Method for detecting residual amount of 19 organochlorine pesticides in pseudo-ginseng
A technique for organochlorine and pesticide residues, which is applied in the field of simultaneous determination of 19 organochlorine pesticide residues in Panax notoginseng, which can solve the problems of high requirements for testing personnel, complicated preparation, and long testing time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] A method for simultaneously measuring 19 kinds of organochlorine pesticide residues in Panax notoginseng, comprising the steps of:
[0062] (1) Preparation of the test solution:
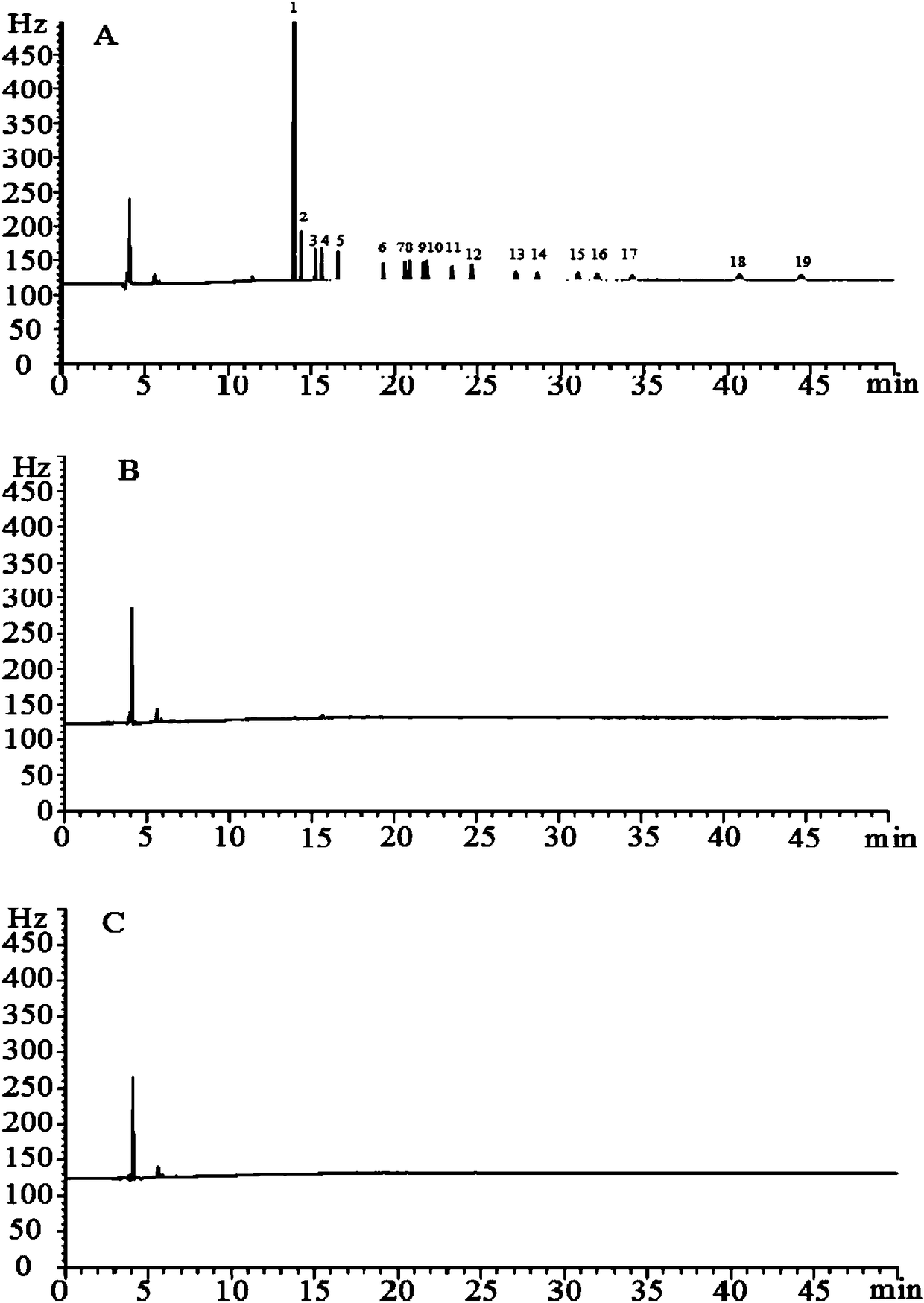
[0063] Take 1 portion of medicinal material powder, weigh it accurately, put it in a 50mL polypropylene plastic centrifuge tube, add petroleum ether 30 times the weight of the medicinal material, soak for 1 hour, filter with suction, wash the residue with petroleum ether 15 times the weight of the medicinal material, and transfer it to a 100mL circular tube. In a bottom flask, evaporate to nearly dryness in a water bath at 40°C. Reconstitute with 2 mL of n-hexane, transfer to a centrifuge tube, add 0.1 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, shake fully for 1 min, after the reaction is complete, centrifuge at 3000 r / min for 5 min, take the supernatant, and put it into GC for testing.
