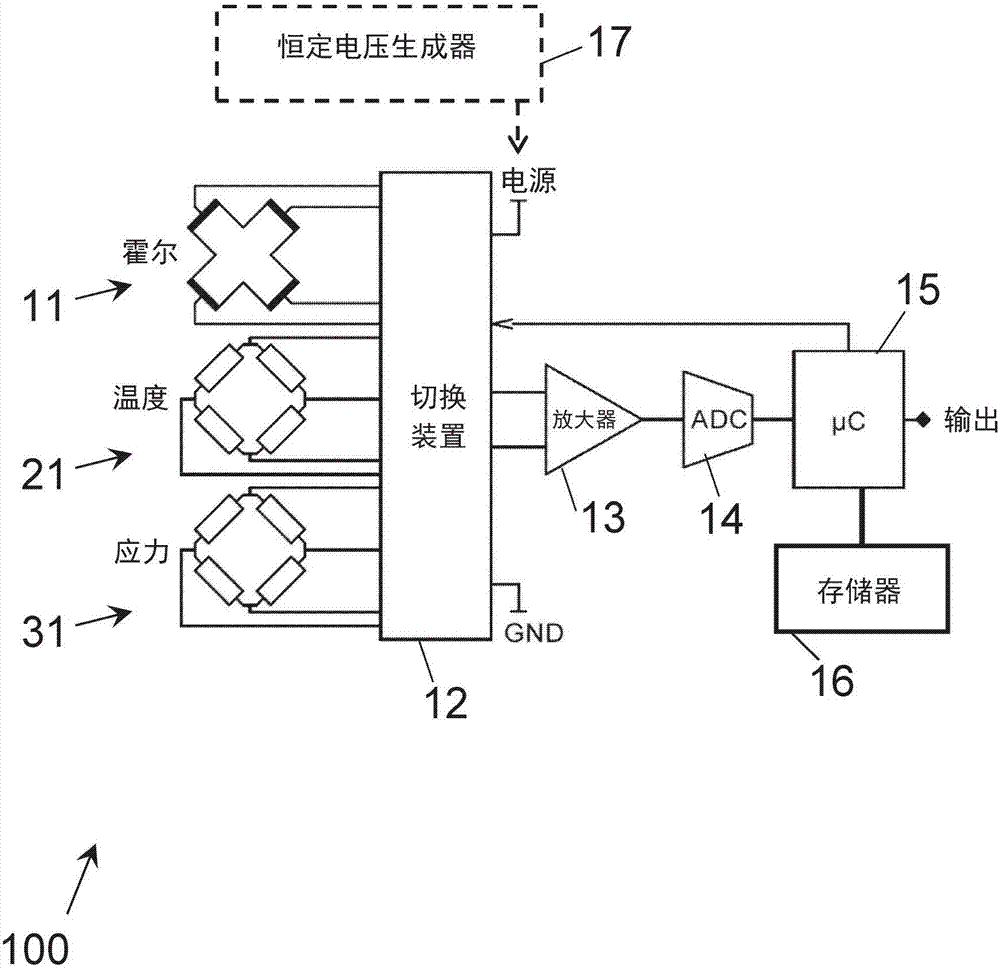
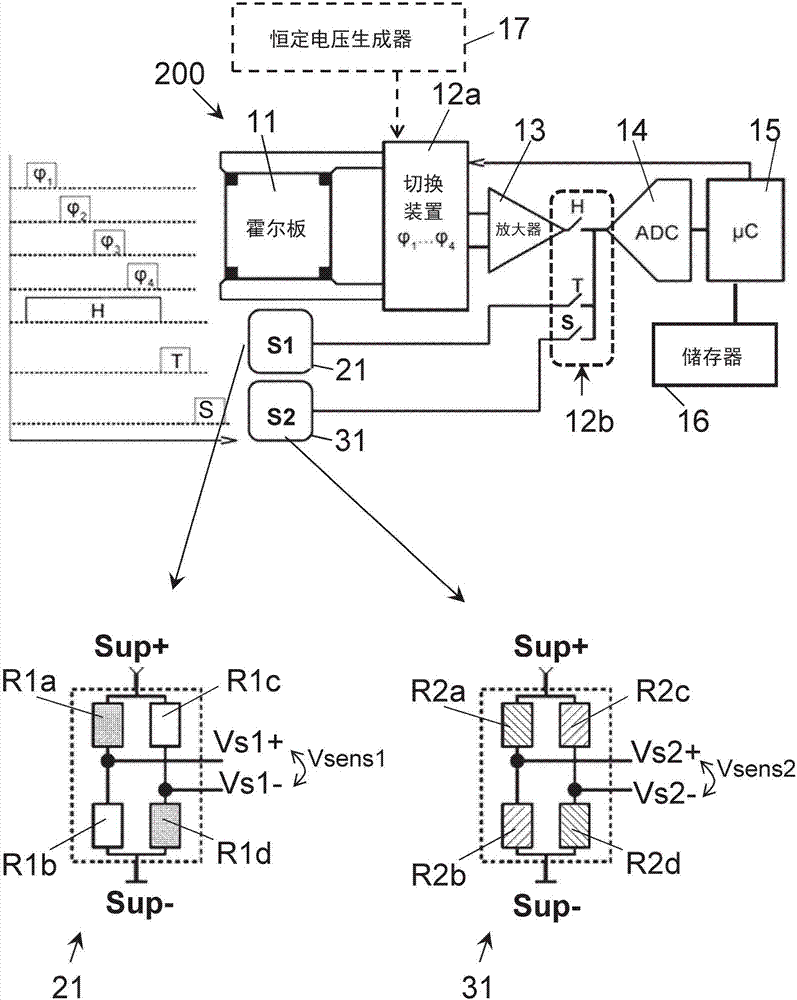
Stress and temperature compensated hall sensor, and method
一种传感器、传感器信号的技术,应用在转换传感器输出、采用电/磁装置传递传感构件、仪器等方向,能够解决方法复杂等问题,达到高灵敏度、容易实现、多自由度的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
[0198] In a variation of Example 1, some coefficients are chosen to be equal to zero, resulting in fewer coefficients to be determined and stored and simpler equations to be solved. The equation system for the second example is:
[0199]
example 3
[0201] The third example is practically the same as the second example, but is formulated differently. The main reason for this example is to show that polynomial representations can also be used to represent "temperature-dependent coefficients". The set of equations [11], [12] can be rewritten as:
[0202]
[0203] or:
[0204]
[0205] where the values of ε1 and ε2 are not constants, but are actually temperature-dependent values ε1(T) and ε2(T), which can be stored in non-volatile memory as, for example, a list of values representing a piecewise linear approximation .
[0206] A possible advantage of this formulation is that the system of equations [16], [17] can be "solved" again by an iterative process starting from Δσ iso and starting with a starting value of ΔT, determine ε 1 (T 0 ) and ε 2 (T 0 ) for corresponding values (which are then considered temporary constants), solving the system of equations (with constant coefficients) to obtain a new set ...
example 4
[0209] As mentioned above, simpler variants can be formulated by setting certain values to zero. For example, if the coefficient α of Example 2 (equations [12], [13]) 11 and beta 11 is also set to zero, the system of equations becomes:
[0210]
[0211] Even this simple set of equations can yield highly accurate results in an application to be discussed further, for compensating Hall sensor readings over a temperature range of about 0°C to about 140°C.
[0212] One advantage is that this equation is particularly easy to solve (e.g., by first eliminating the parameter Δσ iso , then solve the quadratic equation with a single variable ΔT, and then substitute ΔT into one of the equations to find Δσ iso ), but other methods of solving the system of equations can of course also be used. The simplicity of this solution combined with its high accuracy is a major advantage over prior art solutions.
[0213] II. Compensation for Temperature and Stress
[0214] The above descr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com