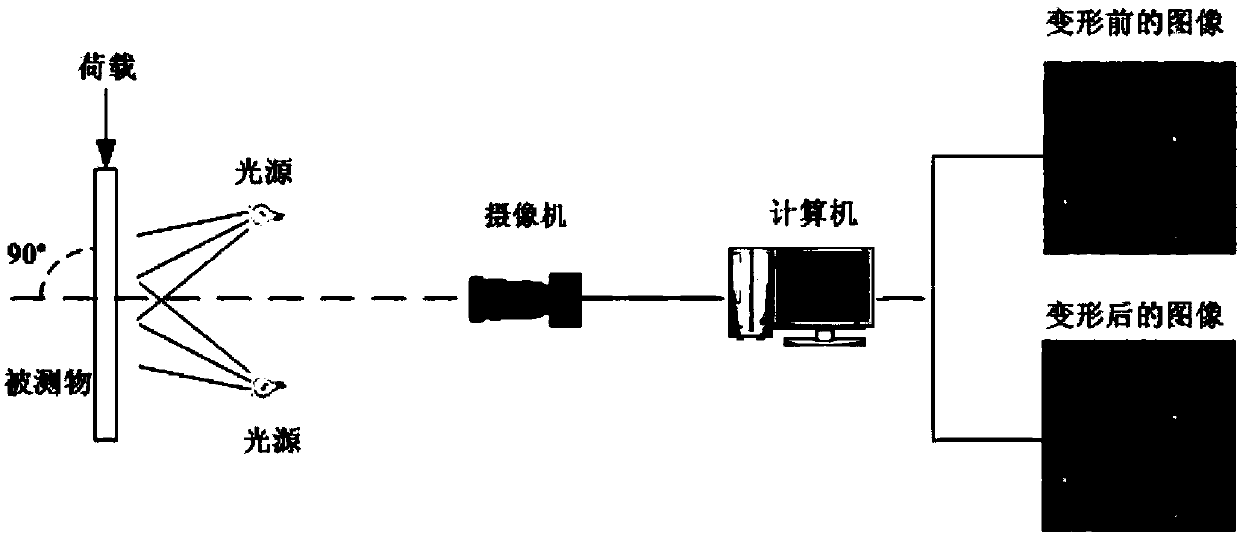
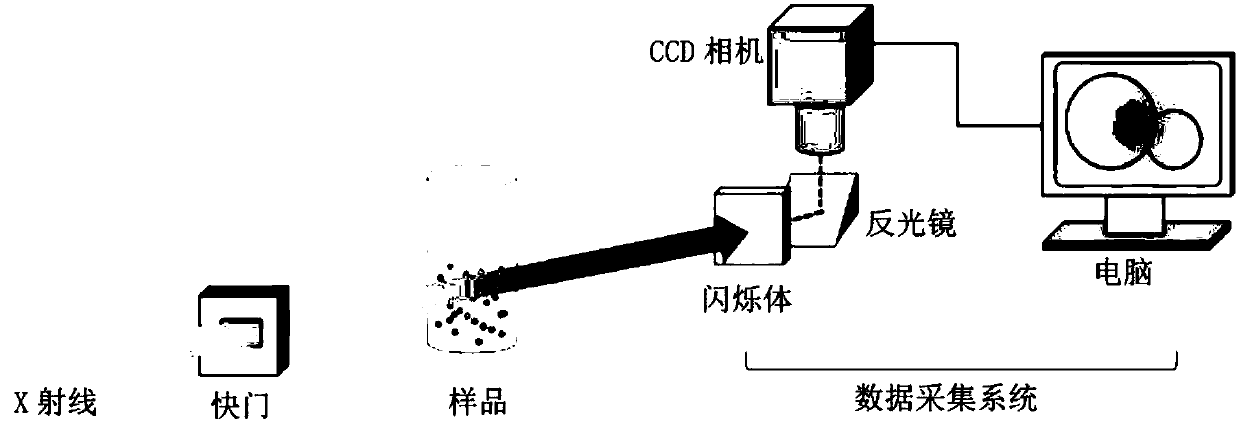
Digital image correlation technical experimental device based on X-ray transmission imaging
A technology of digital images and related technologies, applied in measurement devices, using wave/particle radiation, and using radiation for material analysis, etc., can solve problems such as measurement errors, and achieve the effects of reliable optical speckle, uniform distribution, and high imaging quality.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
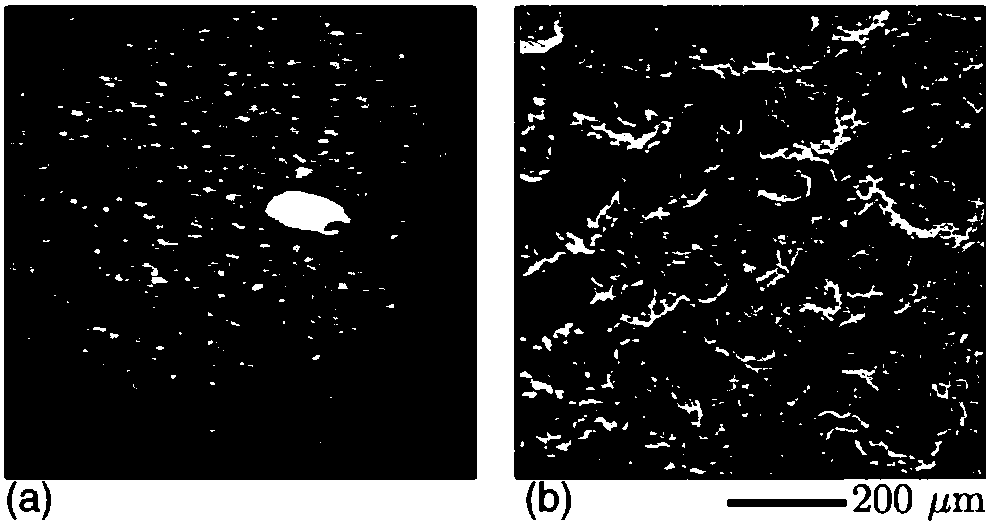
[0033] Example 1: Two dog bone-shaped aluminum samples with a thickness of 0.5 mm were cut, one of the samples was polished, immersed in hydrofluoric acid for 1 min, and then ultrasonically cleaned for 30 min to remove residual particles on the surface. The sample is only polished and not corroded. The effect of etching is to roughen the surface of the specimen, enabling it to produce X-ray spots on the XPCI image. Next, XPCI and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were performed on the two samples to obtain original images, such as image 3 As shown, the XPCI image of the corroded sample ( image 3 (a)) Abundant X-ray spots appear on the surface, which is due to the roughening of the surface by corrosion, which produces subtle thickness differences in the transmission direction of X-rays; this feature is more prominent in the SEM image, from image 3 (b) It can be seen that the corroded aluminum surface has a rich microstructure. However, the uncorroded aluminum sample is r...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The experimental material is the AZ31 magnesium alloy in the rolled state. A thin sheet sample with a size of 2.6mm×2.0mm×1.0mm was prepared and polished, and then the prepared sample was subjected to quasi-static compression experiments under X-ray irradiation, and was analyzed by CCD The camera records the entire loading process, and some representative XPCI images of the sample before and during deformation are displayed on the Figure 5 (a). Figure 5 Time t0 in (a) is the image of the sample before deformation, and t1~t4 are the images of different deformation stages with the increase of the deformation amount, where the fixed compression direction of the right end of the sample is along the positive direction of the x-axis when loading.
[0039] From Figure 5 (a) It can be seen that there are abundant and clear X-ray spots on the XPCI image of the magnesium alloy sample, which is due to the existence of many second phases in the magnesium alloy itself, and the e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com