Monitoring equipment-based target object speed calculation method
A technology of monitoring equipment and speed calculation, which is applied in the field of intelligent transportation, can solve the problems of large speed error and large result error, and achieve the effect of improving precision, accuracy, and calculation accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
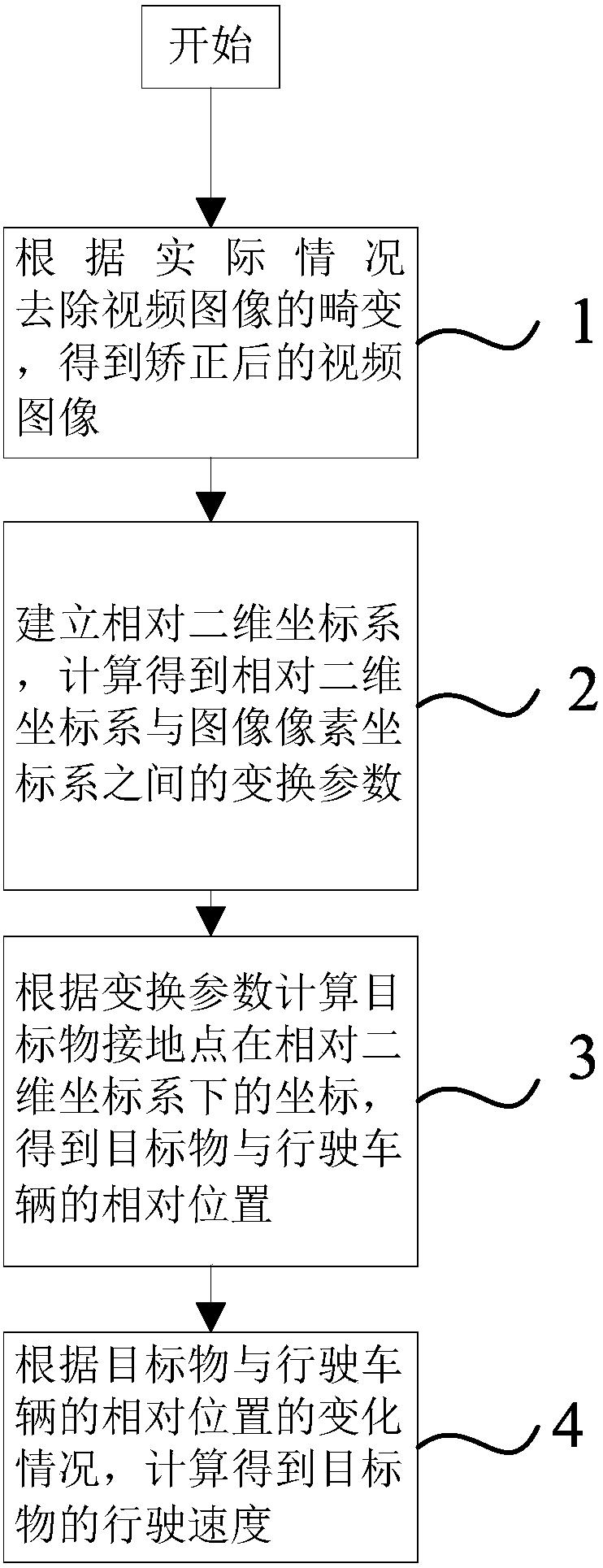
[0057] Such as figure 1 As shown, the purpose of this embodiment is to provide a method for calculating the speed of an object based on monitoring equipment, including the following steps:
[0058] 1) When the coordinates of the original video image in the image physical coordinate system are known, the distortion of the video image is removed to obtain a corrected video image;
[0059] 2) Establish a relative two-dimensional coordinate system, and calculate the transformation parameters between the relative two-dimensional coordinate system and the image pixel coordinate system;
[0060] 3) Calculate the coordinates of the ground point of the target object in the relative two-dimensional coordinate system according to the transformation parameters obtained in step 2), and obtain the relative position of the target object and the driving vehicle;
[0061] 4) According to the change of the relative position of the target object and the driving vehicle, the running speed of the...
Embodiment 2
[0134] Such as figure 1 As shown, the purpose of this embodiment is to provide a method for calculating the speed of an object based on monitoring equipment, including the following steps:
[0135] 1) When the coordinates of the original video image in the image physical coordinate system are unknown, the distortion of the video image is removed to obtain a corrected video image;
[0136] 2) Establish a relative two-dimensional coordinate system, and calculate the transformation parameters between the relative two-dimensional coordinate system and the image pixel coordinate system;
[0137] 3) Calculate the coordinates of the ground point of the target object in the relative two-dimensional coordinate system according to the transformation parameters obtained in step 2), and obtain the relative position of the target object and the driving vehicle;
[0138] 4) According to the change of the relative position of the target object and the driving vehicle, the running speed of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com