Preparation method of branched polyethyleneimine and shale intercalation inhibitor
A technology of branched polyethyleneimine and polyethylene polyamine, which is applied in the field of oil and gas field drilling, to achieve the effects of stable and reliable technology, reduced well wall instability and high productivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] The synthetic steps (step S1) of aziridine are as follows:
[0049] In a low-temperature reaction vessel at 15°C, react ethanolamine with a molar ratio of 1:1.1 and concentrated sulfuric acid:
[0050] S11. First, dissolve 0.5mol ethanolamine in 80ml of toluene, slowly add 32mL of 95% concentrated sulfuric acid dropwise while stirring at low temperature, and drop the concentrated sulfuric acid within 15 minutes; continue stirring for 30 minutes after the dropwise addition, and distill under reduced pressure. When the volume of the mixed system was concentrated to 1 / 4 of the original volume, the temperature was raised to 180° C. until no moisture was evaporated to solidify the material, and the reaction was stopped after heating at 180° C. for 1 h to obtain 69.2 g of solid powder β-aminoethyl sulfate. Productive rate reaches 98%; S12, when the temperature of β-aminoethylsulfate drops to 10 DEG C, slowly add 250g of 40% by mass NaOH solution, heat and stir simultaneously,...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The aziridine and diethylenetriamine prepared by embodiment 1 are used as raw materials, and branched polyethyleneimine is prepared by step-by-step synthesis, and the specific steps are as follows:
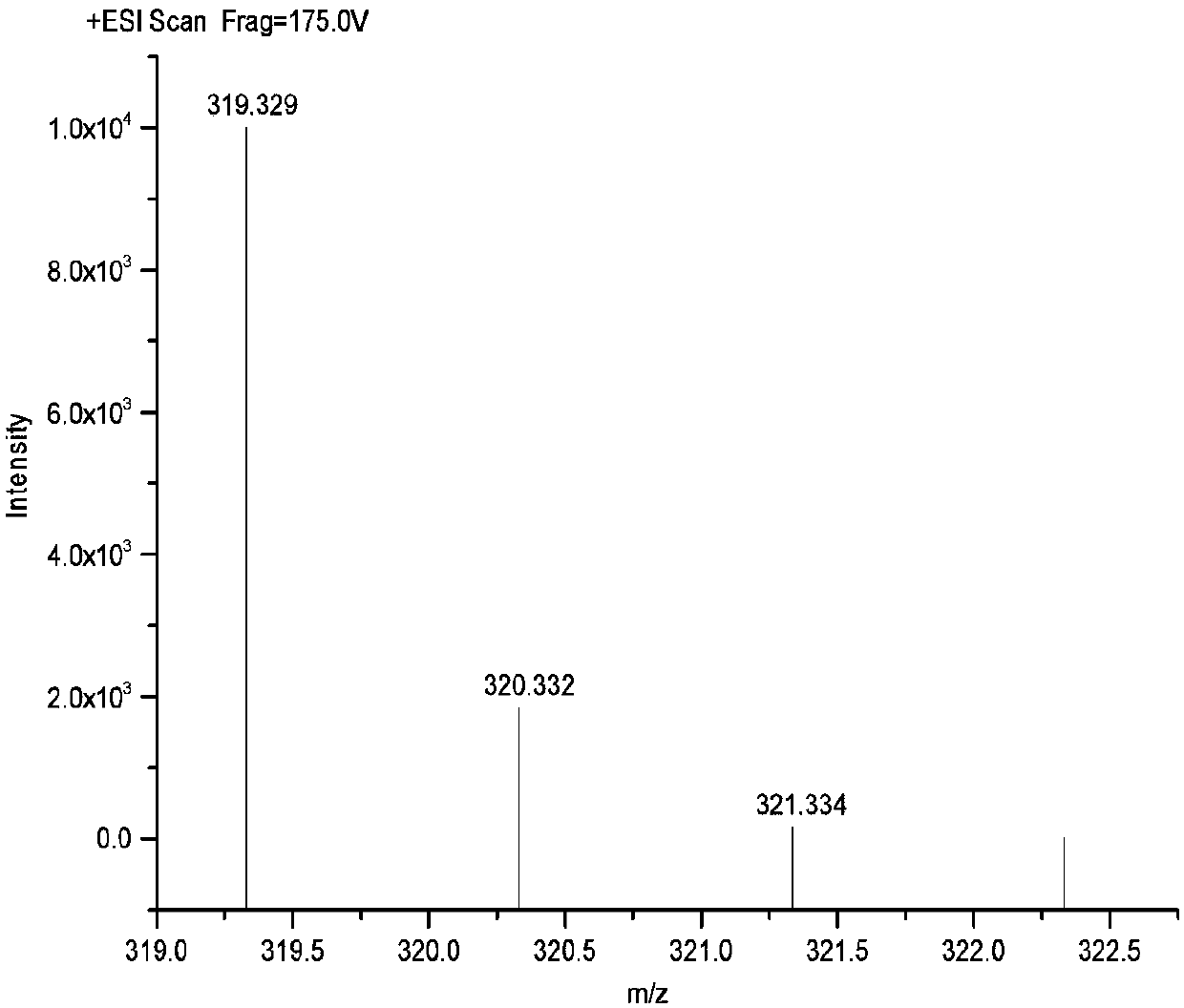
