EpCAM/PSMA dual-antibody-based functionalized micro-fluidic chip as well as preparation method and application thereof
A microfluidic chip and functionalized technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, stress-stimulated microbial growth methods, cell dissociation methods, etc., can solve the problem of slow progress in CTCs research, different, lack of specific target molecules, etc. problem, to achieve high specificity, high sensitivity, high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
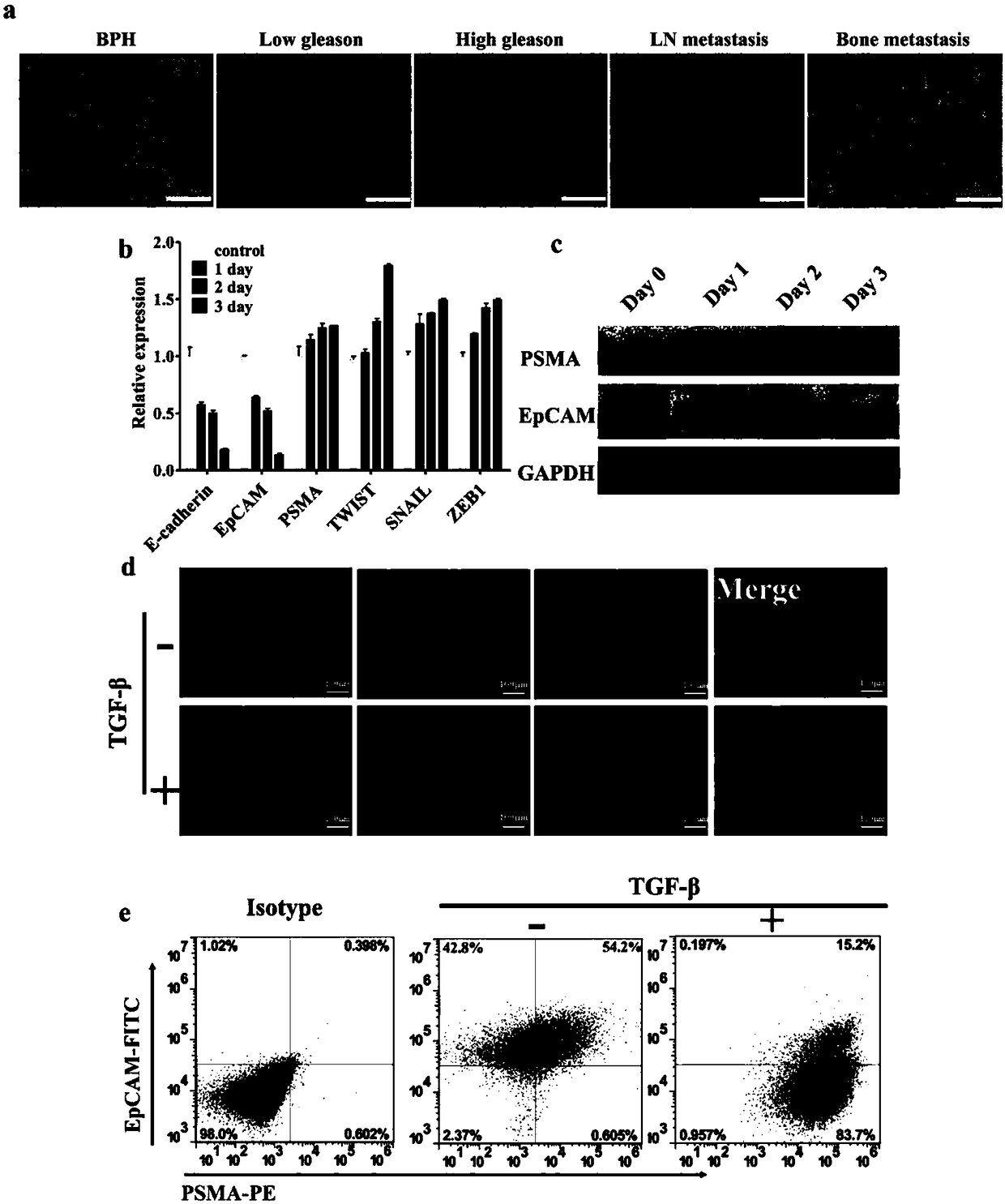
[0089] Example 1: Immunohistochemical detection of PSMA expression level in prostate cancer tissue
[0090] The expression levels of PSMA in tissues of patients with different types of prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia were detected by immunohistochemical technique.
[0091] 1) Collect concomitant bone metastasis (Bone metastasis), lymph node metastasis (LN metastasis) or different Gleason scores (different scores refer to low scores and high scores, low scores refer to gleason scores less than 7, high scores refer to gleason scores Pathological sections of tumor tissue from patients with prostate cancer with a score greater than 7), and the tissue from BPH patients as a control; the above sections are collectively referred to as paraffin tissue sections;
[0092] 2) Put the paraffin tissue sections obtained in step 1) in an oven at 65°C for 2 hours, dewax to water, wash three times with PBS (concentration: 10mM, pH7.2-7.4), and then place the sections in EDTA b...
