Method for restraining Cr(III) oxidization in tanning sludge incineration process
A technology for tannery sludge and inhibitor, which is applied in combustion methods, incinerators, combustion types, etc., can solve the problems of trivalent chromium oxidation and excessive content, and achieve the effects of fast reaction speed, simple components and remarkable effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
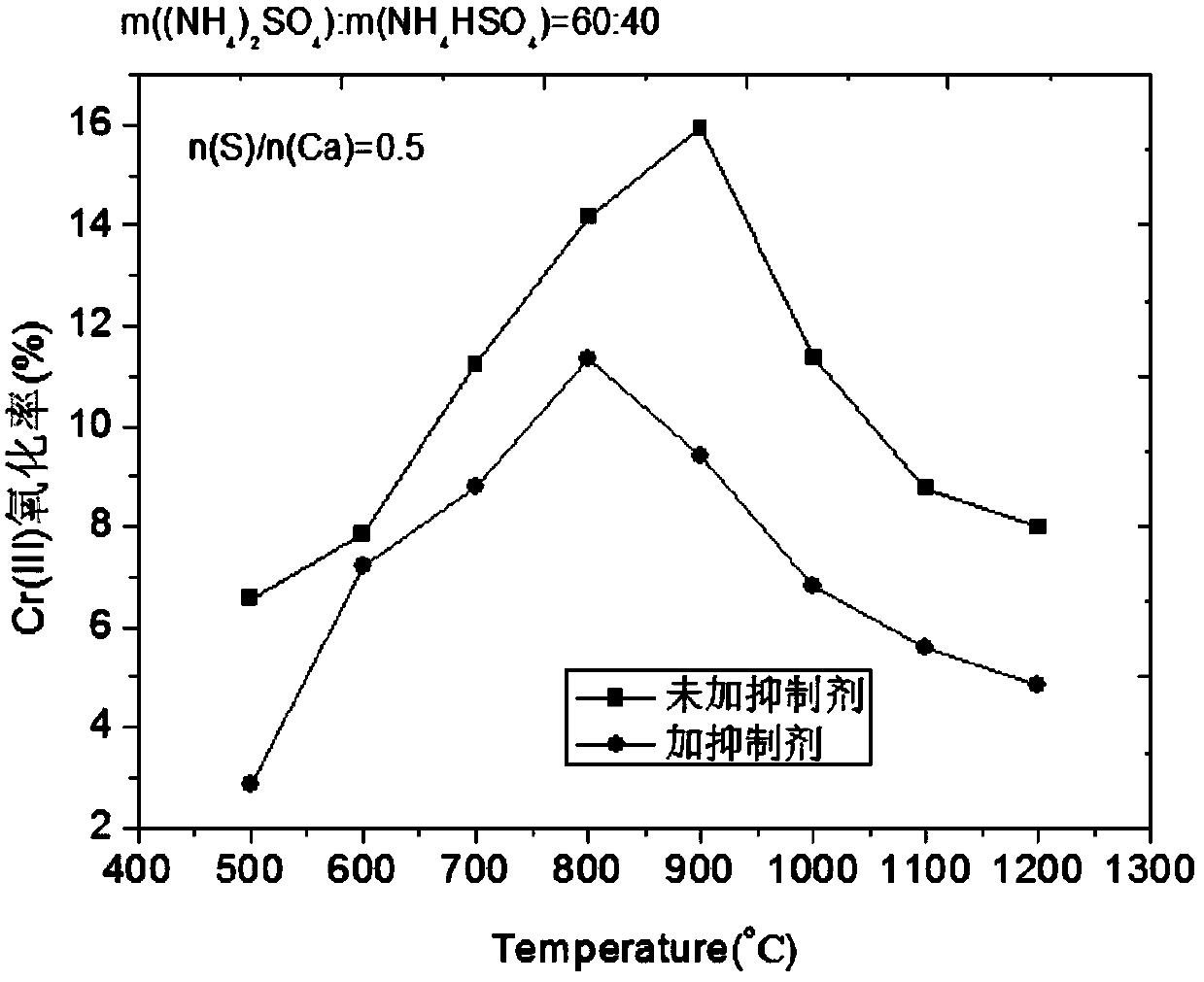
[0016] Using the laboratory to simulate the oxidation process of Cr(III) in the incineration process of tannery sludge, and analyze the pure reagent Cr 2 o 3 The simulated sludge composed of CaO and CaO (n(Ca) / n(Cr)=1) was mixed with a ball mill for 30 minutes. The components of the inhibitor consist of: m((NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ):m(NH 4 HSO 4 )=60:40, the inhibitor was added to the simulated sludge and mixed in a ball mill for 10 minutes, and the amount of inhibitor added was n(S) / n(Ca)=0.5. The mixed material is treated at high temperature in a muffle furnace for 1 hour. The heating rate of the muffle furnace is 5°C / min, and the treatment temperature is 500-1200°C. The inhibitory effect of Cr(III) is as figure 1 , at 900°C, the oxidation rate of Cr(III) dropped from 16% to 10% without inhibitor.