[0064] (2) Preparation of mixed reference substance solution:
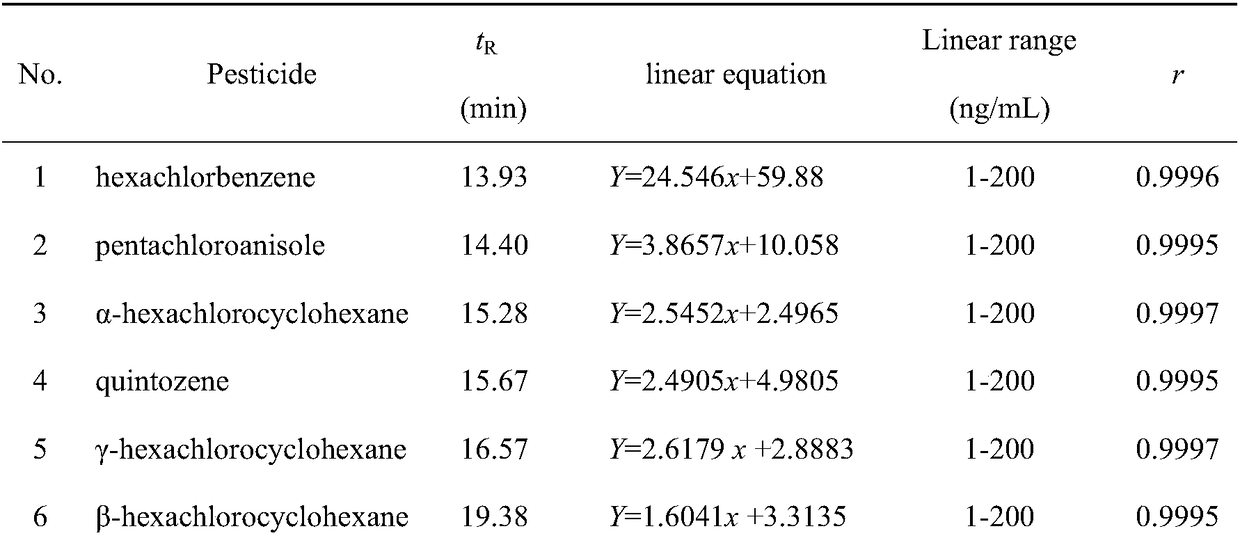
[0065] Precisely measure 1mL of each of the 19 ki...
Embodiment 2
[0071] According to the method of Example 1, 30 batches of Panax notoginseng medicinal materials produced in Yunnan were tested. The test results are shown in Table 4. Among them, the maximum residual amount of pentachloronitrobenzene is 0.32 mg / kg, which exceeds the limit stipulated in the 2015 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, and the remaining pesticide residues are not found to exceed the standard.
[0072] Table 4 Test result table
[0073] Tab.4 Test results
[0074]
[0075]
[0076] (Note: "-" means not detected, "+" means detected, "++" means exceeded).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com