Biodegradable material and biodegradable mulching film
A biodegradable material and biodegradable technology, applied in the field of biodegradable materials, can solve problems such as fragile, persistent pollution, and difficult to eliminate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0032] In the present invention, the preparation method of described polyester plasticizer comprises the following steps:
[0033] Dibasic acid and dibasic alcohol are mixed, melted, and mixed with glycerol to obtain polyester plasticizer.
[0034] In the present invention, the ratio of the substance amount of the dibasic acid to the dibasic alcohol is preferably 1:1.2 to 1.5; The ratio is preferably 1 to 5:100.
[0035] The present invention heats dibasic acid and dibasic alcohol to a molten state, and then adds glycerol when they are viscous. In the present invention, the time for the mixed reaction with glycerol is preferably 25-35 minutes, more preferably 30 minutes.
[0036] The biodegradable material provided by the invention includes 0.5-15 parts of a cross-linking agent. In the present invention, the crosslinking agent can react with the terminal hydroxyl groups and carboxyl groups of the PLA resin and the polyester plasticizer. When the two ends of the crosslinking...
Embodiment 1
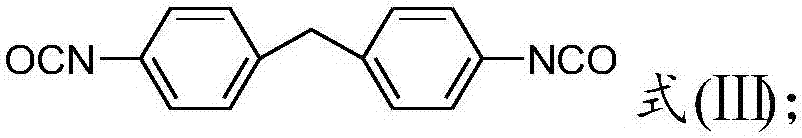
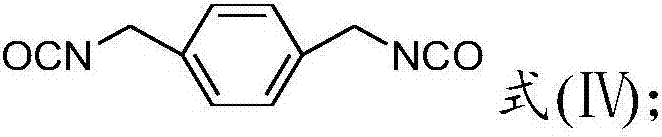
[0071] 50wt% polylactic acid A (number average molecular weight 5×10 4 g / mol), 35wt% polyester plasticizer 1 and 15wt% toluene diisocyanate (TDI) prepared above were mixed in a high mixer for 10 minutes, then added to a twin-screw extruder, extruded and granulated at 150°C , to obtain modified polylactic acid resin particles; the modified resin was blow molded in a film blowing machine at 140°C to obtain a biodegradable mulch film with a film thickness of about 12 μm.
[0072] The above-mentioned biodegradable mulch film and the PE mulch film as a comparison were laid on the spot under the same conditions for 70 days, and the changes in the mechanical properties of the film materials before and after laying were compared. The results are shown in Table 1:
[0073] Table 1 Changes in mechanical properties of PE film, comparative examples and biodegradable mulch films prepared in Examples 1-8
[0074]
[0075] It can be seen from Table 1 that the plasticized biodegradable bi...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Polylactic acid 90wt%A (number average molecular weight 5×10 5 g / mol), 5wt% polyester plasticizer 2 and 5wt% diphenylmethane diisocyanate (MDI) prepared above were mixed in a high mixer for 10 minutes, then added to a twin-screw extruder, and extruded at 220°C Pelletize to obtain modified polylactic acid resin particles; blow mold the modified resin in a film blowing machine at 170°C to obtain a biodegradable mulch film with a film thickness of about 12 μm.
[0078] The above-mentioned biodegradable plastic film was laid on the ground for 70 days, and the mechanical properties of the film material were compared before and after laying. The results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com