Half-bridge flyback resonant circuit
A resonant circuit and circuit technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, adjusting electrical variables, high-efficiency power electronic conversion, etc., can solve the problems of high voltage stress of switching tubes, poor voltage cross-regulation rate, low efficiency, etc., to improve efficiency and improve EMI , cost reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
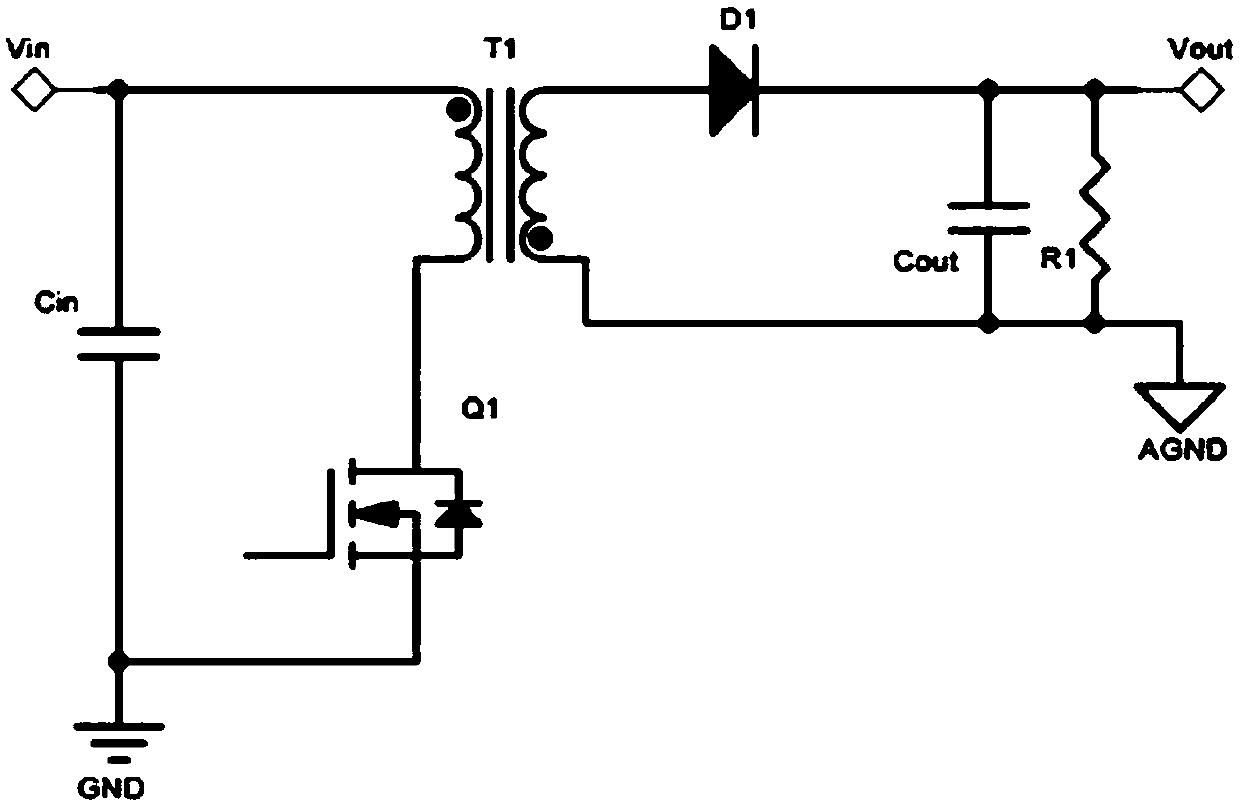
[0041] reference Figure 5 In the first embodiment, the half-bridge flyback resonant circuit mainly includes a half-bridge circuit 100, a primary input circuit 200, and a flyback secondary circuit 300. The half-bridge circuit 100 includes an upper bridge arm and a lower bridge arm. The primary input circuit 200 is connected in parallel with the lower bridge arm and includes an energy storage element and the primary winding of the flyback transformer T1. The structure of the flyback secondary circuit 300 is the same as that of the conventional flyback circuit.
[0042] Specifically, a capacitor Cin is connected between the positive terminal Vin and the negative terminal of the input power source (ie, the ground GND of the input power terminal). The switching element of the upper arm of the half-bridge circuit 100 is specifically an N-type MOS transistor Q1. The switching element specifically uses an N-type MOS tube Q2. The drain of the MOS transistor Q1 is connected to the posit...
