A kind of flexible electrode, its preparation method and a kind of myoelectric sensor
An electrode and conductive connector technology, applied in the field of flexible electronic technology and information control, can solve the problems of liquid metal droplet overflow at the bottom of the electrode, uneven distribution of liquid metal, etc., to prevent liquid metal overflow, high flexibility, and stable performance. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
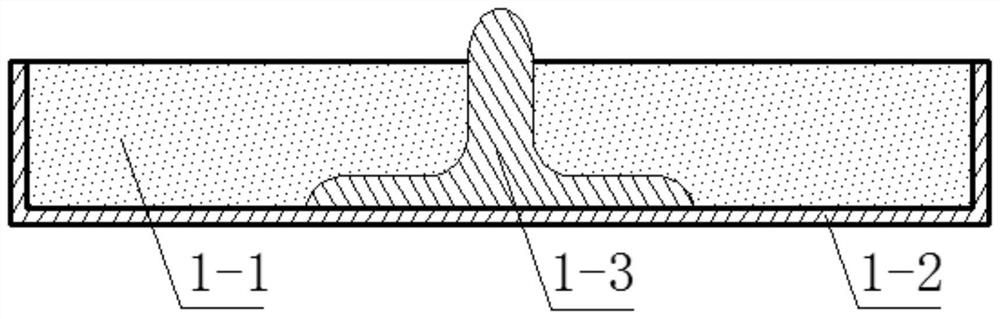
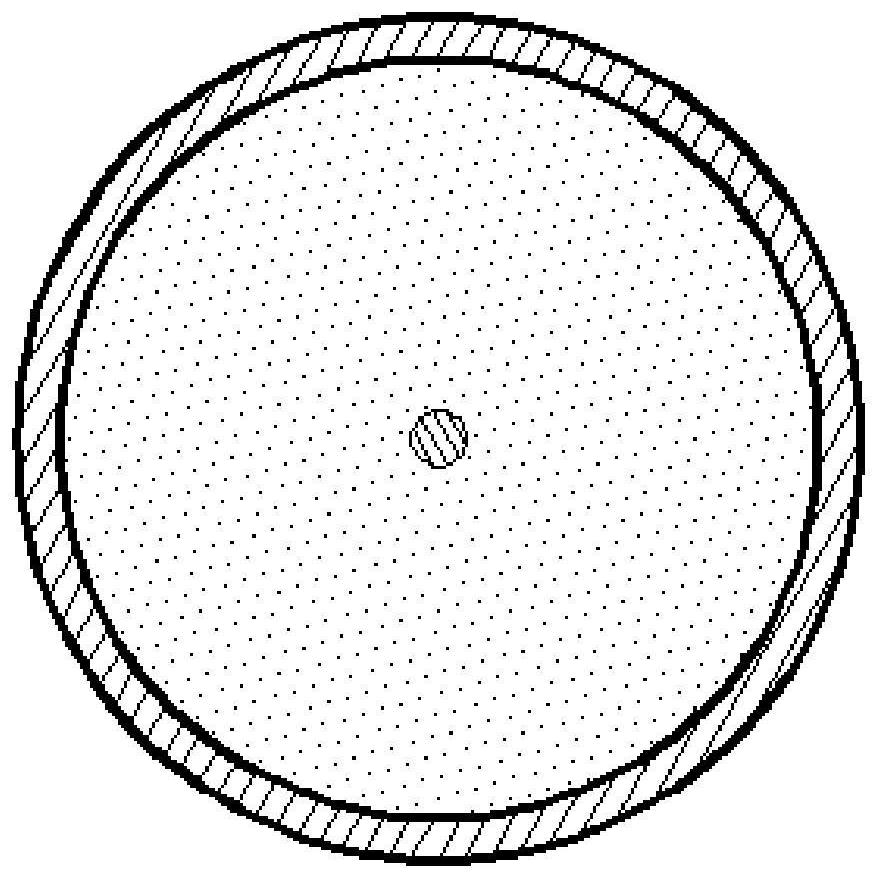
[0054] In this embodiment, the schematic diagram of the structure of the flexible electrode is as follows figure 1 , 2 As shown, it includes an electrode inner layer 1-1, a protective layer 1-2 and a conductive connector 1-3.
[0055] The outer layer of the electrode is conductive and thinly covers the bottom and sides of the inner layer of the electrode.
[0056] The conductive connector 1-3 is an electrode female button of a conductive interface, one end of which extends into the bottom of the inner layer of the electrode and is connected with the outer layer of the electrode, and the other end is connected to an external component to form an electrical connection.
[0057] In this example, the liquid metal is GaInSn, which is an alloy with a mass ratio of Ga:In:Sn=62.5:21.5:16, which is liquid at room temperature and has conductivity. The solid conductive material is carbon nanotubes, preferably nanowires, graphene and the like. The elastomer is PDMS, which is a thermopl...
