A kind of microcable micropipe PBT sheath material and preparation method thereof
A sheathing material and microtube technology, applied in plastic/resin/wax insulators, organic insulators, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of large shrinkage, failure to meet technical requirements, poor hot water performance, etc., to improve Toughness and overall molding shrinkage reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
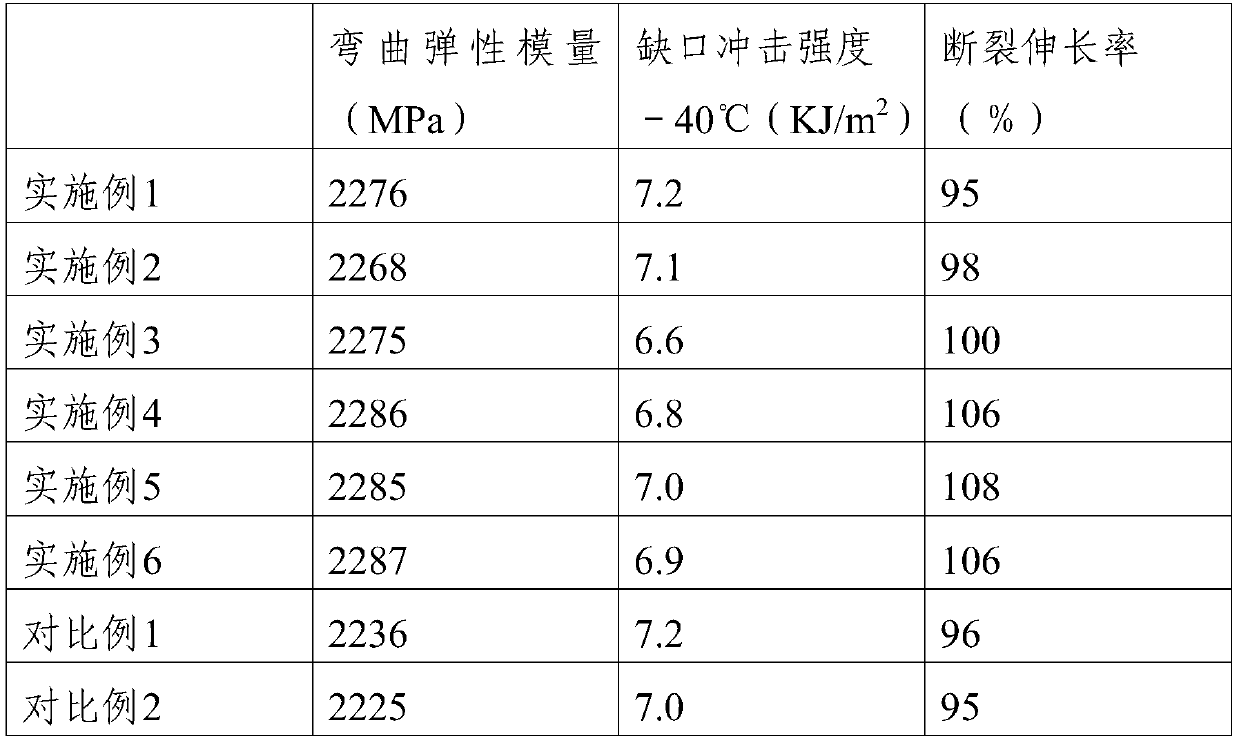
Embodiment 1-3
[0035] The composition of the microcable microtube PBT sheath material in Examples 1-3 is shown in the following table (component data are all calculated in parts by weight), and the polypropylene includes atactic polypropylene with an average molecular weight of 5000-9000.
[0036] The preparation method of sheath material comprises the following steps:
[0037] S1: Add the raw material as claimed in claim 1 to high-speed mixing;
[0038] S2: The reactor is evacuated to a vacuum degree of -0.08MPa, and the mixture is added to the reactor;
[0039] S3: Raise the temperature of the reactor to 180°C, perform solid-phase polycondensation and heat preservation reaction for 12 hours, and cool down to obtain the finished product of PBT sheathing material for microcables and microtubes.
[0040] Example 1 Example 2 Example 3 PBT 88 92 90 thermoplastic elastomer 3 5 4 Epoxy chain extender 2 5 3.5 Polyester nucleating masterbatch 1 3 2 ...