example 2
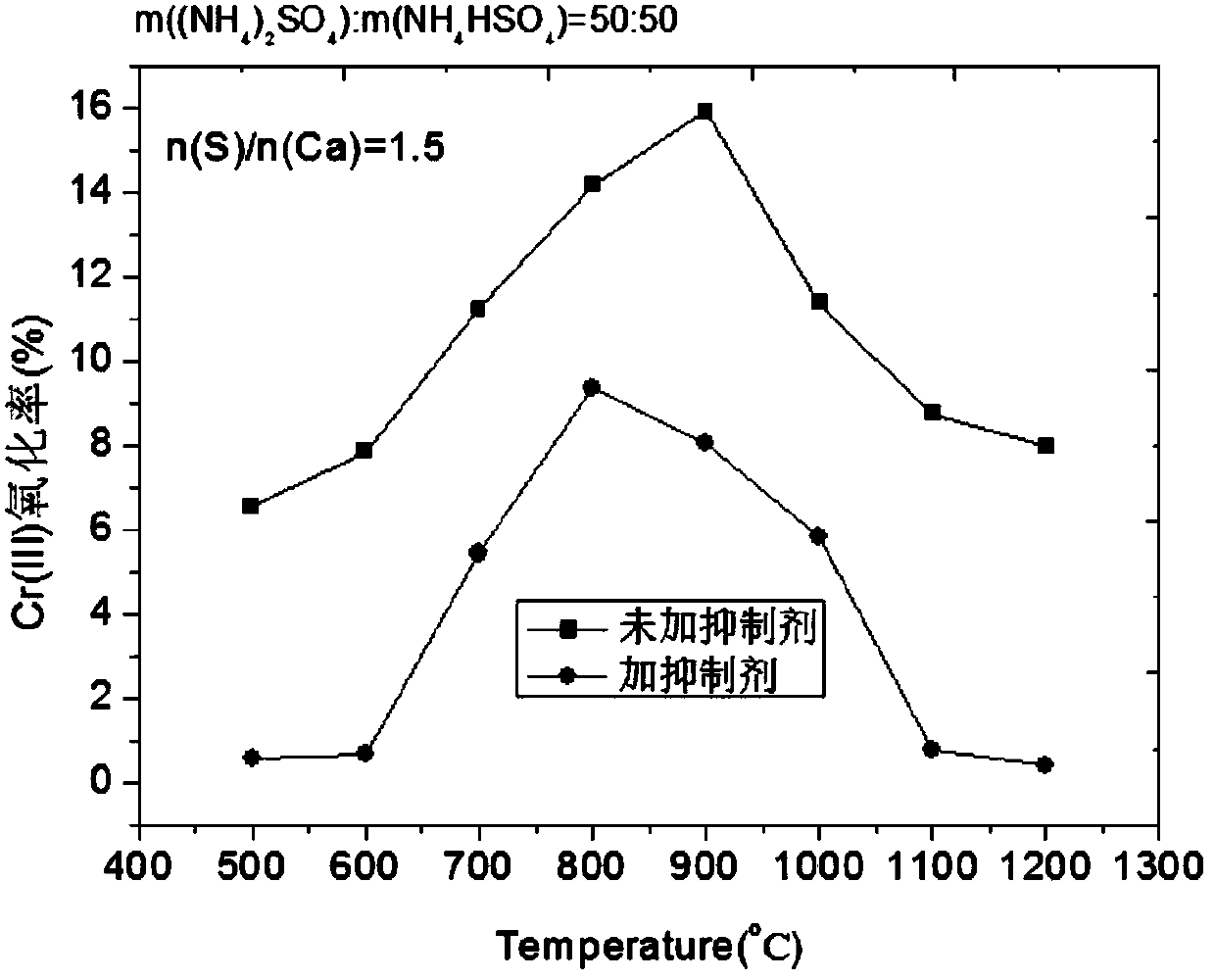
[0018] Using the laboratory to simulate the oxidation process of Cr(III) in the incineration process of tannery sludge, and analyze the pure reagent Cr 2 o 3 The simulated sludge composed of CaO and CaO (n(Ca) / n(Cr)=1) was mixed with a ball mill for 30 minutes. The components of the inhibitor consist of: m((NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ):m(NH 4 HSO 4 )=50:50, the inhibitor was added to the simulated sludge and mixed in a ball mill for 10 minutes, and the amount of inhibitor added was n(S) / n(Ca)=1.5. The mixed material is treated at high temperature in a muffle furnace for 1 hour. The heating rate of the muffle furnace is 5°C / min, and the treatment temperature is 500-1200°C. The inhibitory effect of Cr(III) is as figure 2 , at 900°C, the oxidation rate of Cr(III) dropped from 16% to 8% when no inhibitor was added.