Embodiment 2
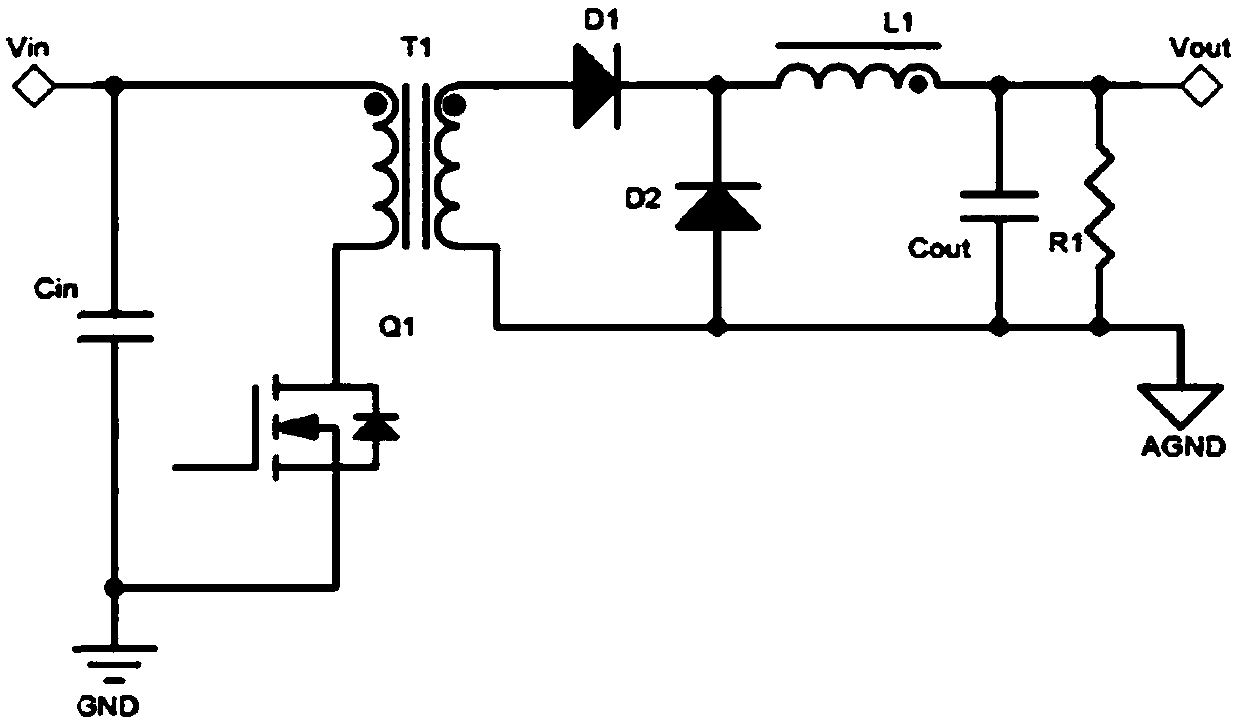
[0052] reference Image 6 Compared with the first embodiment, the second embodiment differs in that the current sampling resistor R2 is added to facilitate the feedback adjustment of the switching power supply terminal. Specifically, the drain of the MOS transistor Q1 is connected to the positive Vin of the input power source, the source of the MOS transistor Q1 is connected to the drain of the MOS transistor Q2, and the source of the MOS transistor Q2 is connected to the primary side of the flyback transformer T1 through the capacitor C1. The opposite end of the winding is connected to one end of the current sampling resistor R2 on the other hand, and the other end of the current sampling resistor R2 is connected to GND.
Embodiment 3
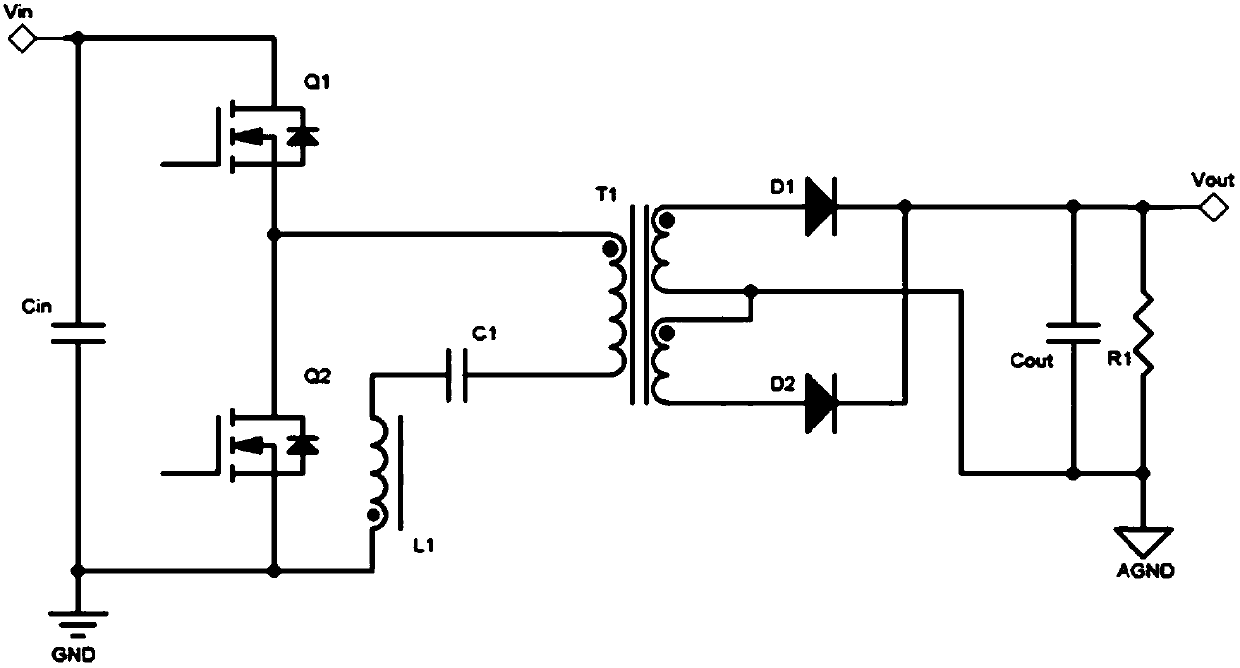
[0054] reference Figure 7 Compared with the first embodiment, the third embodiment is different in that the number of the flyback secondary circuit is two. Specifically, the first flyback secondary circuit 300 includes a first secondary winding, a diode D1, a capacitor Cout, and a resistor R1, and the second flyback secondary circuit 300' includes a second secondary winding, a diode D1', and a capacitor. Cout', resistance R1'.
[0055] In the first flyback secondary circuit 300, the anode of the diode D1 is connected to the opposite end of the corresponding first secondary winding, and the cathode of the diode D1 is connected to the first end of the resistor R1 and the first end of the capacitor Cout, The second end of the resistor R1 and the second end of the capacitor Cout are connected to the same-named end of the first secondary winding. The first end of the resistor R1 is used as the positive Vout for connecting to the external load, and the second end of the resistor R1 is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com