A method of separating rhamnolipids from a fermentation broth
A technology for rhamnolipid and compound, which is applied in the field of separating rhamnolipid from fermentation broth, can solve problems such as high recovery and purification cost of rhamnolipid, and achieve the effects of improving environmental impact and accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
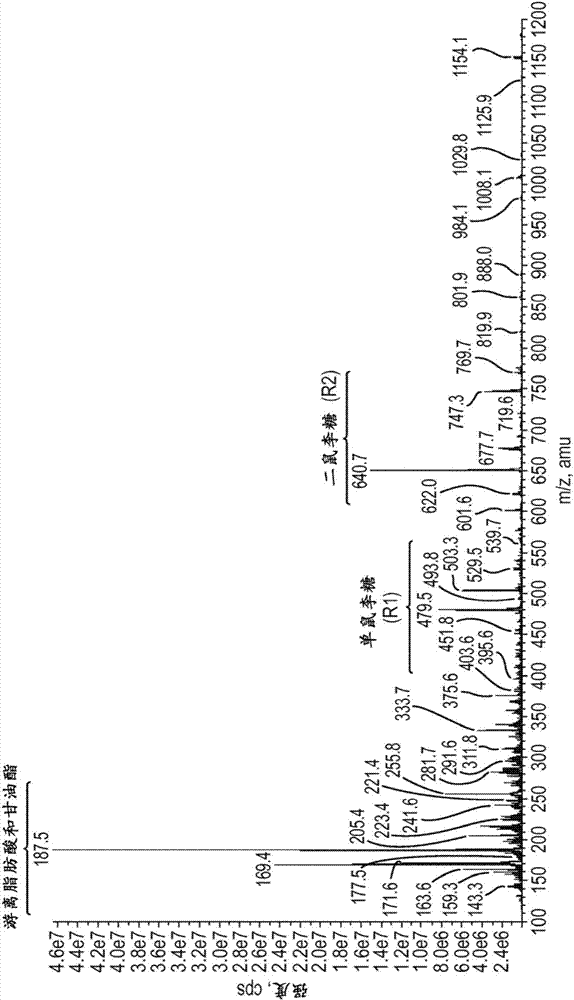
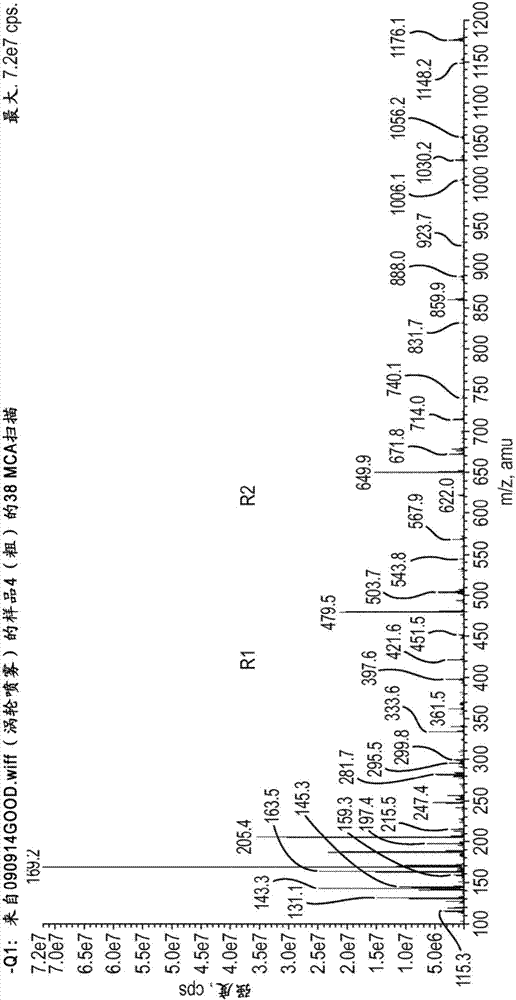
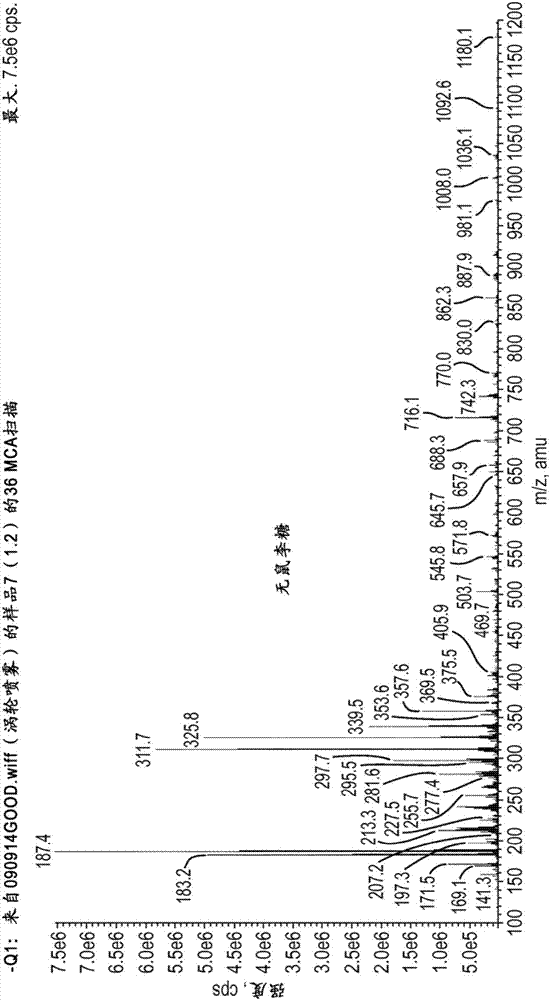
[0042] use has figure 1 The indicated mass spectrometric identification of the composition of the crude rhamnolipid biomass was extracted from the assay. Mass spectrometry was performed after preparing solutions in methanol at 30 mg / L. Electrospray ionization (ESI) was used for analysis in negative ionization mode with a scan range of 100-1200 amu and a flow rate of 20 μL / min. exist figure 1 In , we can see different compounds: fatty acids and glycerides, monorhamnose (R1) and dirhamnose (R2).
[0043] A commercial sample of rhamnolipid JBR425 (from Jeneil) previously stored at 4°C was mixed with an inert adsorption carrier: diatomaceous earth Celite 545 (from Celite Corp) at a ratio of 3.7 parts carrier to 1 part rhamnolipid mixture .
[0044] Extraction was performed via supercritical fluid chromatography using a Thar SFC-1000 with a 1 L extractor on a full volume (16 L) Separex pilot separex 2X16L using two extractors in parallel.
[0045] Fill the extractor with the l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com