Embodiment 2
[0065] In this embodiment, the structure of the flexible electrode is the same as that in Embodiment 1.
[0066] In this example, the liquid metal is GaInSn, which is an alloy with a mass ratio of Ga:In:Sn=62.5:21.5:16, which is liquid at room temperature and has conductivity. The solid conductive material is carbon nanotubes, preferably nanowires, graphene and the like. The elastomer is PDMS, which is a thermoplastic elastomer that can stretch under certain stress.
[0067] In this example, the flexible electrode is made by the overall mold method, as follows:
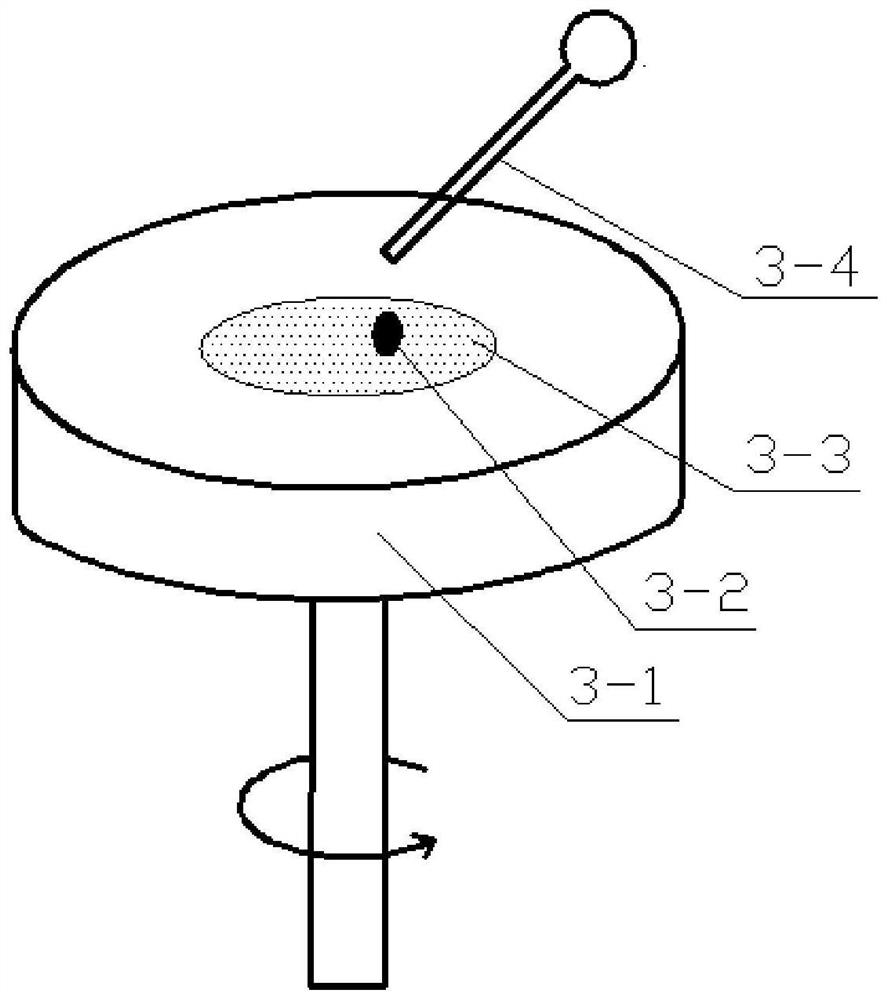
[0068] (1) Prepare the overall mold for the outer layer of the electrode, and its structure is as follows Image 6 As shown; mechanically stir PDMS and curing agent in proportion, then add a certain proportion of carbon nanotubes into an ultrasonic stirring device, and stir in a high-speed shear flow, so that carbon nanotubes are evenly dispersed in PDMS, and the package is prepared. Cover the electrode outer layer...
Embodiment 3
[0071] In this embodiment, the structure of the flexible electrode is the same as that in Embodiment 1.
[0072] In this example, the liquid metal is GaInSn, which is an alloy with a mass ratio of Ga:In:Sn=62.5:21.5:16, which is liquid at room temperature and has conductivity. The solid conductive material is carbon nanotubes, preferably nanowires, graphene and the like. The elastomer is PDMS, which is a thermoplastic elastomer that can stretch under certain stress.
[0073] In this example, the flexible electrode is made by mold method, as follows:
[0074] (1) Prepare the mold at the bottom of the electrode inner layer and the electrode outer layer, which is called the first mold, and its structure is as follows Figure 7 As shown, the bottom has a stepped structure;
[0075] Mechanically stir the PDMS and curing agent in proportion, then add a certain proportion of carbon nanotubes into the ultrasonic stirring device, and stir in the high-speed shear flow, so that the ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com