesoporous carbon) composite and method for degrading sulfachloropyridazine by persulfate activation based on zero-valent iron supported MC (mesoporous carbon) composite
A technology of sulfamethazine and composite materials, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, other chemical processes, chemical/physical processes, etc., can solve problems such as biological toxicity, secondary pollution, and catalysts that are not easy to recycle and reuse, and achieve no The effect of secondary pollution, enhanced adsorption and degradation, and broad practical application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
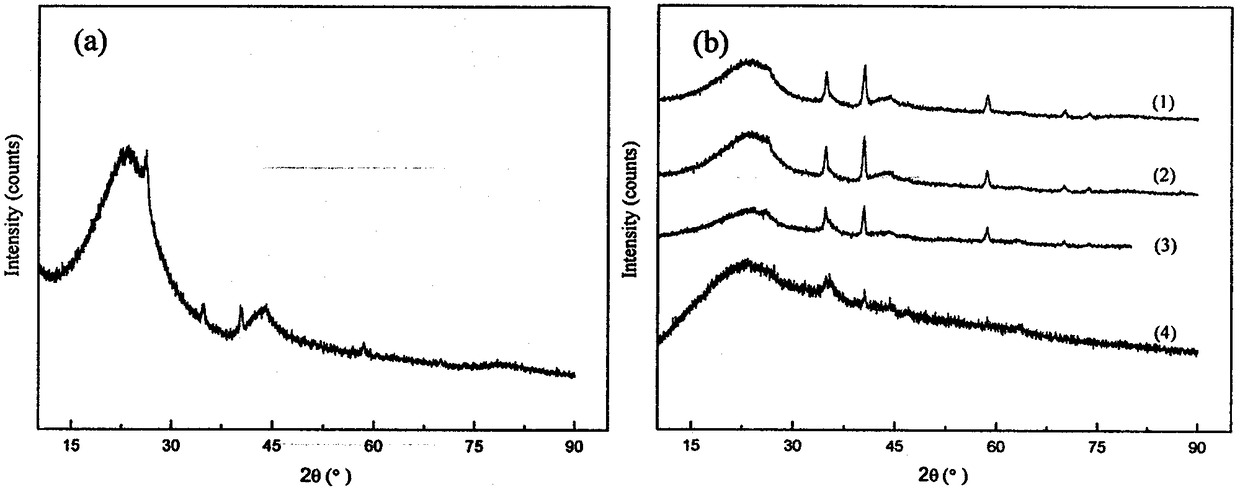
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] In this example, the adsorption efficiency of mesoporous carbon and mesoporous carbon-supported zero-valent iron composite materials under different material dosages was investigated.
[0032] Mesoporous carbon material: put 25g of PVA and 25g of magnesium carbonate in a mortar, mix and grind evenly, and then pass the mixture through a 200-mesh sieve; put the resulting mixture in a tube furnace and raise the temperature to 900°C at 5°C / min, and keep it for 2h, the whole process was protected under a nitrogen atmosphere with a flow rate of 70mL / min; the resulting product was washed three times with 1mol / L dilute sulfuric acid and deionized water, and the concentration of magnesium ions in the solution was measured to make it close to zero. At this time, the solution was Neutral; centrifuge with a high-speed centrifuge (10,000 rpm) to obtain a solid; place the obtained solid in a constant temperature drying oven and dry at 105° C. to obtain a mesoporous carbon material, wh...
Embodiment 2
[0041] This example compares the effect of activated sodium persulfate on the removal rate of sulfamethazine under the conditions of different dosages of mesoporous carbon-loaded zero-valent iron composite materials.
[0042] The preparation method of the mesoporous carbon material and the mesoporous carbon-loaded zero-valent iron composite material involved in this example is the same as that of Example 1.
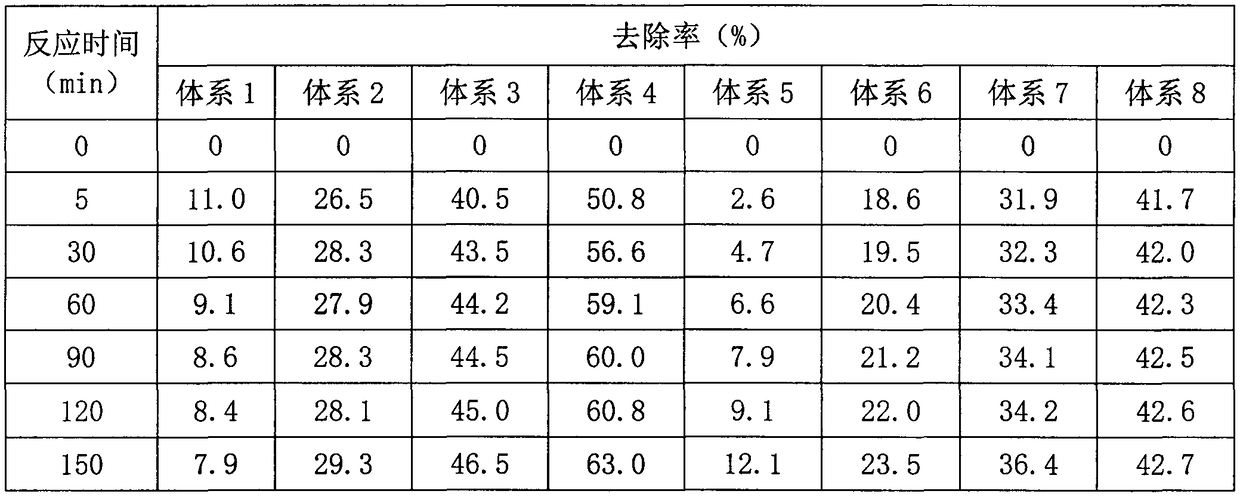
[0043] The prepared mesoporous carbon-supported zero-valent iron composite material was used as the catalyst, and its dosage was 0, 0.0308, 0.0616, 0.0924 and 0.1232 g, which were respectively recorded as systems 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5; sulfamethazine As the target pollutant, the initial concentration of the aqueous solution is 50mg / L, and the volume is 100mL; the mass of sodium persulfate is 0.0476g, the reaction temperature is 30°C, the pH is not adjusted, and the conical flask is used as the reactor. Place it in a constant temperature oscillator and vibrate for a certain per...
Embodiment 3
[0049] This embodiment compares the influence of different qualities of the oxidizing agent sodium persulfate on the degradation rate of sulfamethazine.
[0050] The preparation method of the mesoporous carbon material and the mesoporous carbon-loaded zero-valent iron composite material involved in this example is the same as that of Example 1.
[0051] Utilize the prepared mesoporous carbon loaded zero-valent iron composite material as catalyst, its dosage is 0.0616g, sulfamethazine is target pollutant, the initial concentration of its aqueous solution is 50mg / L, and volume is 100mL; Sodium persulfate The masses are 0, 0.0119, 0.0238, 0.0476, 0.0714 and 0.1190g respectively, which are respectively recorded as systems 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6; the reaction temperature is 30°C, the pH is not adjusted, and the conical flask is used as the reactor . Place it in a constant temperature oscillator and vibrate for a certain period of time, take samples at 15, 30, 45, 60, 75 and 90 minute...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com