[0055] (1) Synthesis of G1 branched polyethyleneimine: Dissolve 0.1mol diethylenetriamine in absolute ethanol, add 0.5mol ethanol solution of aziridine dropwise at 50°C, after the dropwise addition, heat Reflux reaction for 6h, and then vacuum distillation to obtain G1 branched polyethyleneimine with a yield of 97.4%. Molecular formula of G1 branched polyethyleneimine: C 14 h 38 N 8 , exact molecular weight: 318.3219, molar mass: 318.5140, mass-to-charge ratio: 318.322 (100.00%), 319.325 (15.1%), 320.329 (1.1%). Elemental analysis: C, 52.79; H, 12.03; N, 35.18. Such as figure 2 As shown, the mass-to-charge ratio measured by LC-MS is 319.329, because the G1 branched polyethyleneimine obtains a proton, and its molecular weight of 318.329 is consistent with the theoretic...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Aziridine and diethylenetriamine prepared in Example 1 are used as raw materials, and branched polyethyleneimine is prepared by a one-pot synthesis method, and the specific steps are as follows:
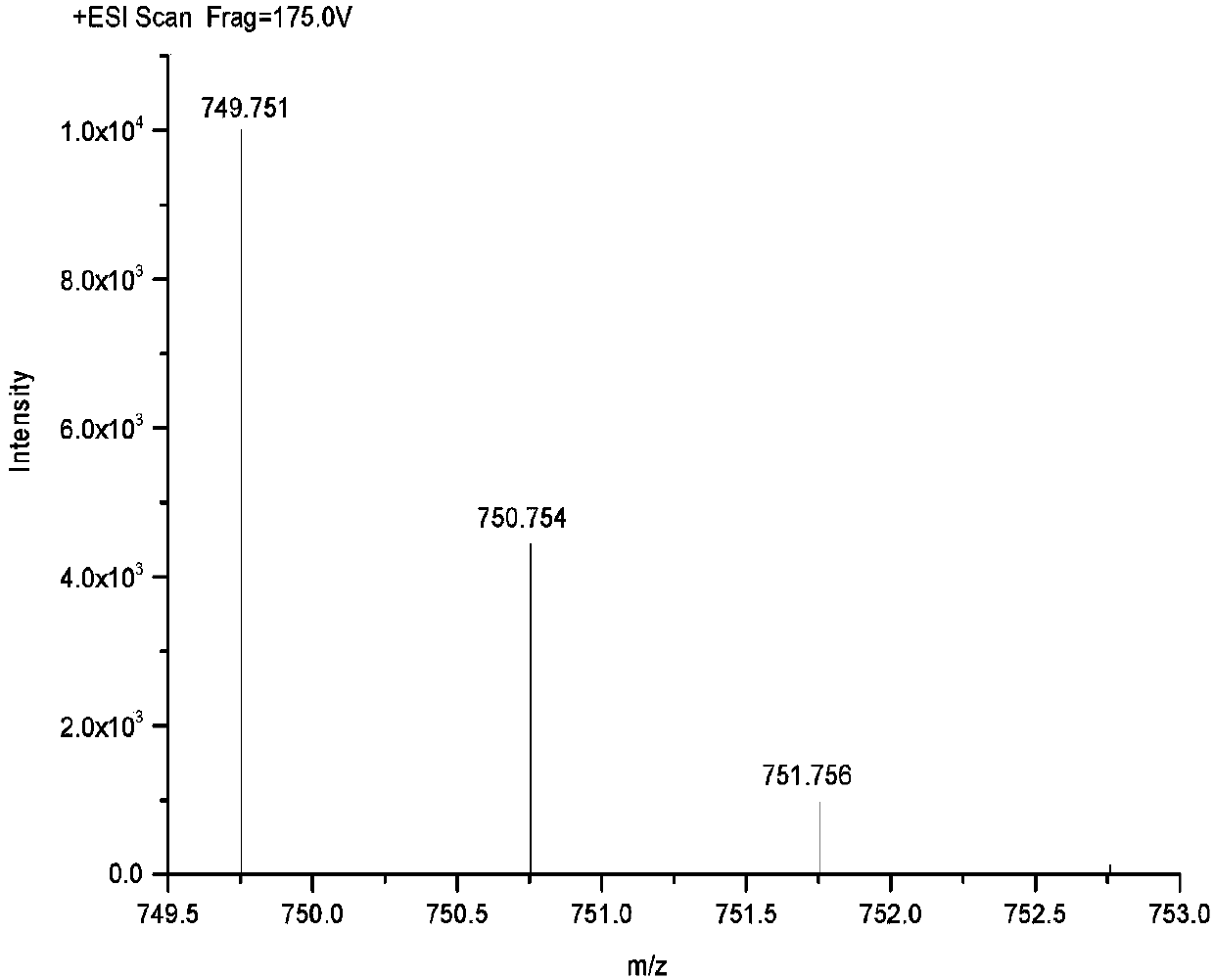
[0063] Dissolve 0.1mol diethylenetriamine in absolute ethanol, add 3.5mol ethanol solution of aziridine compound dropwise at 50°C, after the dropwise addition, reflux for 12 hours, and then distill under reduced pressure to obtain a wide molecular weight distribution The G4 branched polyethyleneimine, the yield is 92.6%. From the mass spectrum ( Figure 5 ), it can be seen that the molecular weight distribution of the branched polyethyleneimine synthesized by the one-pot method is relatively wide, indicating that the G4 branched polyethyleneimine has a variety of molecular structures, including not only the G1 branched polyethyleneimine prepared in Example 2 Amine and G2 branched polyethyleneimine also mainly have the following molecular structural formula:
[0064]
[00...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com