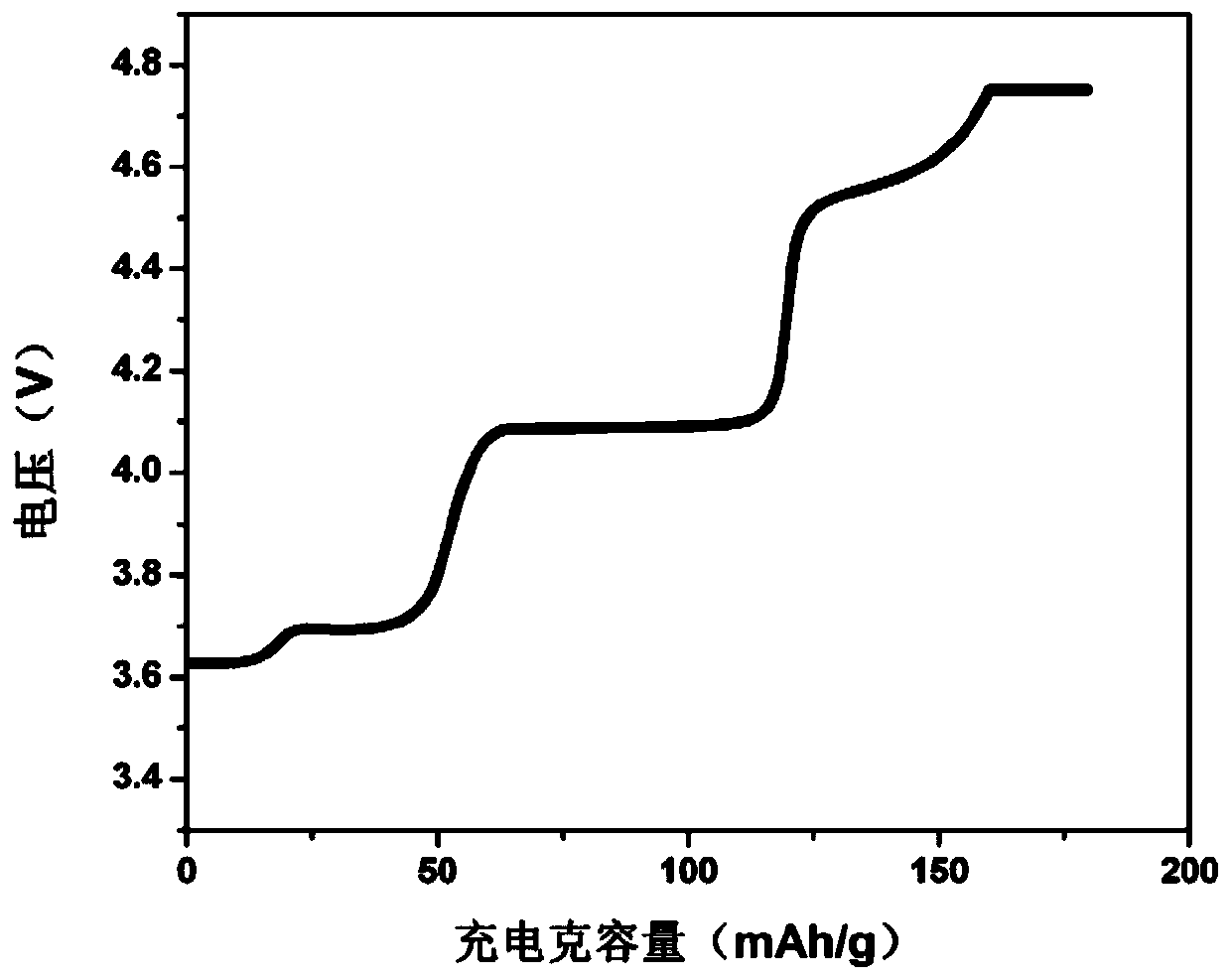
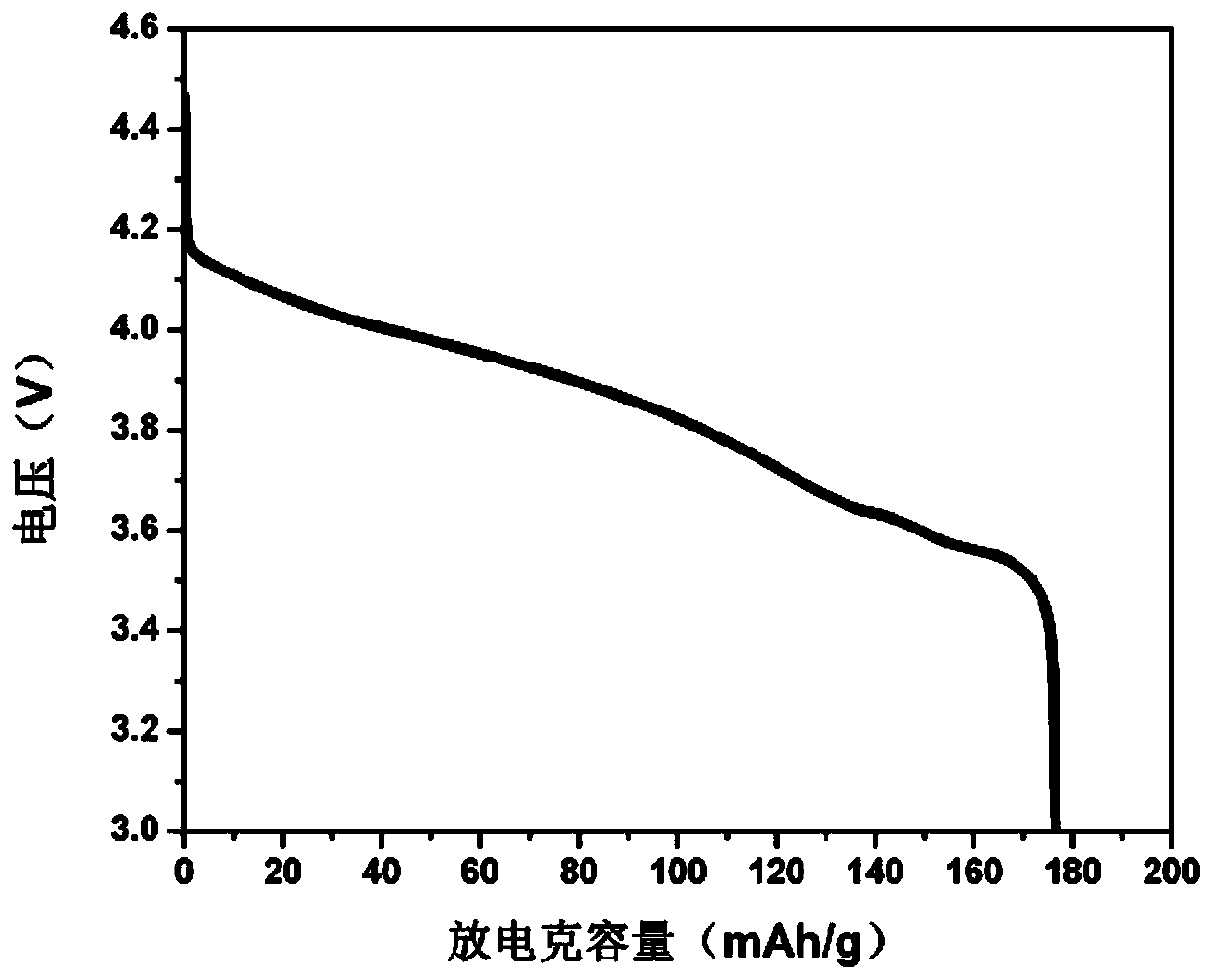
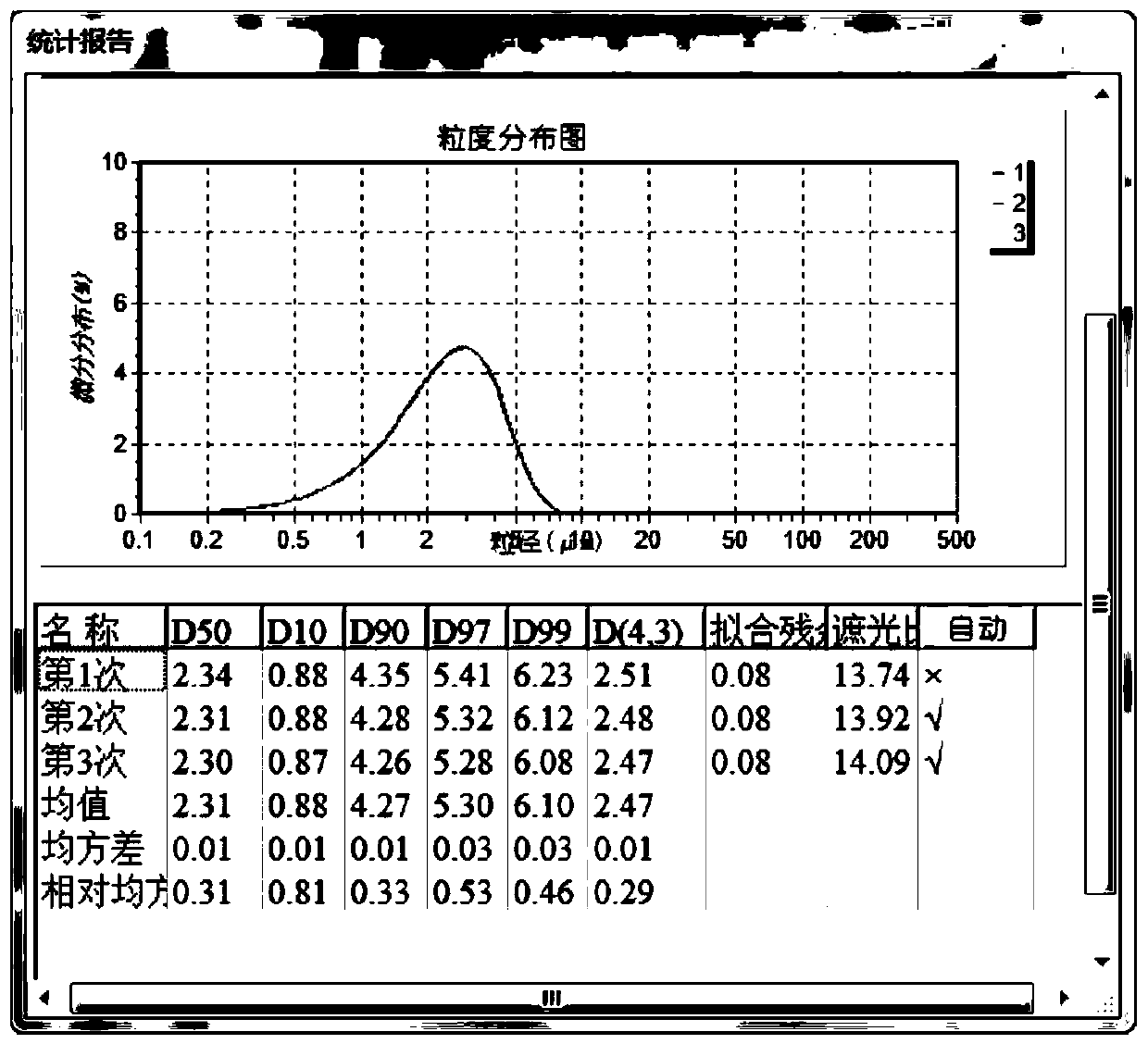
Lithium vanadium phosphate and preparation method thereof
A lithium vanadium phosphate and lithium source technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, structural parts, etc., can solve problems such as uneven dispersion and poor electrochemical performance of lithium vanadium phosphate, and achieve the effect of improving purity and quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0030] The embodiment of the present invention provides a method for preparing lithium vanadium phosphate, which includes the following steps:
