Resonant fiber optic gyroscope coherent demodulation system and method based on external beam interference
A beam and source resonance technology, applied in Sagnac effect gyroscopes and other directions, can solve the problems of inability to completely suppress laser frequency noise, semiconductor laser high frequency noise, etc., to reduce laser frequency noise, clear signal spectrum, reduce effect of influence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
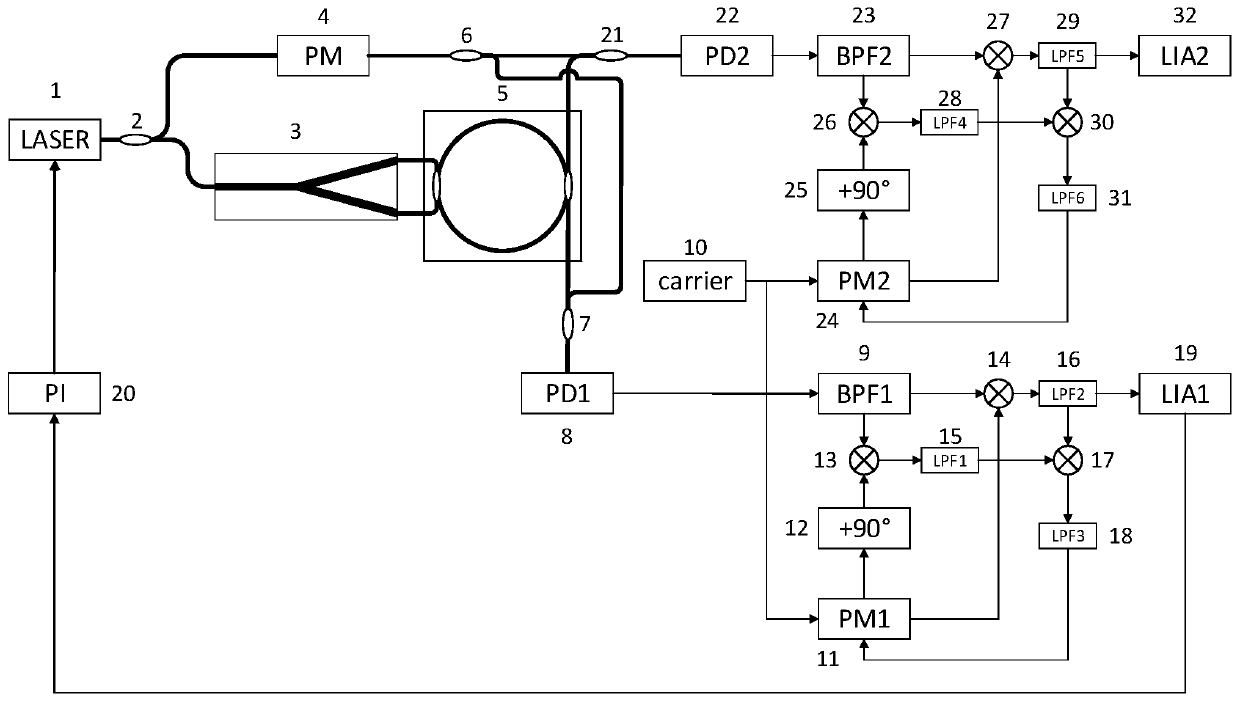
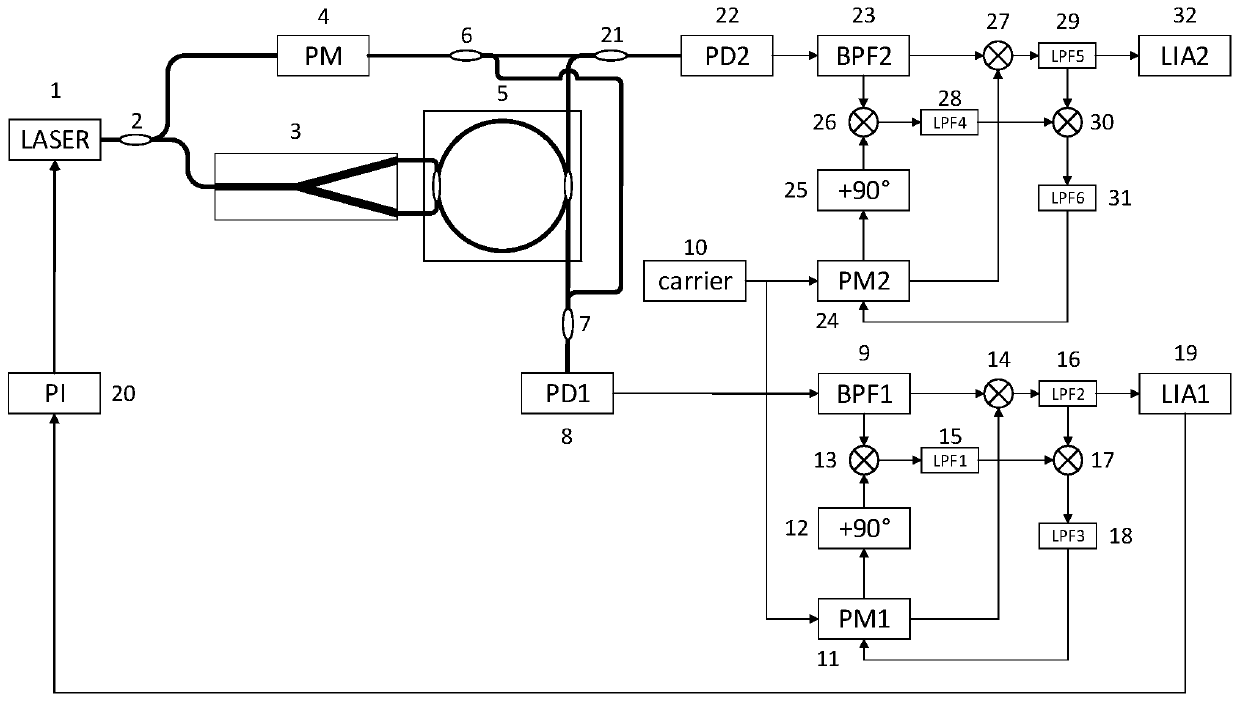
[0022] Such as figure 1As shown, a resonant fiber optic gyro coherent demodulation system based on external beam interference includes a laser 1, a first polarization-maintaining coupler 2, a Y-branch phase modulator 3, a phase modulator 4, a fiber resonator 5, and a second polarization-maintaining coupler A bias coupler 6, a third polarization maintaining coupler 7, a first photodetector 8, a first bandpass filter 9, a second photodetector 10, a local carrier generation module 10, a first local carrier phase shift module 11, 90 ° phase shift module 12, the first multiplier 13, the second multiplier 14, the first low-pass filter 15, the second low-pass filter 16, the third multiplier 17, the third low-pass filter 18, the first A digital lock-in amplifier 19, a PI servo loop 20, a fourth polarization maintaining coupler 21, a second photodetector 22, a second bandpass filter 23, a second local carrier phase shift module 24, and a second 90° phase shift Module 25, the fourth mu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com