Echinocandin fungi residue and sludge mixing wet-type anaerobic digestion cooperated disposal method
An anaerobic digestion and echinocandin technology, which is applied to biological sludge treatment, pyrolysis treatment sludge, waste fuel, etc., can solve the problems of large equipment footprint, large resource consumption, and low treatment efficiency, and achieve Improve biochemical properties, improve nutrient ratio, and ensure activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
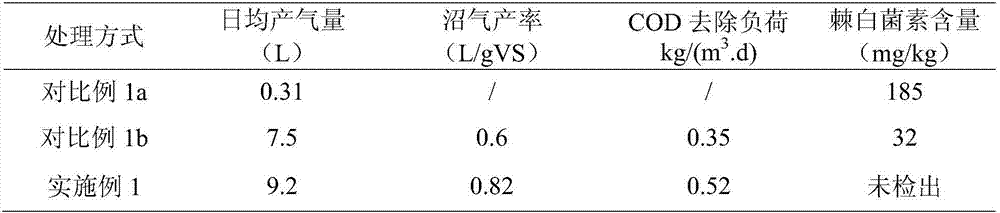
Embodiment 1
[0025] (1) Alkali-thermal modification of echinocandin bacteria residue
[0026] Get 2L of echinocandin bacterial residue (pH value 7.1, water content 97%, volatile solid VS 92.5%, crude protein 38.1%, crude fiber 8.91%, crude fat 2.01%) of certain biopharmaceutical factory; With 0.05g ( NaOH) / g(TS) ratio was added to NaOH, then treated in a 70°C water bath for 2h, cooled to room temperature, and set aside.
[0027] (2) thermal hydrolysis of sludge
[0028] Take 1L of sewage biochemical treatment sludge (pH value 6.75, water content 96.5%, VS 56.2%), put the sludge in a high-temperature cooking pot at 121°C for 30 minutes, cool to room temperature, and set aside.
[0029] (3) Mixing of bacteria residue and sludge
[0030] The echinocandin bacterial residue modified by step (1) and the sludge thermally hydrolyzed in step (2) are uniformly mixed at a volume ratio of 2:1 to obtain a mixed material of bacterial residue and sludge.
[0031] (4) Anaerobic digestion to produce bio...
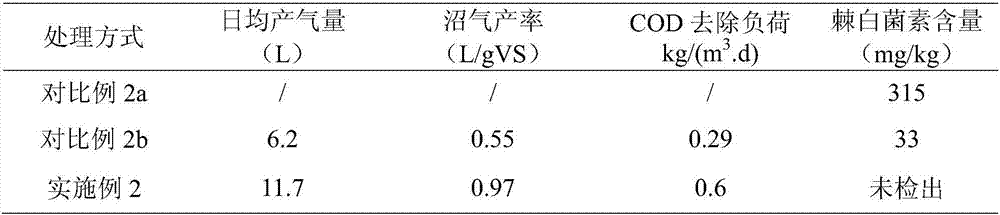
Embodiment 2
[0045] (1) Alkali-thermal modification of echinocandin bacteria residue
[0046] Take 3L of echinocandin bacteria residue (pH value 7.3, water content 96%, VS 93.7%, crude protein 49.3%, crude fiber 1.79%, crude fat 5.23%) from a biopharmaceutical factory. Add NaOH at a ratio of 0.08g(NaOH) / g(TS), then treat in a water bath at 80°C for 1h, and cool to room temperature for use.
[0047] (2) thermal hydrolysis of sludge
[0048] Take 1L of sewage biochemical treatment sludge (pH value 6.5, water content 97.2%, VS 52%), and put the sludge in a high-temperature cooking pot at 150° C. for 15 minutes for hydrolysis. Cool to room temperature and set aside.
[0049] (3) Mixing of bacteria residue and sludge
[0050] The echinocandin slag modified by step (1) and the sludge subjected to thermal hydrolysis in step (2) are uniformly mixed at a volume ratio of 3:1 to obtain a mixed material of slag and sludge.
[0051] (4) Anaerobic digestion to produce biogas
[0052] Put 4L of mixe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com