example 3
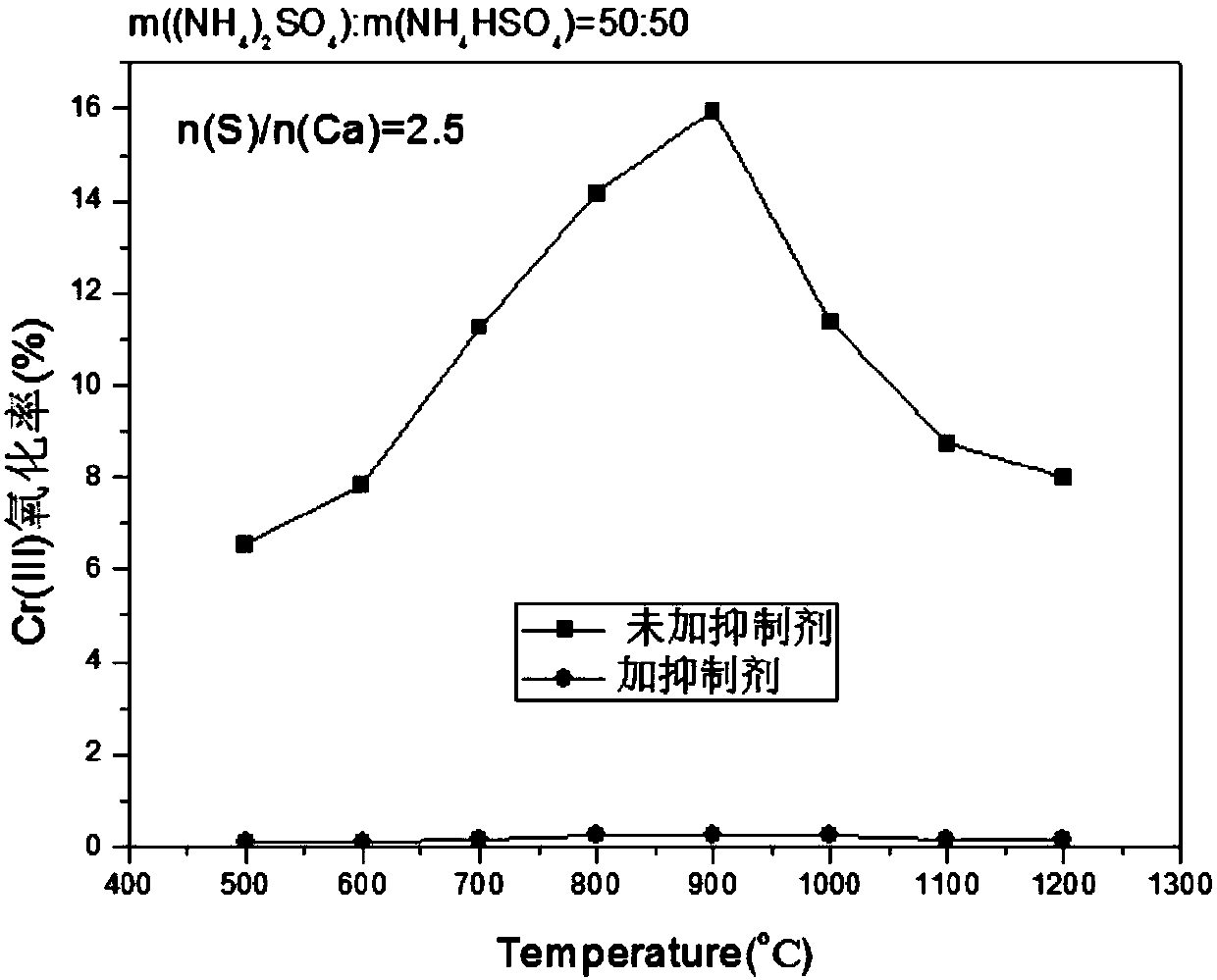
[0020] Using the laboratory to simulate the oxidation process of Cr(III) in the incineration process of tannery sludge, and analyze the pure reagent Cr 2 o 3 The simulated sludge composed of CaO and CaO (n(Ca) / n(Cr)=1) was mixed with a ball mill for 30 minutes. The components of the inhibitor consist of: m((NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ):m(NH 4 HSO 4 )=50:50, the inhibitor was added to the simulated sludge and mixed in a ball mill for 10 minutes, and the amount of inhibitor added was n(S) / n(Ca)=2.5. The mixed material is treated at high temperature in a muffle furnace for 1 hour. The heating rate of the muffle furnace is 5°C / min, and the treatment temperature is 500-1200°C. The inhibitory effect of Cr(III) is as image 3 , at 900°C, the oxidation rate of Cr(III) dropped from 16% to 0.24% without inhibitor.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com