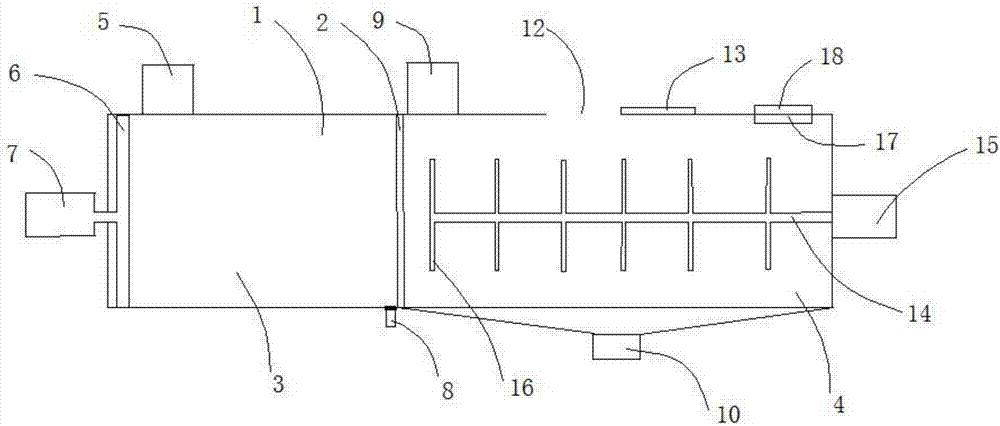
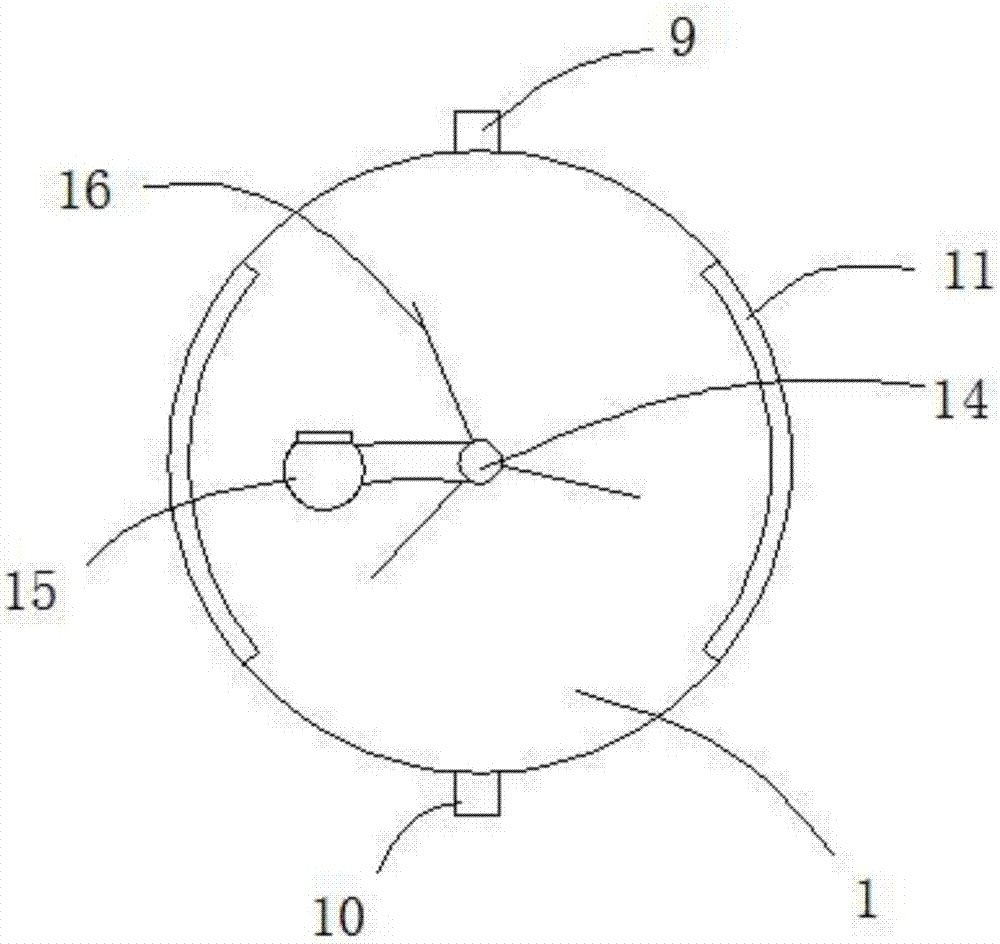
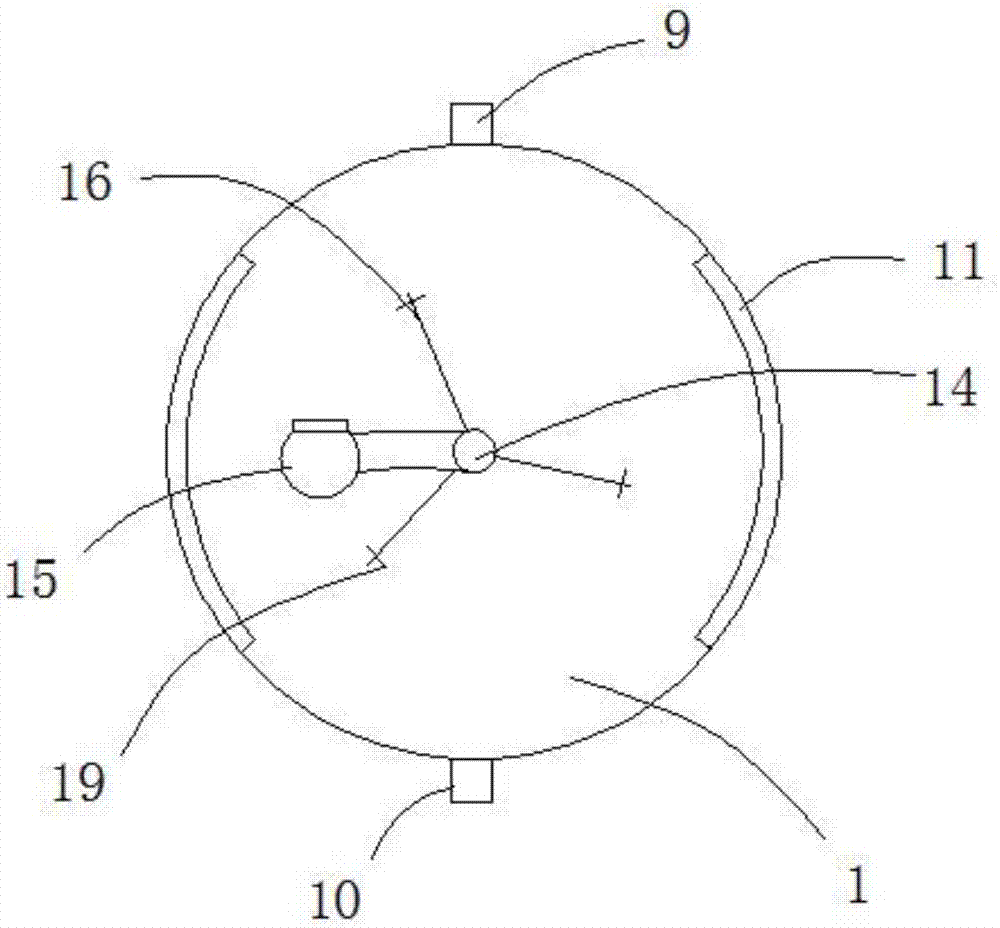
Cow dung treatment method
A treatment method, cow dung technology, applied in the field of animal husbandry, can solve the problems of cultivating substrate pathogenic bacteria and parasites, difficult to use crude fiber, high nitrogen content of cow dung, etc., to achieve suitable fertility, fast drying speed, and reduce fertility Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] The processing method of cow dung may further comprise the steps:
[0052] (1) Pre-dehydration: placing untreated cow dung in a fermenter to remove moisture until the moisture percentage of cow dung is 60%;
[0053] (2) Pre-fermentation: After adding microbial inoculum to cow dung, ferment at 35°C for 7h; said microbial inoculum is composed of Bacillus mycoides and Bacillus subtilis; 5% of mass;
[0054] (3) Batching: add in the fermenter the adjuvant that is made up of 10 parts of Chinese medicine dregs of mass parts, 5 parts of lime, 20 parts of bacterium chaff after mixing; , Gynostemma pentaphyllum, peppermint, water calamus, cassia bark, rhubarb; the mass ratio of the cow dung and auxiliary materials is 10:1;
[0055] (5) Main fermentation: Add the fermented bacteria consisting of cellulose-degrading bacteria, xylan-degrading bacteria, and EM bacteria at a ratio of 1:2:9 to the fermenter and continue at 45°C Lower fermentation for 5h; the addition of the ferment...
Embodiment 2
[0058] The processing method of cow dung may further comprise the steps:
[0059] (1) Pre-dehydration: untreated cow dung is placed in a fermenter to remove moisture until the moisture percentage of cow dung is 50%;
