Long wave light guide infrared detector non-uniformity correction circuit
A non-uniformity correction and infrared detector technology, which is applied in optical radiation measurement, electric radiation detectors, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of circuit output swing exceeding the dynamic range, uneven resistance, etc., and achieve low power consumption and applicable Wide range and good repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
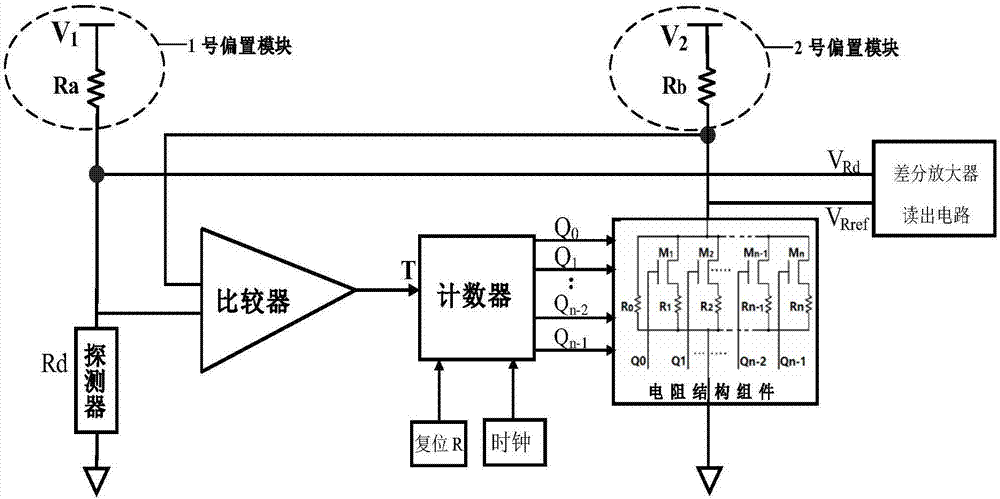
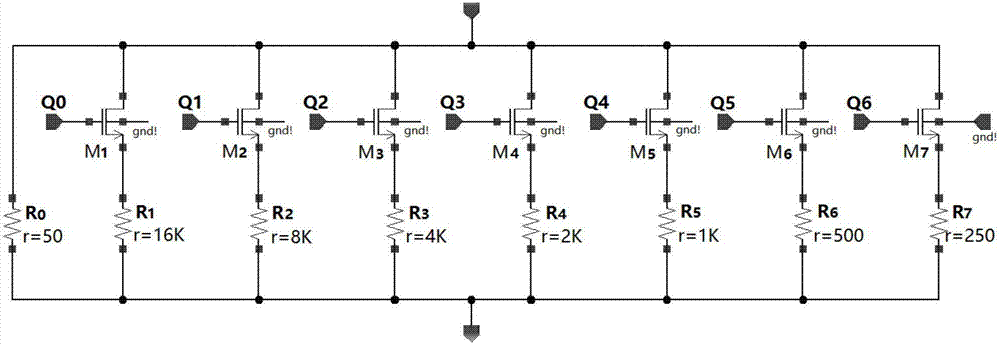
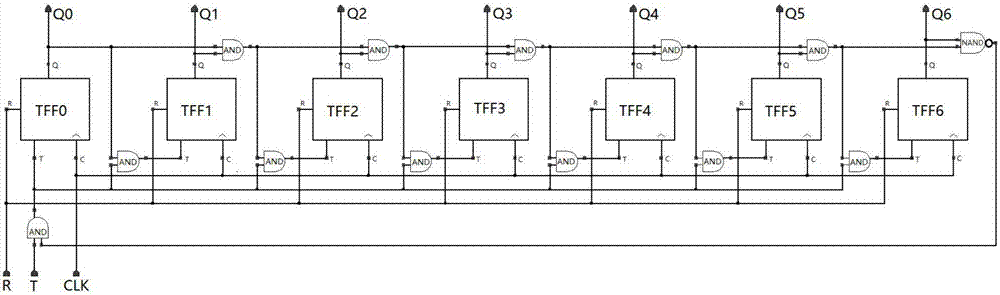
[0025] The unit structure of the correction circuit is as figure 1 Shown, including comparator, counter, resistor structure components and two bias blocks. V can be adjusted according to different detector resistances and resistance structure components 2 Adjustments are made to adjust the voltage division range of the resistive structural components. The voltage source of the bias module should not be too large or too small. If it is too large, the detector will heat up, and if it is too small, the signal of the detector will be small. The resistance of the detector is about 40Ω. When the process error of the resistance structure components is not considered, it can be set, V 1 =2.5V, V 2 = 2.5V, R a =R b = 1KΩ. The specific process of the circuit work is divided into two steps, taking the counter as an example of an addition counter, the first step, the comparator and the counter are powered on, the reset potential and the counting pulse are input, the comparator circu...
Embodiment approach 2
[0034] Let the resistance Rd of a certain detection element be 40Ω, set V 1 =V 2 = 2.5V, R a =R b =1KΩ, using a 7-bit synchronous binary addition counter, at a low temperature of 66K, in the Cadence software environment, using the Specter emulator for simulation, the corresponding correction simulation timing diagram is as follows Figure 5 shown, where the resistive structure component divides the voltage V Rref change process such as Figure 6 As shown, the value of the binary counter after correction is 1010001, and the resistive structure component divides the voltage V Rref It is 95.89mV, which is 0.26mV different from the detector pixel voltage division of 96.15mV. Within the error range, when the detector resistance changes below 200Ω, the difference between the resistance structure components and the detector resistance value of the calibration result is within 0.5% relative to the detector. , that is, the non-uniformity after correction is controlled within 0.5%,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com