Streptococcus salivarius and application thereof in preparing ozostomia eliminating drug
A technology for streptococcus salivarius and halitosis, applied in the field of microorganisms, to achieve the effect of wide application prospects and value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
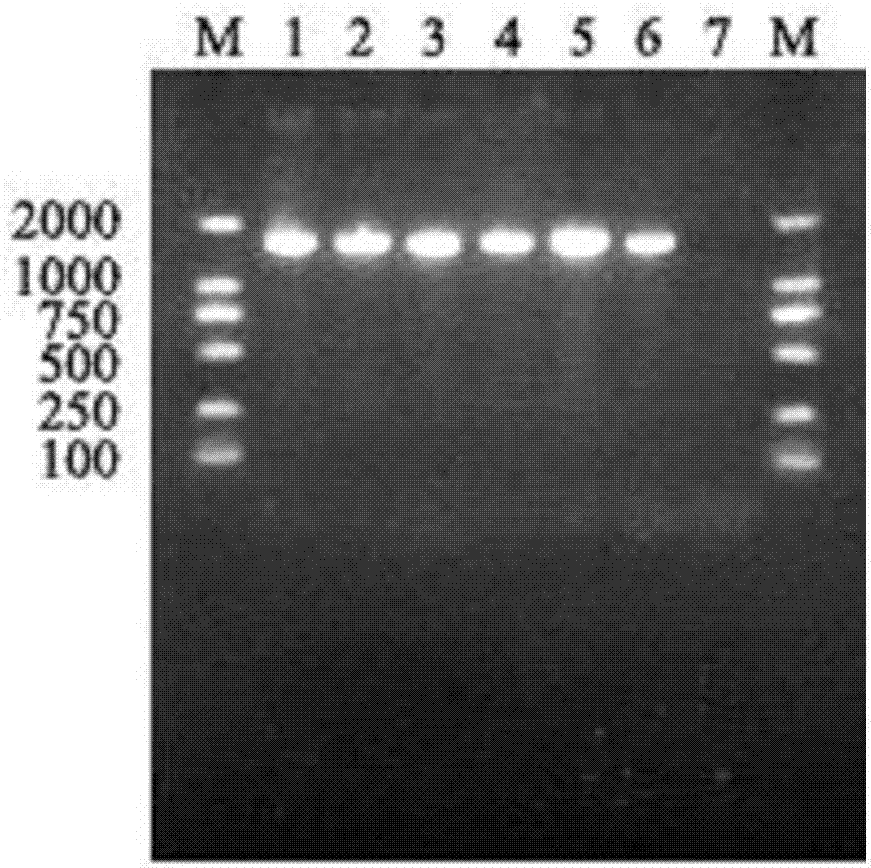
[0019] The screening of embodiment 1 bacterial strain
[0020] Implementation goal: To find natural bacteria that can inhibit halitosis by isolating the oral dominant flora from the saliva of 250 children without halitosis and detecting the decomposition of sulfur-containing compounds.
Embodiment approach
[0022] (1) Sampling: 250 normal children aged 4-7 years, without bad breath, without oral diseases, without family genetic diseases, without systemic diseases, and without long-term medication history. Before saliva collection, the purpose and process of the experiment were explained to the school and parents, and consent was obtained. Children should not eat or drink within 2 hours after breakfast. Use a 15ml sterile sample collection tube to naturally collect about 2ml of saliva without external stimulation of saliva secretion. Each sample is divided into three tubes, which are used for PCR identification, bacterial culture and storage respectively.
[0023] (2) Separation and culture: All samples were separated and cultured, diluted with PBS, evenly spread on the brain heart infusion BHI culture dish, placed at 37°C, 5% CO 2 incubator for cultivation.
[0024] (3) Identification by matrix-assisted laser desorption tandem time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS):
...
Embodiment 2
[0087] Embodiment 2. The use and effect of bacterial strains preventing and treating halitosis
[0088] Detection of the ability of dominant Streptococcus salivarius to decompose volatile sulfide produced by standard strains of bad breath:
[0089] By detecting the concentration of hydrogen sulfide and methyl mercaptan in the gas above the co-culture solution of Clostridium nucleatum and dominant Streptococcus salivarius. Gas chromatography was used to detect the sulfur-containing gas concentrations of hydrogen sulfide and methyl mercaptan in the upper gas after co-cultivation of Clostridium nucleatum and dominant Streptococcus salivarius. The results showed that there were higher concentrations of hydrogen sulfide and methyl mercaptan ( Figure 4 ), while the concentration of hydrogen sulfide decreased by 64.6% and the concentration of methyl mercaptan decreased by 71.9%% ( Figure 5 ).
[0090] Table 1 is the specific detection value
[0091] Table 1. HPLC detection of s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com