Low time jitter fiber femtosecond laser based on narrowband spectrum filtering
A femtosecond laser and spectral filter technology, used in lasers, laser components, phonon exciters, etc., can solve the problem of reducing system repeatability and long-term stability, offsetting the practical advantages of fiber lasers, and the difference in time jitter levels and other problems, to achieve the effect of reducing the pulse spectral width, eliminating the time jitter component, and weakening the influence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] The specific implementation manners of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
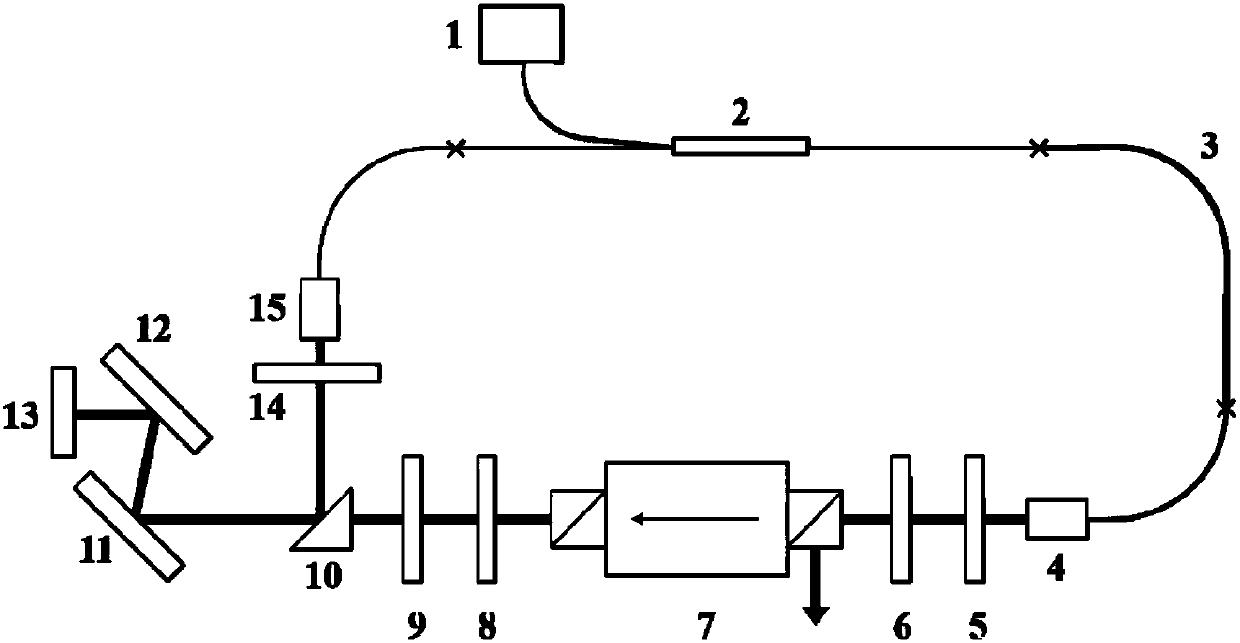
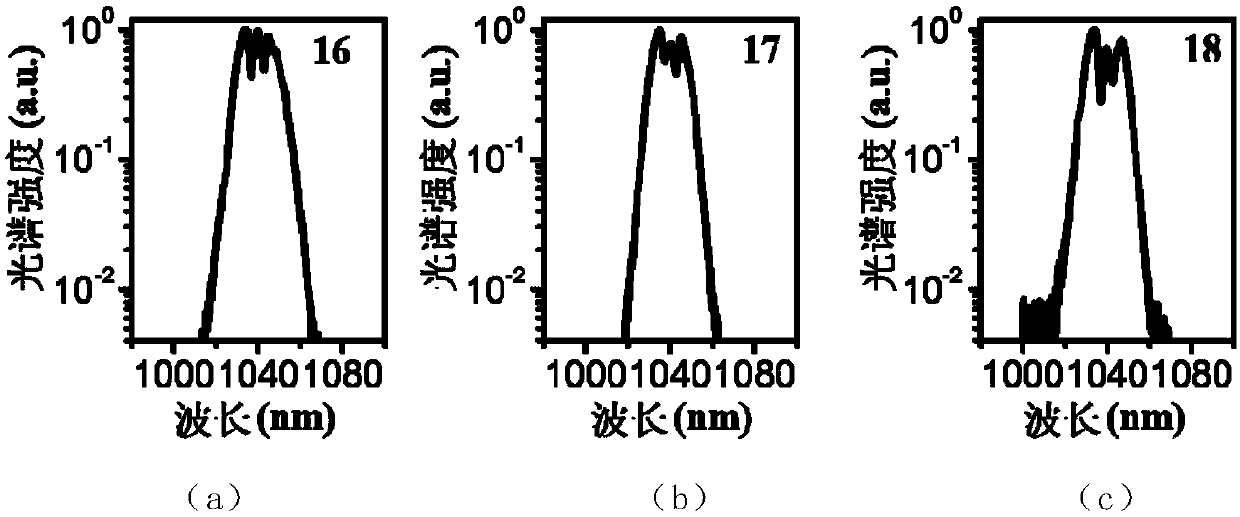
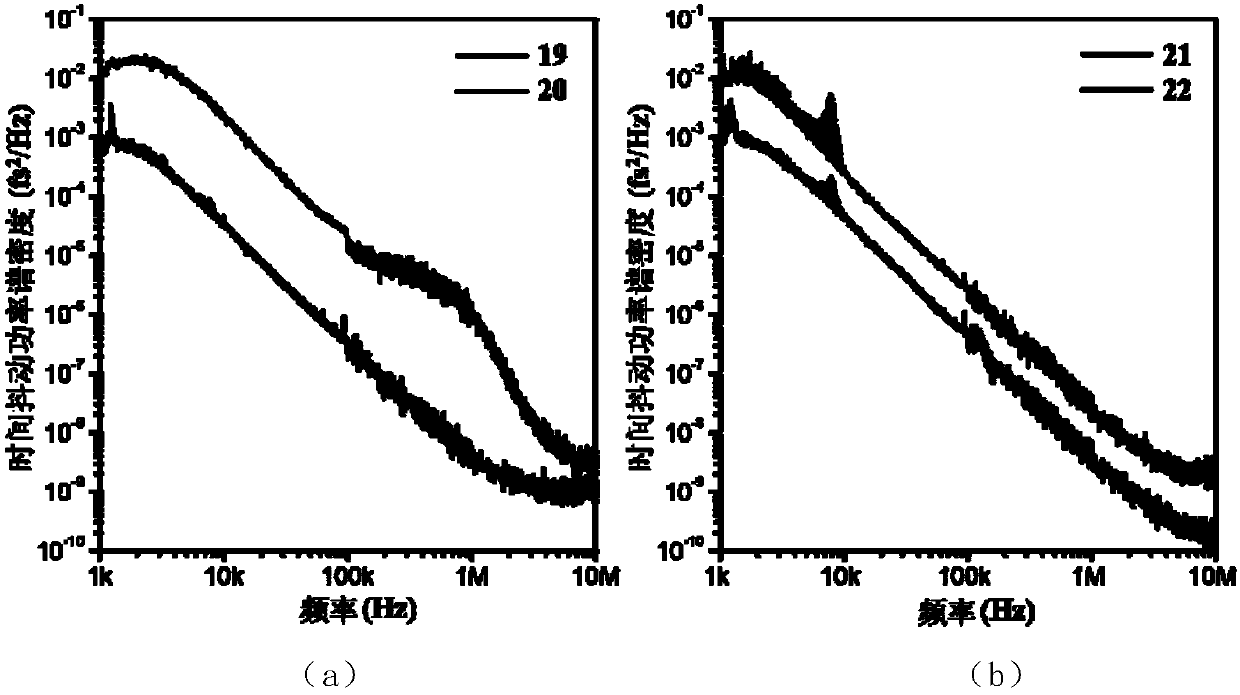
[0031] The femtosecond laser of the present invention uses narrow-band spectral filtering to significantly enhance the restoring force effect brought about by the limited bandwidth of the gain fiber, and further suppresses the random drift of the center wavelength caused by the amplified spontaneous radiation noise during the amplification process of the pulse in the gain fiber, and then from Fundamentally, the time jitter component caused by the instability of the pulse spectrum component and coupled into the pulse by the intracavity dispersion is greatly weakened. On the other hand, the spectral components far away from the center wavelength in the large chirped pulse are often located at the two edges of the pulse. When passing through the narrow-band spectral filter, the two edges of the pulse will be weakened, so tha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com