Composite phase-change material used at temperature of 2-8 DEG C and preparation method thereof
A composite phase change material and phase change material technology, which is applied in the field of 2-8°C composite phase change material and its preparation, can solve the problems of reducing energy storage, small thermal conductivity, and easy oxidation of phase change materials, and achieve the purpose of inhibiting phase change. Stratification, less undercooling, and reduced phase separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
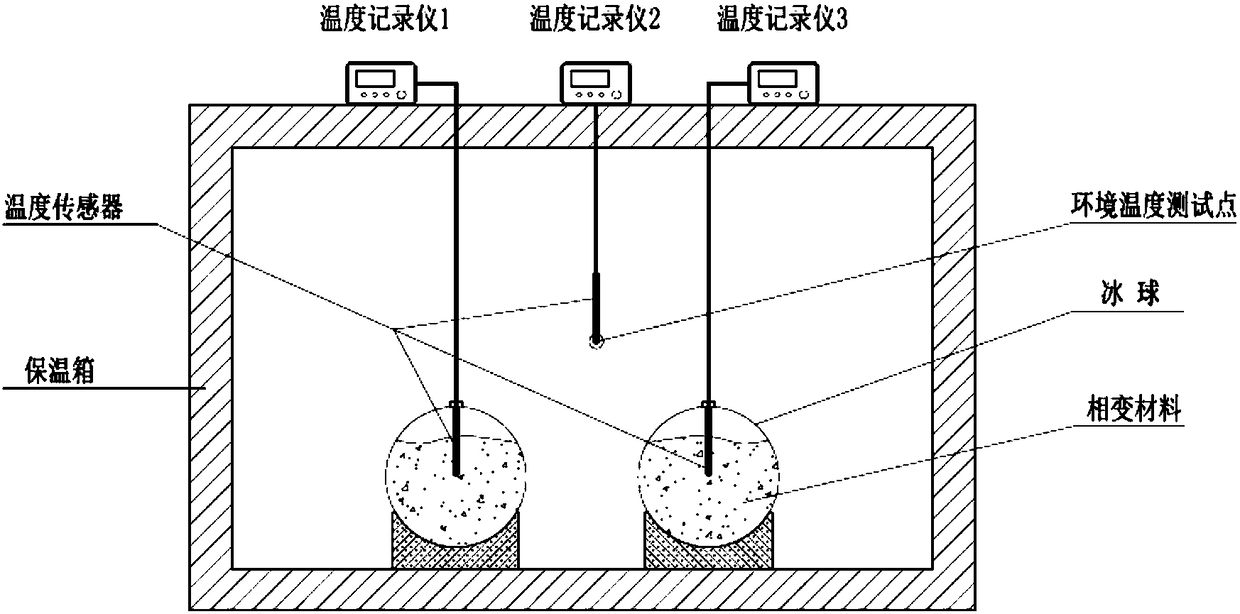
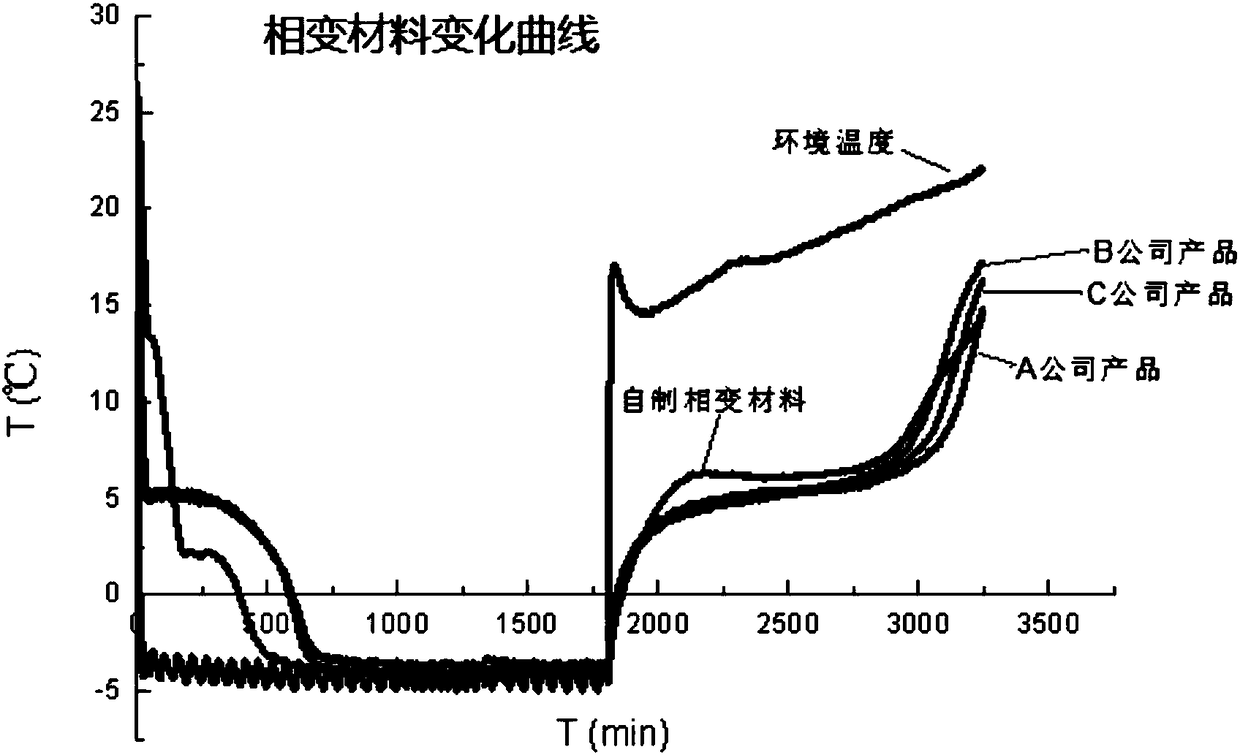
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] A method for preparing a composite phase change material at 2-8°C includes the following steps:
[0021] Step 1: Place the anhydrous sodium sulfate raw material in a blast drying box and dry it to constant weight at 100°C;
[0022] Step 2: According to the mass parts of each raw material, weigh 35 parts of anhydrous sodium sulfate, 5 parts of sodium chloride, 10 parts of potassium chloride, 20 parts of ammonium chloride, 2 parts of boric acid, 2 parts Borax, 1 part of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, 1 part of hydrophilic aerogel are mixed, and then ground in a ball mill until the particle size of the mixture reaches 80-100μm;
[0023] Step 3: Add 24 parts of distilled water to the ground mixture and stir it into a uniform molten slurry at 40°C to obtain a 2-8°C composite phase change material.
Embodiment 2
[0025] A method for preparing a composite phase change material at 2-8°C includes the following steps:
