Stem cell compositions and methods of producing stem cells for therapeutic applications
A stem cell and composition technology, applied in the field of stem cell populations, can solve the problems of reduced cardioprotective effect, limited use, cell aging, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
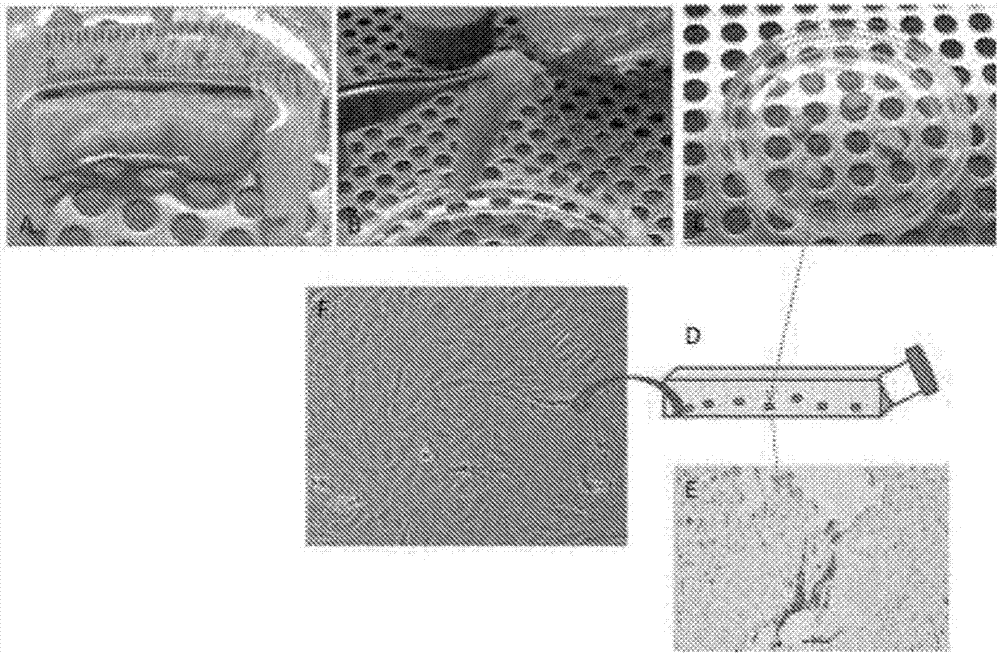
[0080] Example 1: Vitality of dental pulp
[0081] Maher Al-Atari Abou-Asi et al. (2011) claim that the origin of pluripotent cells extracted from dental pulp (DP) according to the publication of Kerkis et al., 2006 cannot be dental pulp because patients aged 5 to 7 years do not have dental Instead of the pulp, the so-called tooth germ is an aggregate of undifferentiated cells that will form the future tooth with different parts: enamel, pulp, gum, cementum, bone, blood vessels and nerves. However, Cordeiro et al. (2008) found that stem cells from human exfoliated primary teeth generated DP-like tissues in vivo. The authors transplanted SHEDs grown in biodegradable scaffolds prepared within human tooth slices into immunodeficient mice. They observed tissue formation from these cells, demonstrating a structure and cellularity very similar to physiological DP. Ultrastructural analysis of dentin sialoproteins by transmission electron microscopy and immunohistochemistry demonst...
Embodiment 2
[0089] Example 2: Stem cells from dental pulp explants
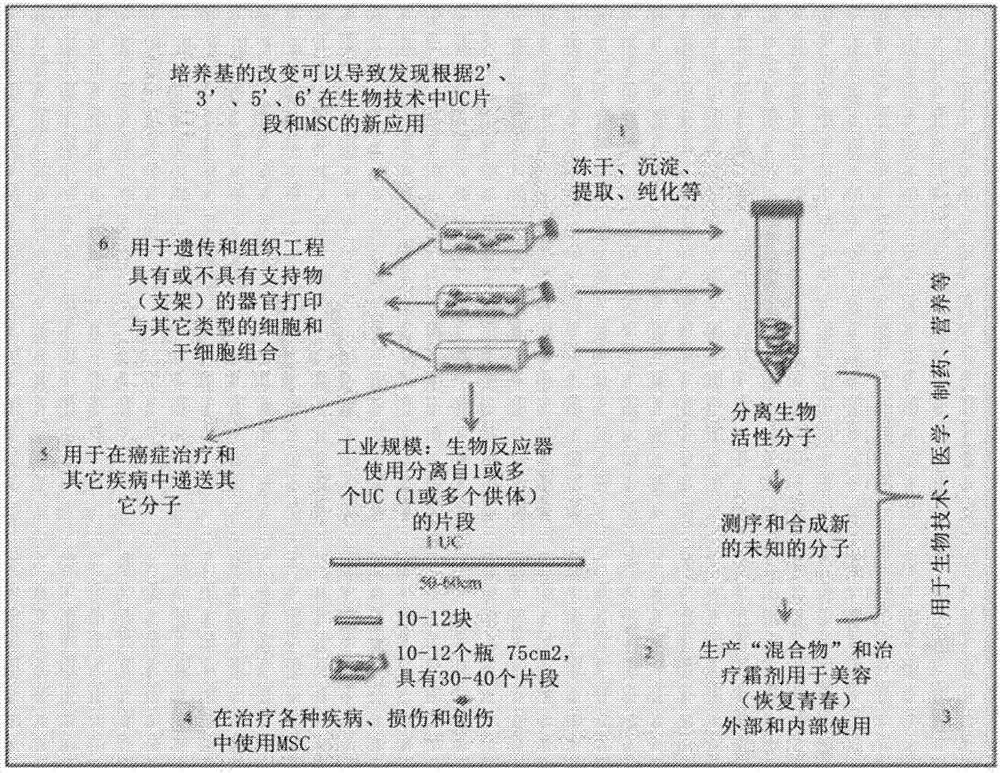