Embodiment 3
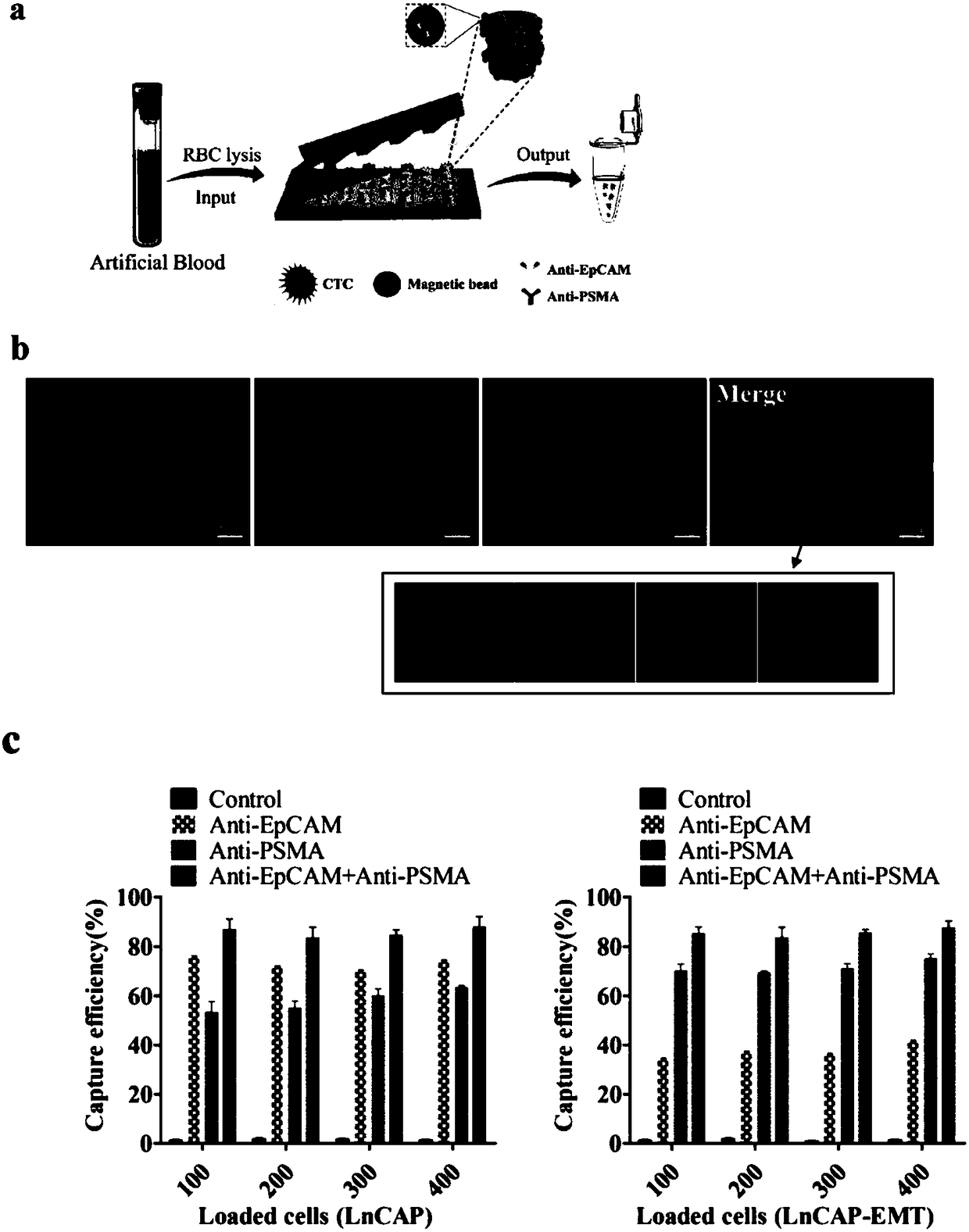
[0189] Example 3 Validation of Prostate Cancer CTCs Capture Efficiency in Simulated Blood Environment
[0190] Take an appropriate amount of prostate cancer cell LnCAP and LnCAP-EMT stimulated by TGF-β1 and add it to 1mL peripheral whole blood of healthy subjects, and mix well, so as to simulate the detection of circulating tumor cells in the peripheral blood environment. After adding erythrocyte lysate to remove erythrocytes, the EpCAM / PSMA double antibody functionalized microfluidic chip was used to identify and capture prostate cancer cells in the peripheral blood simulated environment, and the captured cells were identified by immunofluorescence.
[0191] 1) 2 mL of peripheral venous blood was collected from 24 healthy individuals, and stored in EDTA (Ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) vacuum blood collection tubes for anticoagulation.