[0026] Step 1: Place the anhydrous sodium sulfate raw material in a blast drying box and dry it to constant weight at 110°C;
[0027] Step 2: According to the mass parts of each raw material, weigh 50 parts of anhydrous sodium sulfate, 8 parts of sodium chloride, 10 parts of potassium chloride, 15 parts of ammonium chloride, 3 parts of boric acid, 3 parts Borax, 2 parts of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, 3 parts of hydrophilic aerogel are mixed, and then ground in a ball mill until the particle size of the mixture reaches 90-120μm;
[0028] Step 3: Add 40 parts of distilled water to the ground mixture and stir at 50°C to form a uniform molten slurry to obtain a 2-8°C composite phase change material.
Embodiment 3
[0030] A method for preparing a composite phase change material at 2-8°C includes the following steps:
[0031] Step 1: Place the anhydrous sodium sulfate raw material in a blast drying box and dry it to constant weight at 110°C;
[0032] Step 2: According to the mass parts of each raw material, weigh 40 parts of anhydrous sodium sulfate, 8 parts of sodium chloride, 15 parts of potassium chloride, 15 parts of ammonium chloride, 2.5 parts of boric acid, 2.5 parts Borax, 4 parts of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, 1 part of hydrophilic aerogel were mixed, and then ground in a ball mill until the particle size of the mixture reached 200-240μm;
[0033] Step 3: Add 50 parts of distilled water to the ground mixture, and stir at 60°C to form a uniform molten slurry to obtain a 2-8°C composite phase change material.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com