Plant ecologically concentrated feed and preparation method thereof
A technology of concentrated feed and plants, applied in the direction of animal feed, animal feed, additional food elements, etc., can solve the problems of not knowing the conversion relationship, unsafe feed, and ineffective disease prevention and control.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
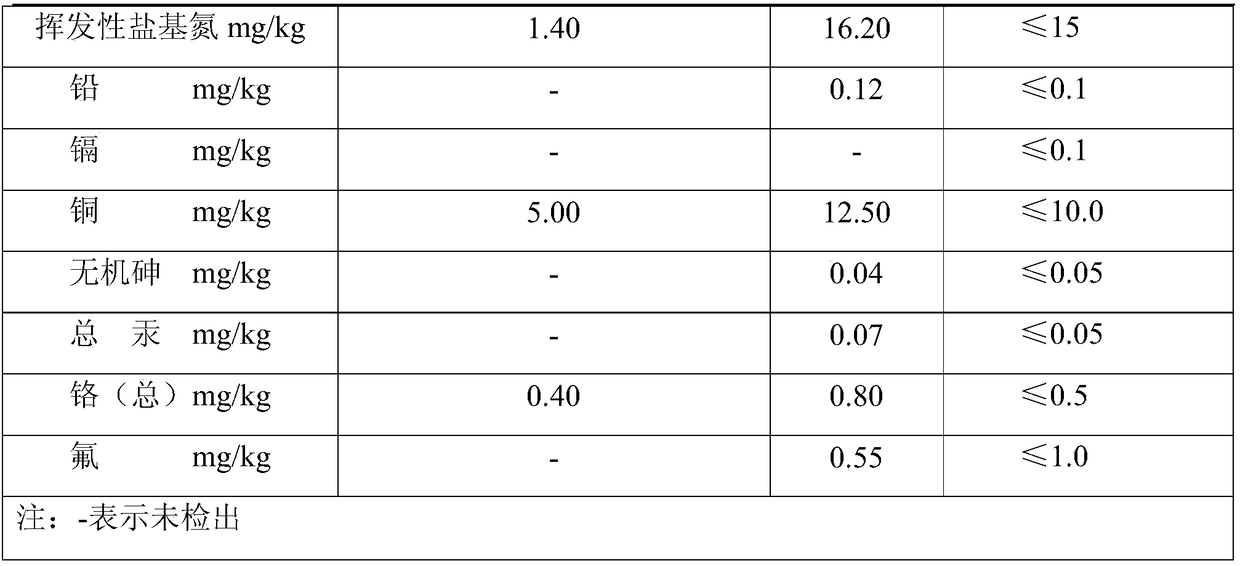
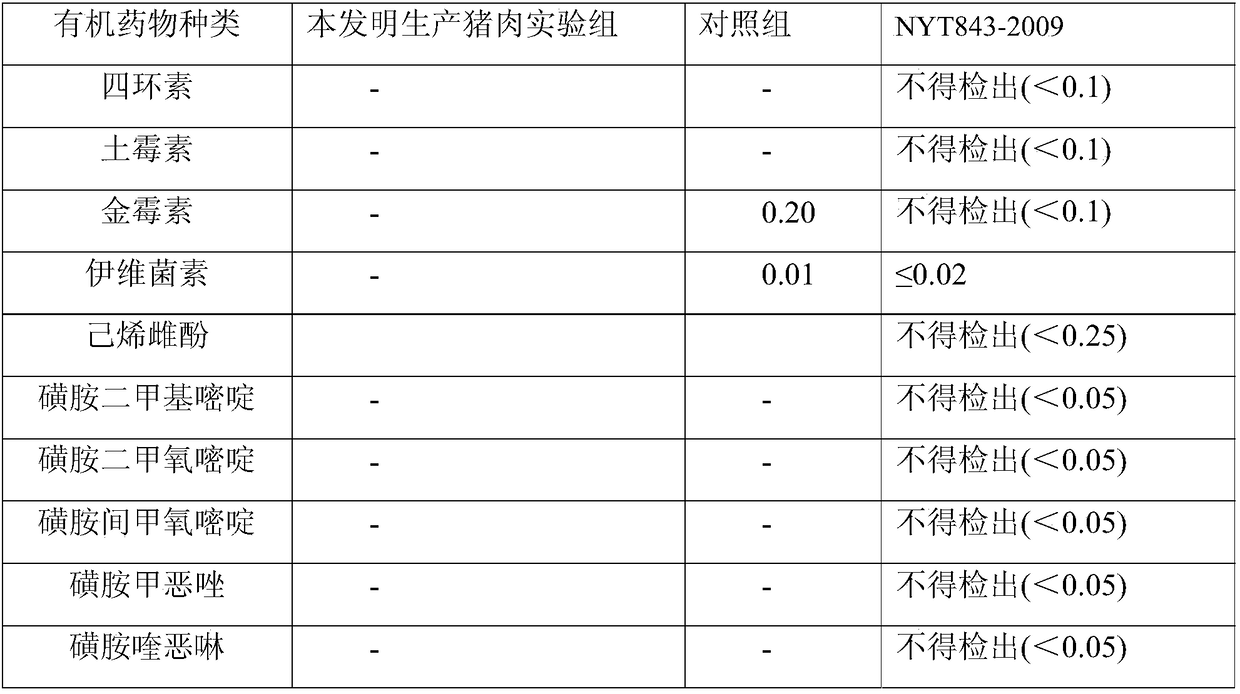
[0070] A plant ecological concentrated feed, comprising the following components by weight: 0.7 parts of plant polysaccharides, 0.4 parts of plant saponins, 1.4 parts of plant flavonoids, 1.4 parts of aerobic probiotics, 3.5 parts of anaerobic probiotics, 4.7 parts of brown sugar, 1.1 parts of sodium chloride, 1.4 parts of calcium chloride, 0.5 parts of zinc sulfate, 0.5 parts of manganese sulfate, 0.1 parts of sodium selenite, 18.9 parts of soybean meal, 47.3 parts of corn grits, and 23.6 parts of wheat bran.
[0071] Plant polysaccharides are obtained by the following methods:
[0072] A. Take the same amount of Radix Pseudostellaria Pseudostellariae and Angelica Sinensis, chop, wash, soak in cold water for 2 hours until the medicinal core of the plant is fully soaked, then add water 12 times the total weight of the plant, heat to boiling; Carry out heat reflux extraction and concentration, heat reflux extraction and concentration for 180 minutes to obtain concentrated medic...
Embodiment 2
[0098] A plant ecological concentrated feed, comprising the following components by weight: 0.1 parts of plant polysaccharides, 0.1 parts of plant saponins, 0.1 parts of plant flavonoids, 2.0 parts of aerobic probiotics, 0.5 parts of anaerobic probiotics, 15.0 parts of soybean meal, Corn grits 45.0 parts, wheat bran 15.0 parts, brown sugar 2.0 parts, sodium chloride 0.5 parts, calcium chloride 0.5 parts, zinc sulfate 0.5 parts, manganese sulfate 0.5 parts, sodium selenite 0.1 parts.
