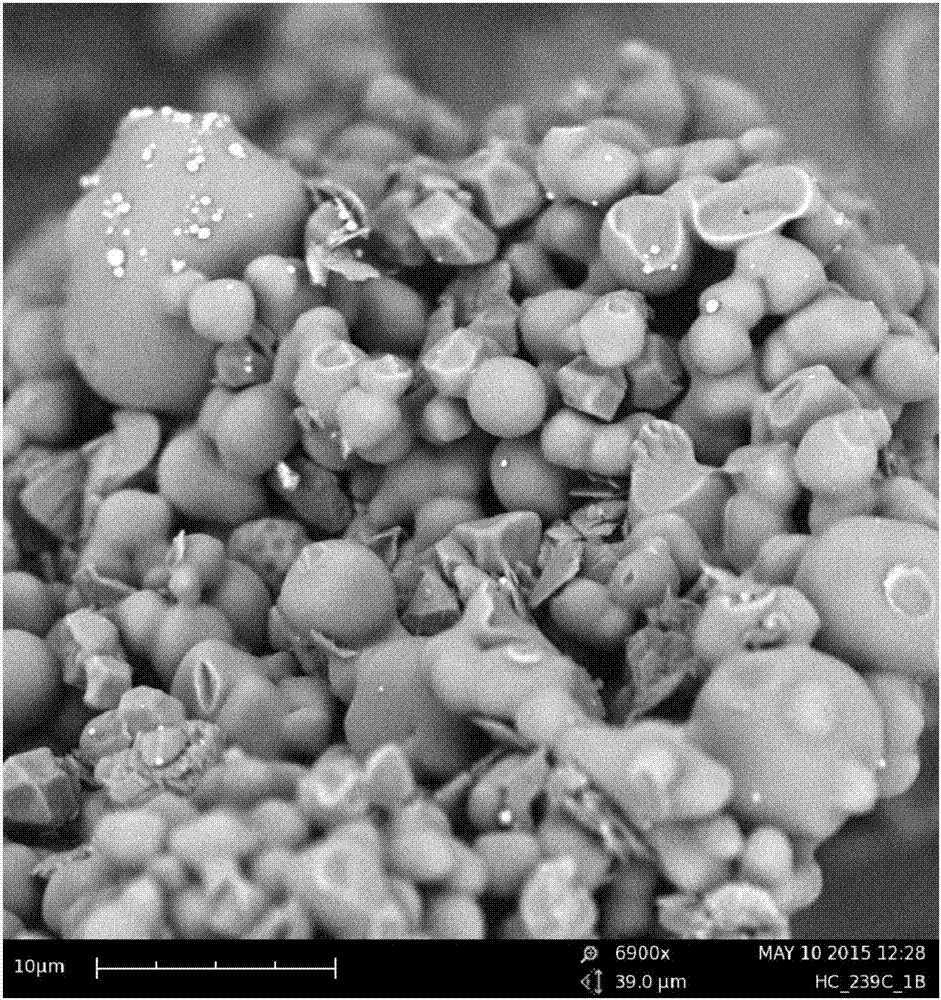
Preparation method and uses of starch-based composite hard carbon negative electrode material
A negative electrode material, starch-based technology, applied in the field of preparation of starch-based composite hard carbon negative electrode materials, can solve the problems of low efficiency restricting industrial application, graphite layer peeling and pulverization, SEI film instability and other problems, and achieve high current charging Good discharge performance, low cost, common source of raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] The starch was first kept at a constant temperature of 170°C for 48 hours in an air atmosphere until the starch completely turned into a black powder, then raised to 900°C at a rate of 2°C / min under a nitrogen atmosphere, kept for 4 hours, and then naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain starch-based hard carbon .
[0021] Mix starch-based hard carbon with sucrose and flaky graphite with a D50 of 1 μm in a weight ratio of 20:3:0.1 to obtain a raw material mixture, and add the raw material mixture to twice its volume of deionized water, stir or sonicate for 1 hour , and dried at 80°C until it became a solid powder to obtain a carbon precursor.
[0022] Put the carbon precursor into the furnace, and carbonize at a high temperature of 700°C for 1 hour under a nitrogen atmosphere to obtain composite carbonized particles.
[0023] After the carbonized particles are sieved through 60 meshes, the under-sieves are taken, and classified in a classifier at a frequency of ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] The starch was first kept at a constant temperature of 250°C for 24 hours in an air atmosphere until the starch completely turned into a black powder, then raised to 1100°C at a rate of 2°C / min under a nitrogen atmosphere, kept for 1 hour, and then naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain starch-based hard carbon .
[0027] Mix starch-based hard carbon with sucrose and flake graphite with a D50 of 5 μm in a weight ratio of 20:3:3 to obtain a raw material mixture, and add the raw material mixture to twice its volume of deionized water for stirring or ultrasonication for 1 h, Dry at 80°C until it becomes a solid powder to obtain a carbon precursor.
[0028] Put the carbon precursor into the furnace, and carbonize at a high temperature of 850° C. for 4 hours under a nitrogen atmosphere to obtain composite carbonized particles.
[0029] After the carbonized particles are sieved through 200 meshes, the undersieves are taken and classified in a classifier at a frequenc...
Embodiment 3
[0032] The starch was first kept at a constant temperature of 200°C for 36 hours in an air atmosphere until the starch completely turned into a black powder, then raised to 1000°C at a rate of 2°C / min under a nitrogen atmosphere, kept for 2 hours, and then naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain starch-based hard carbon .
[0033] Mix starch-based hard carbon with sucrose and flake graphite with a D50 of 3 μm in a weight ratio of 20:3:1 to obtain a raw material mixture, and add the raw material mixture to twice its volume of deionized water for stirring or ultrasonication for 1 h, Dry at 80°C until it becomes a solid powder to obtain a carbon precursor.
[0034] Put the carbon precursor in the furnace, and carbonize at a high temperature of 800°C for 2 hours under a nitrogen atmosphere to obtain composite carbonized particles.
[0035] After the carbonized particles are sieved through 150 meshes, the undersieve is taken, and classified in a classifier at a frequency of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| D50 | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com