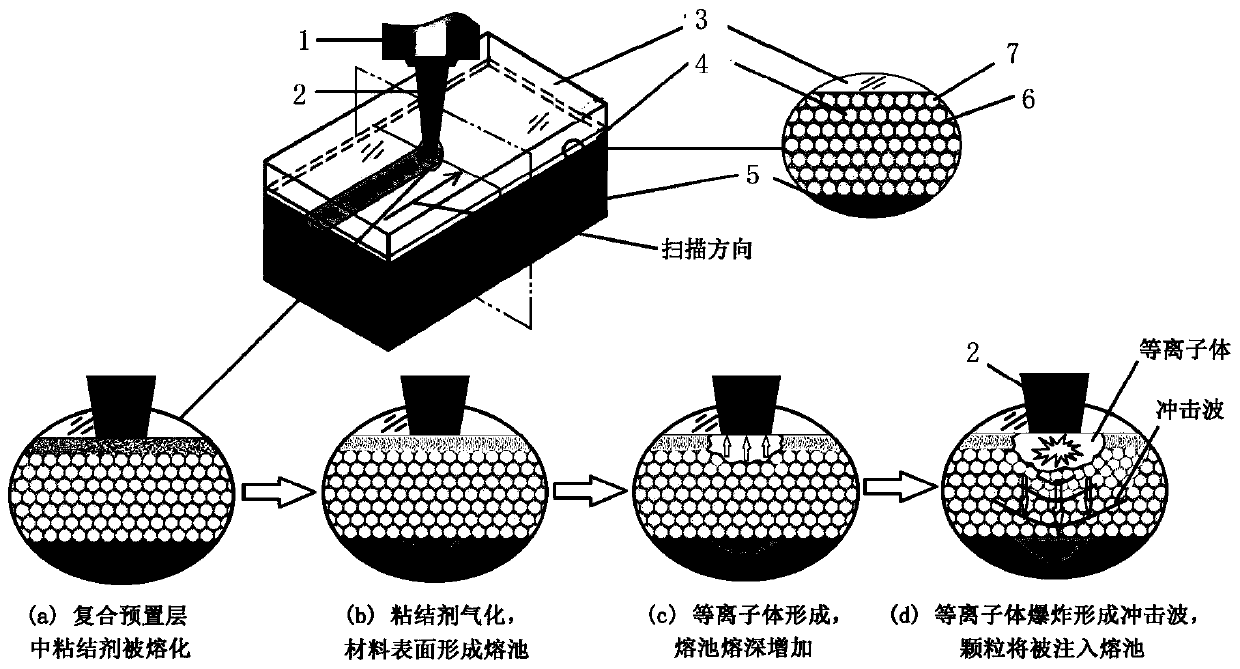
A method for continuous laser shock fusion injection of fine particles by forming injection force with laser shock energy
A technology of fine particle and laser shock, applied in the direction of metal material coating process, coating, etc., can solve the problems of restriction and difficulty in realizing the injection of fine particles, and achieve the effect of strong adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
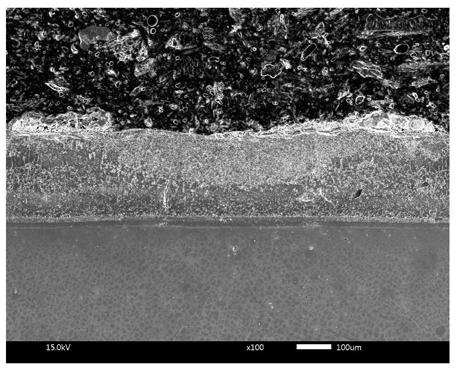
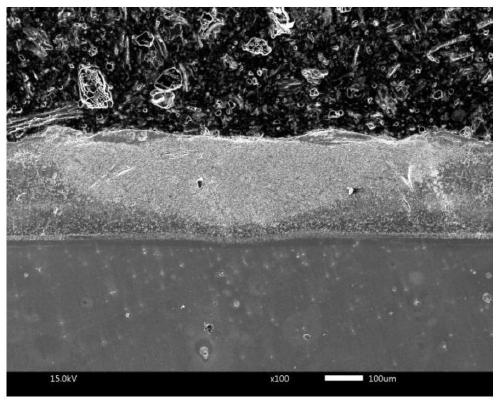
[0038] The material to be modified is an aluminum-silicon coating on the surface of a nickel-based superalloy (its melting point is about 1420°C), the binder is sodium chloride (its melting point is 891°C, its boiling point is 1413°C), and the fine particles to be melted are average Cerium oxide with a particle size of 1 μm (its melting point is 2397°C, when the particle size exceeds 100nm, its melting point basically does not decrease with the decrease of the particle size), the thickness of the composite pre-layer is 0.5mm; fiber laser is used in the melting process, The laser process parameters are 450W power, 1250mm / min scanning speed, 0.8mm spot diameter, and zero defocus; the constrained layer is covered with a coated quartz glass constrained layer on the composite preset layer.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com