[0031] S01. Provide lithium source, vanadium source, and phosphorus source, first dissolve the lithium source in inorganic acid, then add the vanadium source, phosphorus source, and complexing agent to mix, and react at a temperature below 100°C to obtain Precursor solution
[0032] S02. The precursor solution is vacuum dried under conditions below 0°C to obtain a lithium vanadium phosphate precursor;
[0033] S03. The lithium vanadium phosphate precursor is sequentially subjected to a first sintering treatment and a second sintering treatment to obtain lithium vanadium phosphate, wherein the second sintering treatment is performed in an inert atmosphere.
[0034] The preparation method of lithium vanadium phosphate provided by the embodiment of the present invention has the following advantages:
[0035] First of all, on the one hand, the use...
Embodiment 1
[0053] A preparation method of lithium vanadium phosphate includes the following steps:
[0054] Weigh lithium hydroxide and dissolve it in nitric acid, then add vanadium pentoxide, diammonium hydrogen phosphate and citric acid, (lithium source: vanadium source: phosphorus source is 1.08:1:1) and stir at 70℃. Carry out low-temperature (-40°C) vacuum drying to obtain a lithium vanadium phosphate precursor. The lithium vanadium phosphate precursor is pre-sintered, and the temperature is raised to 350°C at a rate of 5°C / min, and sintered for 4 hours. The reaction chamber is replaced with nitrogen gas, and then the temperature is raised to 800°C at a rate of 10°C / min. 10h.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com