[0060] (2) Pre-fermentation: After adding microbial inoculum to cow dung, ferment at 40°C for 5h; the microbial inoculum is composed of Bacillus mycoides and Bacillus subtilis; 5% of mass;
[0061] (3) Batching: add in the fermenter the adjuvant that is made up of 10 parts of Chinese medicine dregs of mass parts, 5 parts of lime, 20 parts of bacterium chaff after mixing; , Gynostemma pentaphyllum, peppermint, water calamus, cassia bark, rhubarb; the mass ratio of the cow dung and auxiliary materials is 10:1;
[0062] (5) Main fermentation: Add the fermented bacteria consisting of cellulose-degrading bacteria, xylan-degrading bacteria, and EM bacteria at a ratio of 1:5:5 to the fermenter and continue at 50°C Lower fermentation for 3h; the addition of the fermen...
Embodiment 3
[0065] The processing method of cow dung may further comprise the steps:
[0066] (1) Pre-dehydration: untreated cow dung is placed in a fermenter to remove moisture until the moisture percentage of cow dung is 55%;
[0067] (2) Pre-fermentation: After adding microbial inoculum to cow dung, ferment at 38°C for 6h; said microbial inoculum is composed of Bacillus mycoides and Bacillus subtilis; 3% of mass;
[0068] (3) Batching: add in the fermenter the adjuvant that is made up of 12 parts of Chinese medicine dregs, 3 parts of lime, 25 parts of bacterium bran of mass parts and mix and stir evenly; , Gynostemma pentaphyllum, peppermint, water calamus, cassia bark, rhubarb; the mass ratio of the cow dung and auxiliary materials is 8:1;
[0069] (5) Main fermentation: Add the fermented bacteria consisting of cellulose-degrading bacteria, xylan-degrading bacteria, and EM bacteria at a ratio of 1:3:8 to the fermenter, and continue at 48°C Lower fermentation for 4h; the addition of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com