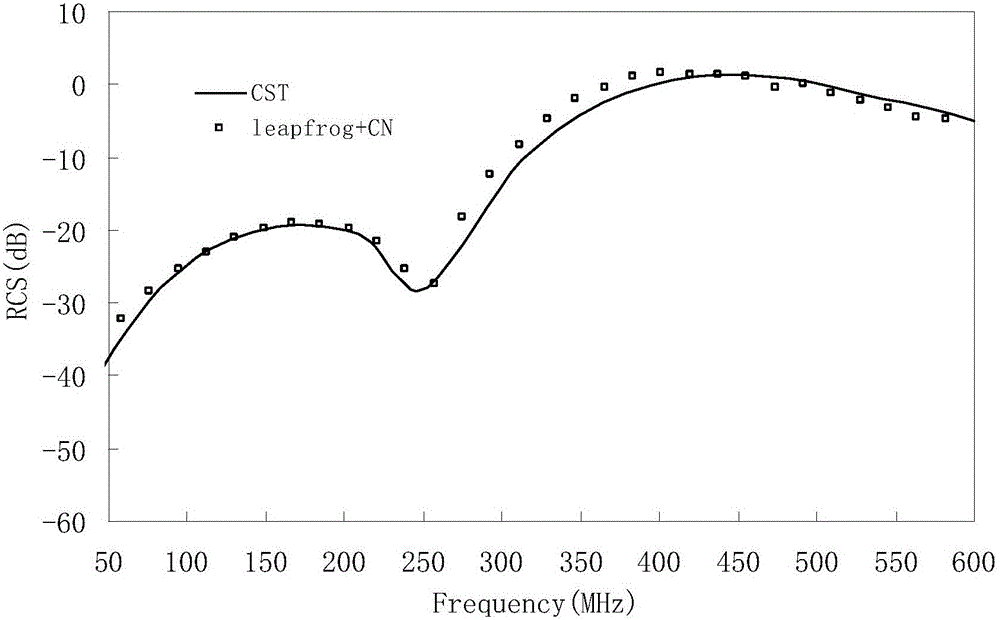
Parallel explicit and implicit mixed discontinuous Galerkin finite element time domain method
A finite element method, explicit and implicit technology, applied in the field of large-scale parallel computing, can solve problems such as inability to achieve high parallelism and inability to enlarge time steps, and achieve the effect of reducing time and amplifying time steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0016] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0017] The present invention is a parallel explicit and implicit mixed discontinuous Galerkin time domain finite element method, the steps are as follows:
[0018] The first step is to establish a solution model, discretize the model with a tetrahedral grid, and obtain the structural information of the model, including the node information and unit information of the tetrahedron.
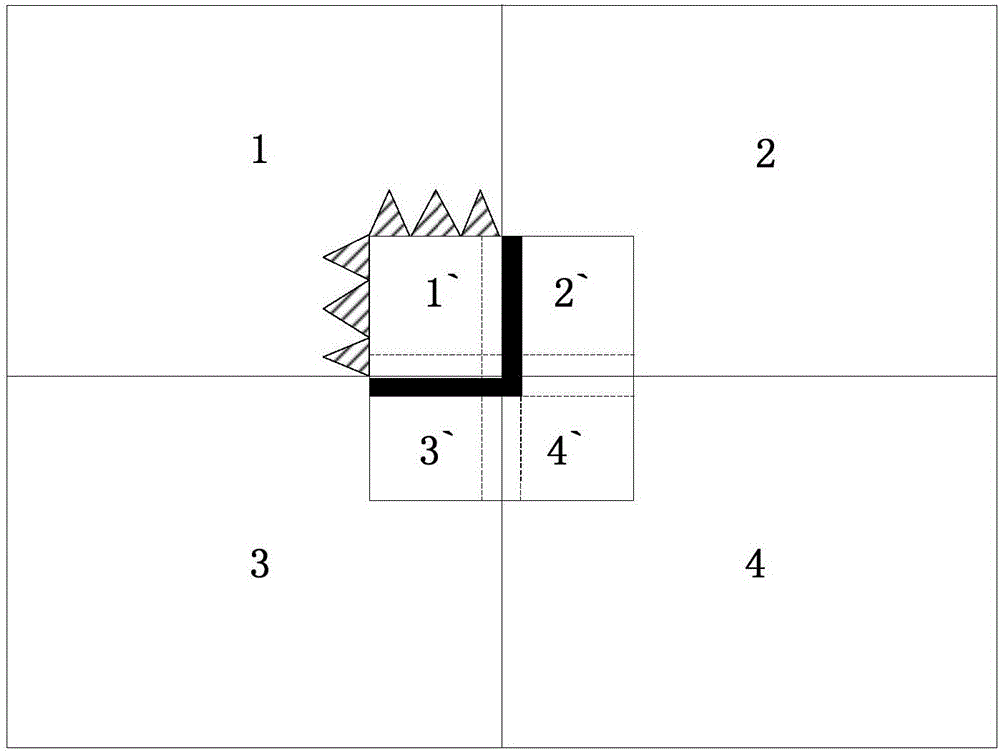
[0019] The second step: MPI (Message Passing Interface) initialization, divide the tetrahedron unit into different regions according to the coordinates of the center point, determine the total number of processes, number each process, execute the pre-processing of the program, and find out the explicit and hidden respectively Formula solution area, the implicit difference scheme is used to solve the area with a small discrete grid size, and the explicit difference scheme is used to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com