Preparation method of good-biocompatibility, enzyme-responsive and antibacterial titanium material
A biocompatible, enzyme-responsive technology, used in tissue regeneration, surface reaction electrolytic coating, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of antibiotics not diffusing freely, low bacterial efficiency, etc., and achieve good biocompatibility and responsiveness. The effect of antibacterial ability, simple operation and strong controllability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] A method for preparing a biocompatible enzyme-responsive antibacterial titanium material, characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0068] 1) Utilize the anodic oxidation method to construct the titanium dioxide nanotube that pipe diameter is 70nm as drug reservoir, and carry out the loading of antibiotic to it;
[0069] 1.1) Wash the titanium foil (10mm×10mm) with ethanol, acetone, ethanol and distilled water for 15 minutes respectively; after drying, perform electrochemical corrosion;
[0070] The temperature of the drying process is 60°C;
[0071] In the electrochemical corrosion process: the platinum foil is used as the cathode, and the titanium foil is used as the anode; the electrolytic solution is a water / glycerol mixture containing ammonium fluoride, the concentration of the ammonium fluoride is 0.27M, and the volume ratio of the water and glycerin is 1:1;
[0072] In the electrochemical corrosion process, the constant voltage is 20V, and the e...
experiment example 1
[0107] Release of CecB and degradation of multilayer films
[0108] In this experimental example, different concentrations of hyaluronidase (0.01, 0.05 and 0.5mg / ml) and Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli with OD=0.5 were used to study the effect of hyaluronidase on the multilayer film on the surface of the material. Responsive release situation; specifically include the following steps:
[0109] 1) In order to verify the effect of hyaluronidase on drug release, 6 samples of each group (TNT@Van-LBL and TNT@Van-LBLc) were soaked in 500 μL PBS and PBS containing different concentrations of hyaluronidase (HAase- PBS) solution;
[0110] After incubation (37°C) for different times (2, 4, 8, 12, 24, 48, 72 h), 5 μL of leachate was taken from each group of samples to detect the release rate of Van.
[0111] In this experiment, the release amount of Van was measured by Nanodrop at a wavelength of 237nm, and the calculation formula was: Van (%)=(total release amount of Van) / (...
experiment example 2
[0123] Detection of osteoblast adhesion and differentiation on the material surface
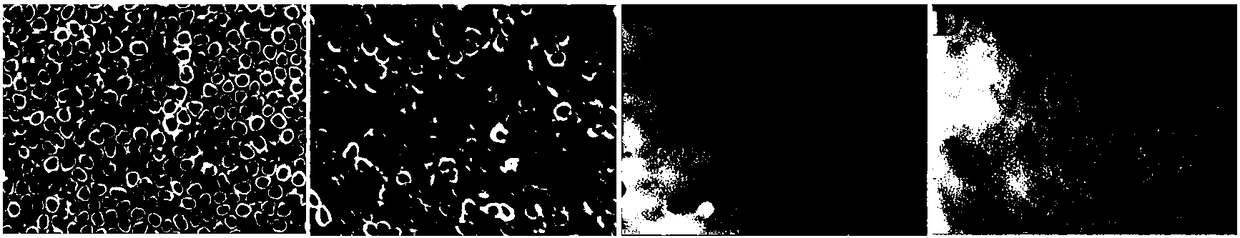
[0124] When the osteoblasts grow to the third generation, 2×10 4 The density of one / well was inoculated on the surface of each titanium substrate, and cultured for 1 hour. Hochest33258 was used to stain the nucleus of osteoblasts for 5 minutes. The adhesion and differentiation of osteoblasts were observed under an inverted fluorescent microscope, and the number of cells was counted.
[0125] Figure 7 It is the cell adhesion situation (the blue color in the figure is the nucleus stained by H33258) of osteoblasts on the surface of different modified samples after culturing for 1 hour;
[0126] like Figure 7 As shown in (c), the surface of the Chi / HA multilayer film without catechol group modification is not conducive to the adhesion and differentiation of osteoblasts, and it is easy to aggregate into clumps, while Chi-c / HA-c The surface of the polyelectrolyte multilayer film promotes the a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com