[0192] 2) Take 1 mL of the prepared LnCAP-EMT single cell suspension stimulated by LnCAP and TGF-β1, and...
Embodiment 4
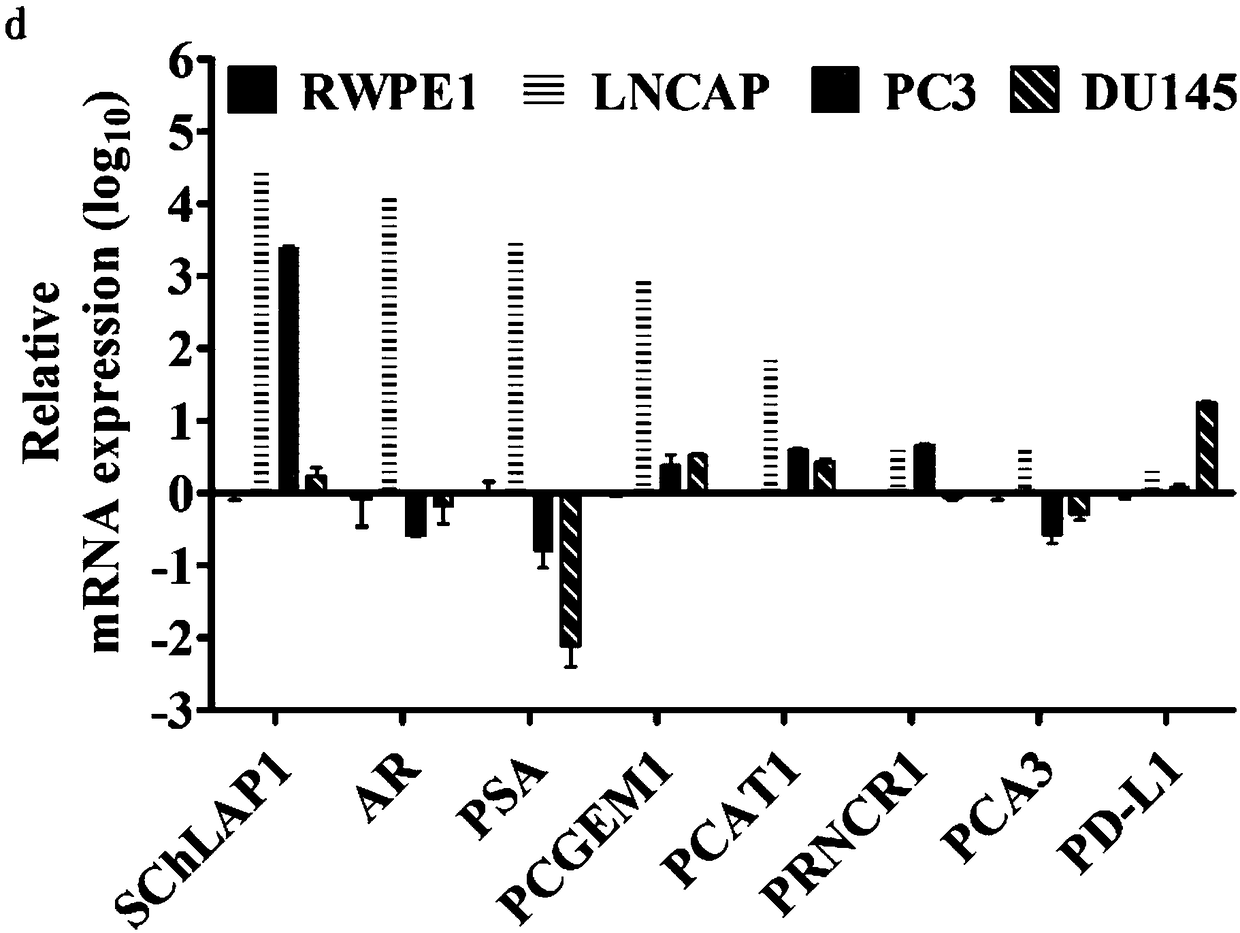
[0202] Example 4 Capture and Identification of CTCs in Peripheral Blood of Prostate Cancer Patients
[0203] Collect 1 mL of peripheral blood samples from patients with clinical prostate cancer, add erythrocyte lysate to remove red blood cells, and further identify and capture prostate cancer cells in the peripheral blood environment by EpCAM / PSMA double antibody functionalized microfluidic chips, and capture the captured prostate cancer cells Cells were identified by immunofluorescence.
[0204] 1) Put the peripheral blood of the prostate cancer patient into a centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 3000rpm for 5min, and discard the supernatant.
[0205] 2) Add 5 mL of erythrocyte lysate, mix the cells well, and lyse at room temperature for 5 minutes, shaking 1-3 times during the period.
[0206] 3) Centrifuge at 300g for 5 minutes, remove the supernatant, and observe whether the erythrocytes in the bottom cell pellet are completely lysed. If not, follow the above steps to lyse again...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com