[0090] Different examples of dental tissue described in detail in a recent review of stem cells derived from dental origin (Deepa Ponnaiyan 2014) describe different characterizations of biomarkers in stem cells derived from dental tissue, such as dental pulp stem cells, periodontal ligament stem cells, stem cells from human Stem cells from exfoliated deciduous teeth, dental follicle progenitor stem cells from the apical papilla, oral periosteum stem cells and most recently from the gingival connective tissue. Strikingly, most markers were similar between different dental stem cells, but the expression of Notch and CD29 markers was different between stem cells from various dental origins. The in vitro and in vivo marker expression of cells obtained by our disclosed method was identical.
Embodiment 3
[0091] Example 3: Human IDPSCs from Teratomas Harvested Repeatedly at Early Passages
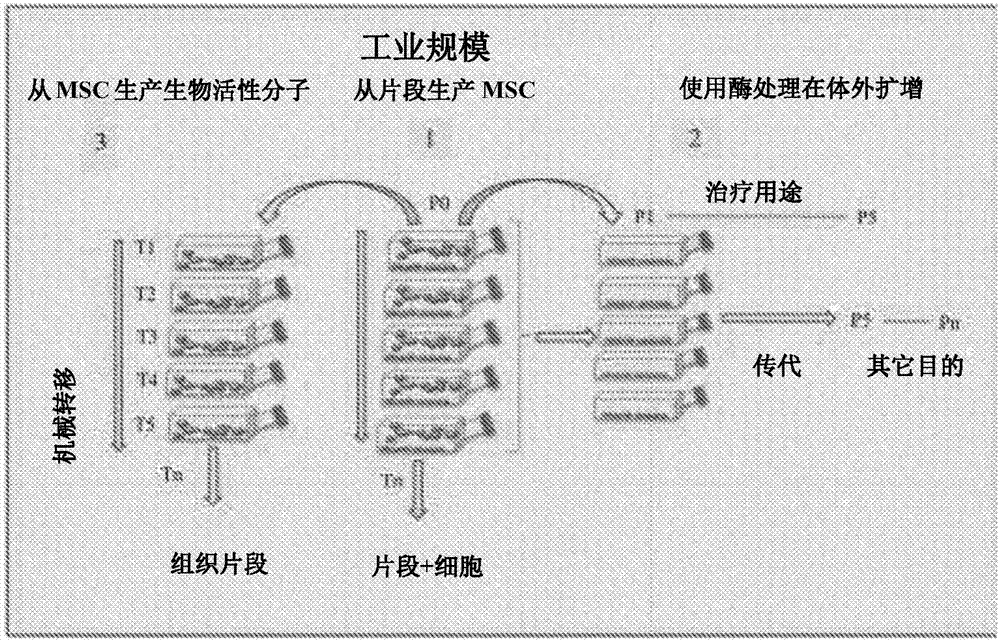
[0092] Teratoma formation is an important tool for determining the pluripotency of cells such as embryonic stem cells (ES cells) or induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells). Our studies used a consistent protocol similar to that recently published by Gropp et al. (2012) for assessing the teratoma-forming capacity of cells. When 10 6 cells (Gropp et al. used 10 5 cells) of mouse ES cells and human iPS cells subcutaneously co-transplanted into immunodeficient mice with artificial basement membrane (Matrigel), our method was shown to be highly reproducible and efficient. In 100% of cases, we observed teratoma formation in a large number of animals, even at follow-up examinations up to 6 months after transplantation. We used this method for biosafety analysis of other adult mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), such as those derived from the pulp of primary teeth, umbilical cord, adipose tissue, e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com