[0099] For plant polysaccharides, take Codonopsis pilosula as a raw material, and use the extraction method of Example 1; for plant saponins, take ginseng vines as a raw material, and use the extraction method of Example 1; for plant flavonoids, take bamboo leaves as a raw material, and use the extraction method of Example 1.
[0100] Plant ecological concentrated feed preparation method adopts the preparation method of embodiment 1 (aerobic probiotics are made up of bacillus, saccharomycetes by t...
Embodiment 3
[0111] A plant ecological concentrated feed, comprising the following components by weight: 5.0 parts of plant polysaccharides, 5.0 parts of plant saponins, 5.0 parts of plant flavonoids, 10.0 parts of aerobic probiotics, 10.0 parts of anaerobic probiotics, 25.0 parts of soybean meal, Corn grits 65.0 parts, wheat bran 45.0 parts, brown sugar 15.0 parts, sodium chloride 10.0 parts, calcium chloride 15.0 parts, zinc sulfate 2.2 parts, manganese sulfate 1.5 parts, sodium selenite 1.3 parts.
[0112] For plant polysaccharides, kiwifruit stems and leaves are used as raw materials, and the extraction method of Example 1 is used; for plant saponins, asparagus stalks are used as raw materials, and the extraction method of Example 1 is used; for plant flavonoids, tea tree branches and leaves are used as raw materials, and the extraction method of Example 1 is used. method.
[0113] The preparation method of plant ecological concentrated feed adopts the preparation method of embodiment ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com