Method for fermenting high-yield echinocandins B through aspergillus nidulans
An echinocandin and Aspergillus nidulans technology is applied in the field of using Aspergillus nidulans to ferment high-yield echinocandin B, can solve the problems of high viscosity of fermentation broth, hindered dissolved oxygen mass transfer, etc., and achieves good application prospects and fermentation products. Yield improvement effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: Preparation of Echinocandin B (ECB) by Fermentation of Aspergillus nidulans A.nidulans ZJB 09223
[0029] Dig an area of about 1cm with an inoculation shovel 2 A. nidulans ZJB09223 (CCTCC M 2012300, disclosed in patent application CN 103509840A, CN 201310478251.6) plate colony was inoculated into a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 50ml of seed medium, and cultured at 25°C for 48h to obtain seed liquid. Seed medium (g / L) preparation: soybean cake powder 25, glucose 10, glycerin 10, solvent is distilled water, pH value is natural, sterilized at 115°C for 30 minutes.
[0030] In order to investigate the influence of a single carbon source in the medium on the fermentation level and cell morphology of ECB, five different fermentation mediums were designed, the volume of the shake flask was 50ml / 250ml, and the composition of the fermentation medium was as follows:
[0031] Fermentation medium (g / L) I (original medium): mannitol 97, glycerol 10.0, peptone 8.6, ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: Fermentation of Aspergillus nidulans A.nidulans ZJB 09223 to prepare ECB
[0040] Dig an area of about 1cm with an inoculation shovel 2 The plate colony of Aspergillus nidulans (A. nidulans) ZJB 09223 was inoculated into a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 50.0ml of seed medium, and cultured at 25°C for 48h to obtain a seed solution. Seed culture medium is with embodiment 1.