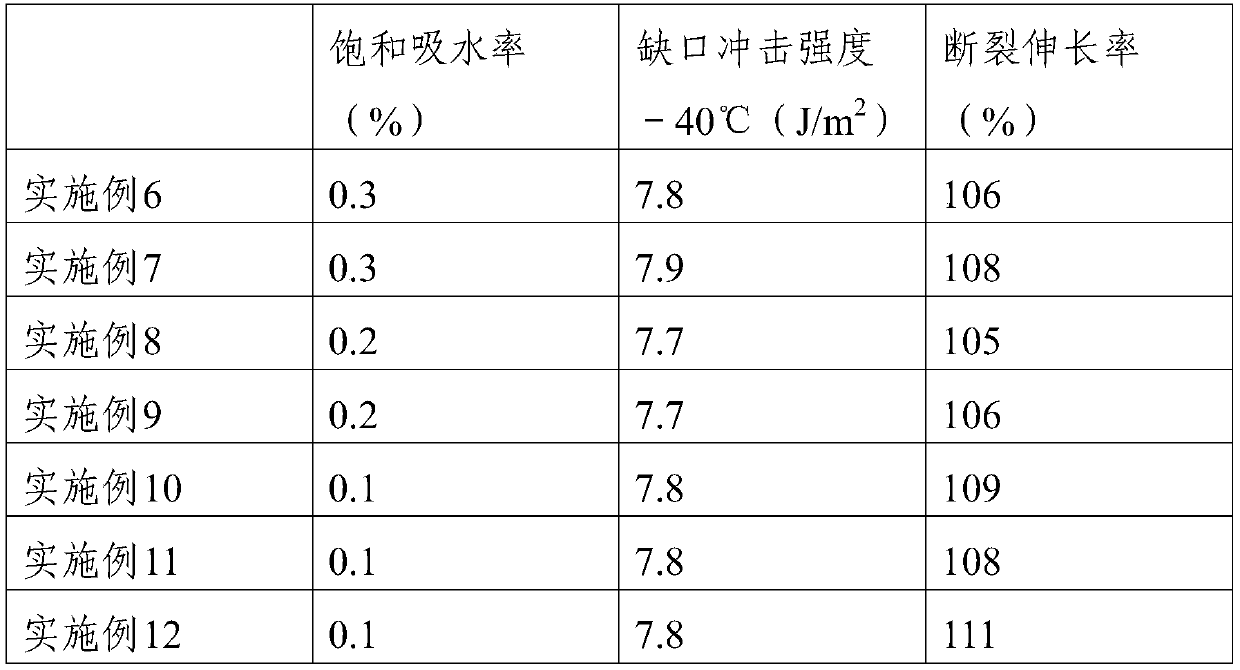
Embodiment 4-6
[0043] Examples 4-6 are based on Example 3, with the difference that: the polypropylene is a combination of atactic polypropylene and syndiotactic polypropylene, and the weight percentages of atactic polypropylene in the composition are 50%, 90%, and 70%, respectively.
[0044] The difference between the production process of embodiment 4-6 and embodiment 1-3 is:
[0045] S2: The reaction kettle is evacuated to a vacuum degree of -0.1MPa, and the mixture is added to the reaction kettle;
[0046] S3: The temperature of the reactor was raised to 250° C., and the solid-phase polycondensation reaction was carried out for 8 hours.
Embodiment 7
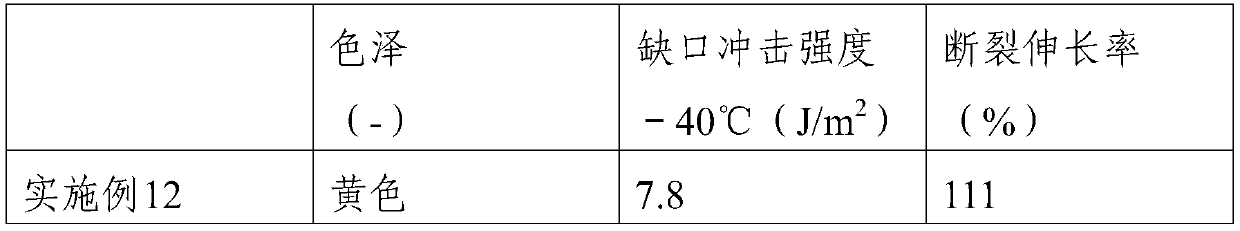
[0048]Embodiments 7-11 are based on Embodiment 6, and the difference is that the thermoplastic elastomer in Embodiment 7 is hydroxyl-terminated thermoplastic styrene-butadiene rubber, the thermoplastic elastomer in Embodiment 8 is a combination of polyether-type TPU, and the thermoplastic elastomer in Embodiments 9-11 The body is composed of hydroxyl-terminated thermoplastic styrene-butadiene rubber and polyether TPU, and the weight percentages of the thermoplastic elastomer polyether TPU are 25%, 53%, and 38% respectively.
[0049] In Examples 7-10, the Shore hardness of the hydroxyl-terminated thermoplastic styrene-butadiene rubber is not less than 68A, and the Shore hardness of the polyether TPU is 60-75A.
[0050] The difference between the production process of embodiment 7-10 and embodiment 1-3 is:
[0051] S2: The reactor is evacuated to a vacuum degree of -0.09MPa, and the mixture is added to the reactor;
[0052] S3: Raise the temperature of the reactor to 210° C., a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Shore hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Shore hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Shore hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com