Application of ABCG1 gene as molecular marker for diagnosis of exposure to heavy ion radiation
A technology of molecular markers and heavy ion radiation, which is applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of inability to study the molecular mechanism and microscopic changes of radiation damage, difficult molecular markers, small doses, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1: Preliminary Screening of Gene Molecular Markers for Heavy Ion Radiation Exposure Diagnosis
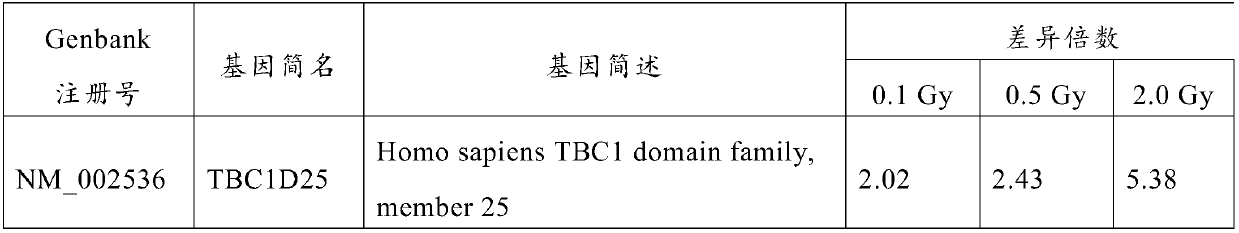
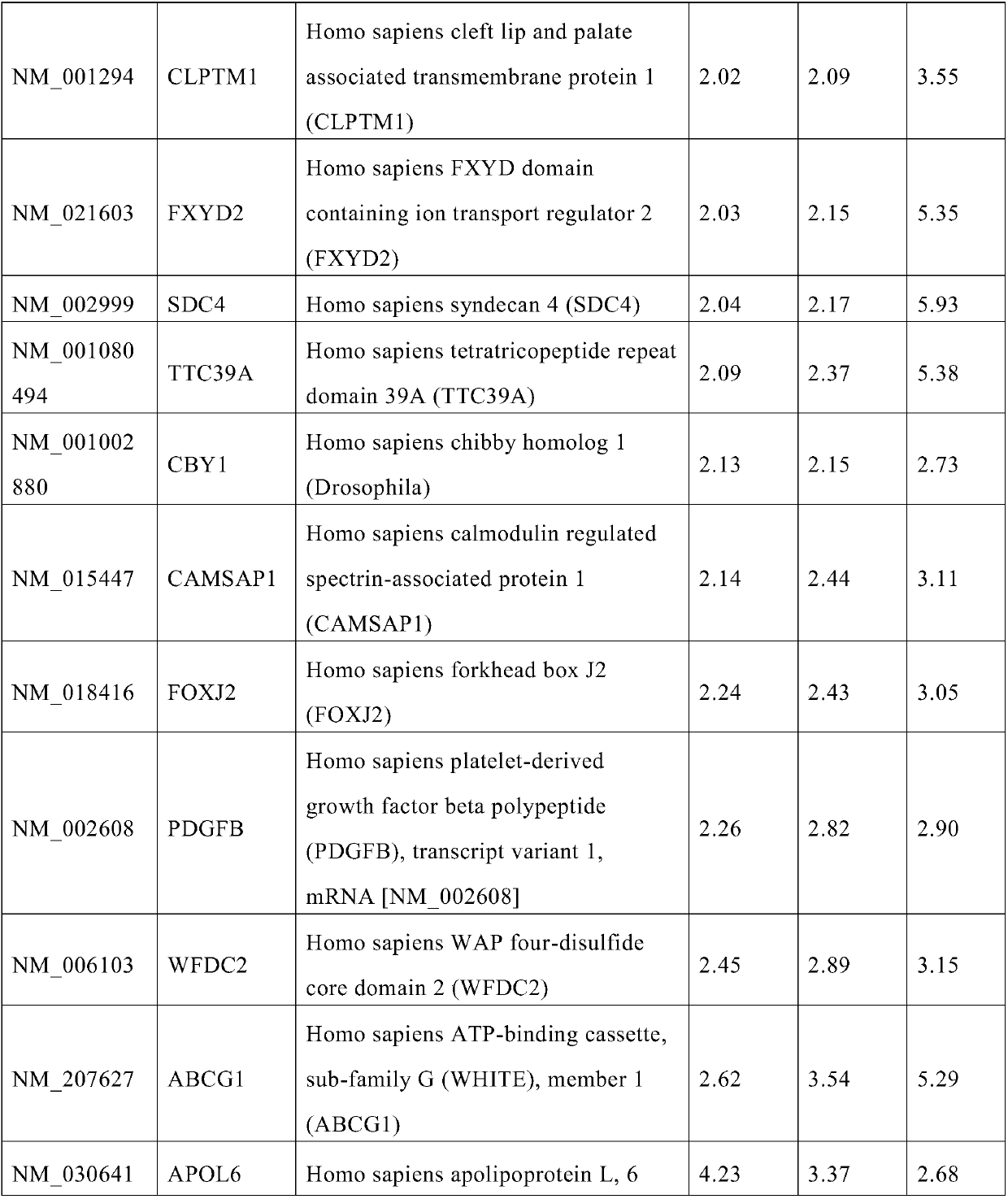
[0024] Using gene chip technology, by detecting the differential expression of different genes in human lymphocytes after heavy ion radiation exposure, the gene molecular markers for the diagnosis of heavy ion radiation exposure were initially screened.
[0025] 1) Extraction, quantification, quality inspection and purification of total cellular RNA
[0026] Human lymphocytes were subjected to 0.1, 0.5, 2.0Gy 12 C 6+ Cultivate for 24 hours after ion radiation irradiation (these three groups are the experimental group; non-irradiation is the control group). Total RNA was extracted from the four groups of cells according to the Trizol reagent extraction instructions. Concentration and purity were measured by spectrophotometer, and 5 g of total RNA was taken for electrophoresis inspection in 1% formaldehyde-agarose gel. According to QIAGEN Kit (QIAGEN, Germany) was...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: PCR verification confirms the feasibility of ABCG1 gene as a molecular marker for the diagnosis of heavy ion radiation exposure
[0039] Extract the total RNA of the radiation-irradiated group and the non-irradiated group with Trizol reagent, measure the concentration with an ultraviolet spectrophotometer, use the total RNA as a template, and reverse-transcribe cDNA according to the instructions of the reverse transcription kit. The reverse transcription system is 20 μl.
[0040] A proper amount of cDNA samples from the radiation exposure group and the control group were taken to verify the differentially expressed genes of ABCG1 by PCR. The primer sequences and PCR amplification conditions are shown in Table 2.
[0041] Table 2 Primer sequences and amplification conditions of RT-PCR amplified genes
[0042]
[0043] Result analysis: Compared with the cells of the control group, there were 504 differentially expressed genes in the three dose groups, includi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com