[0041] In order to investigate the effect of different concentrations of methyl oleate on the fermentation level of ECB, five different fermentation media were designed, the liquid volume of the shake flask was 50ml / 250ml, and the composition of the fermentation media was as follows:
[0042] Medium (g / L) I: methyl oleate 54, peptone 8.6, soybean cake powder 40.0, peanut oil 20.0, L-threonine 2.1, L-ornithine 6.1, K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O 3.2, CaCl 2 0.5, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.5, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.5, MnSO 4 ·H 2 O 0.2, CuSO 4 ·5H 2 O 0.6, the solvent is distilled water, the pH value ...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3: Fermentation of Aspergillus nidulans A.nidulans ZJB 09223 to prepare ECB
[0051] Dig an area of about 1cm with an inoculation shovel 2 The plate colony of Aspergillus nidulans (A. nidulans) ZJB 09223 was inoculated into a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 50.0ml of seed medium, and cultured at 25°C for 48h to obtain a seed solution. Seed culture medium is with embodiment 1.
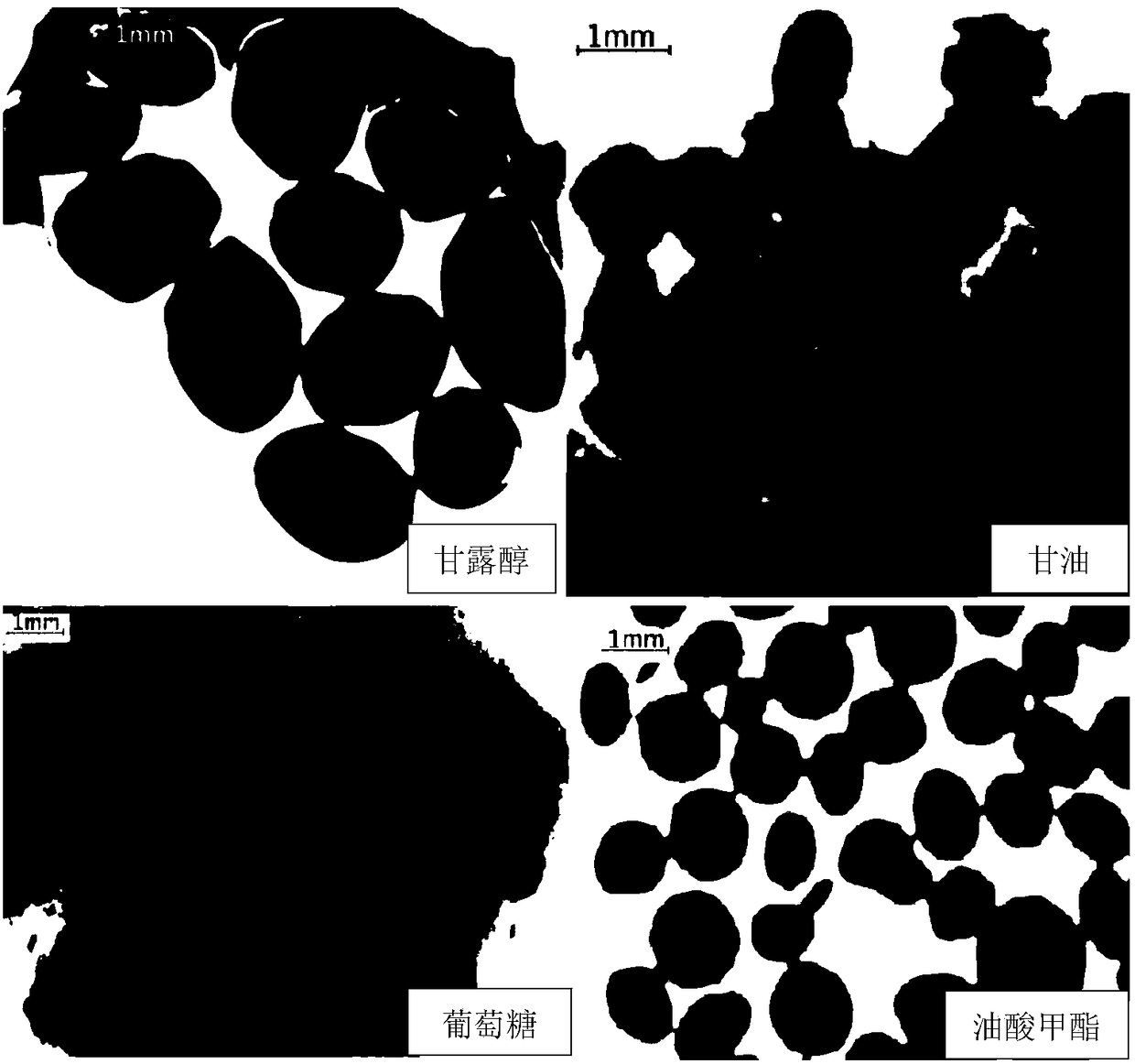
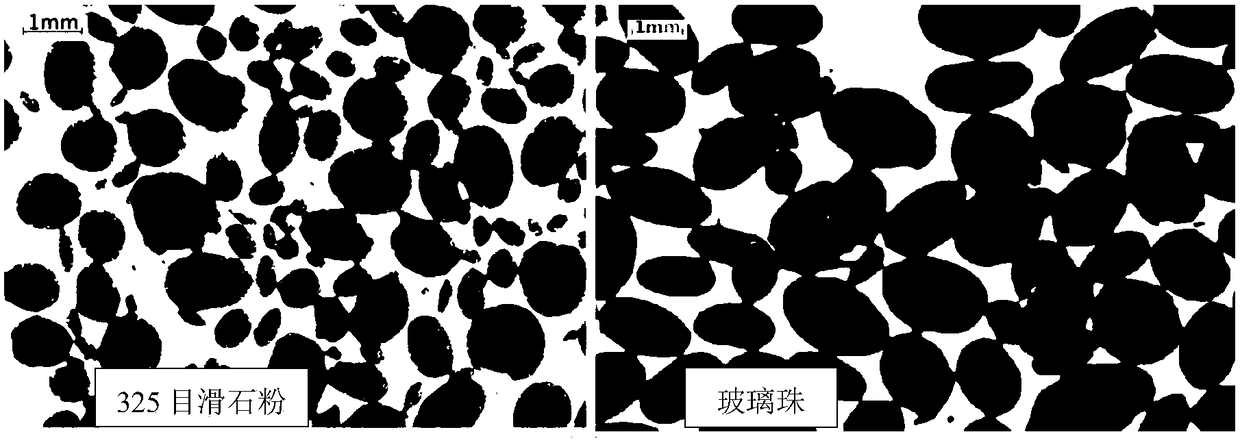
[0052] In order to investigate the effect of different particle additions on ECB fermentation level and cell morphology (see figure 2 ) influence, based on the culture medium in embodiment 3, design 5 different fermentation mediums, the liquid volume of shaking the flask is 50ml / 250ml, and the fermentation medium composition is respectively:
[0053] Medium (g / L) I (blank control): methyl oleate 114, peptone 8.6, soybean cake powder 40.0, peanut oil 20.0, L-threonine 2.1, L-ornithine 6.1, K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O 3.2, CaCl 2 0.5, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.5, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.5, MnSO 4 ·H 2...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com