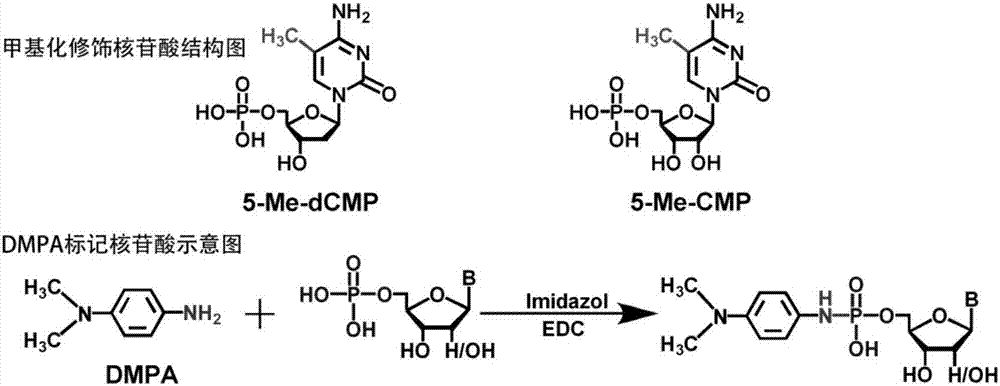
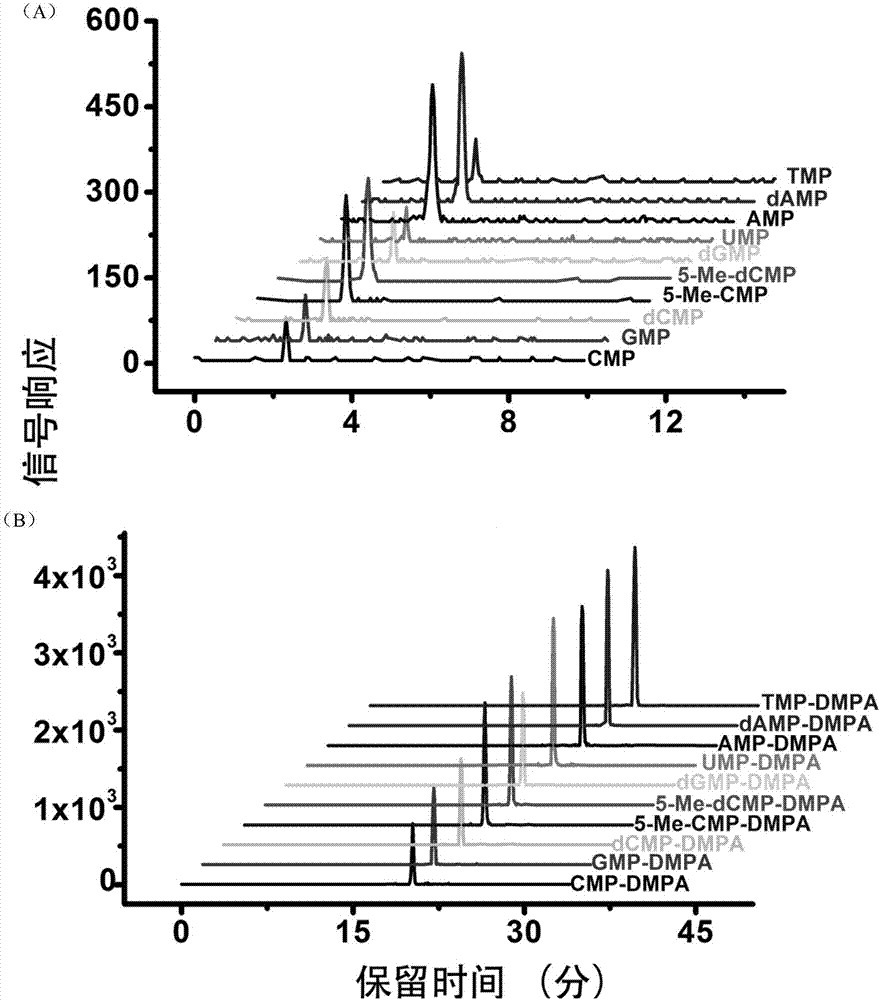
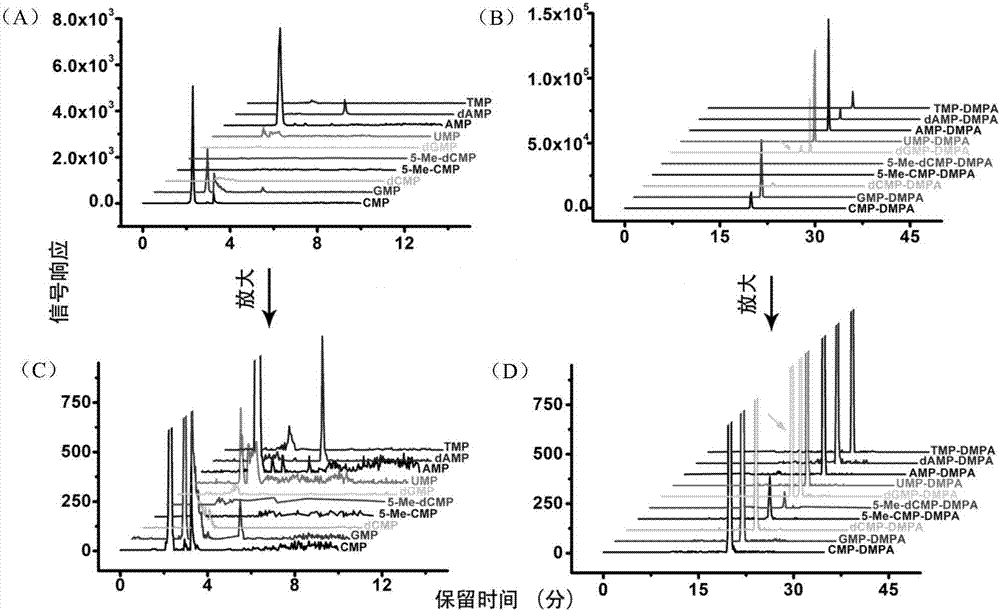
Chemical labeling and LC-MS combined method, and applications thereof in nucleotide analysis
A chemical labeling and combination technology, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve the problems of limited sensitivity of nucleotides, and achieve the effects of quantitative analysis, high labeling efficiency, and improved separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] 1. First prepare the working solution: (1) Dissolve the labeling reagent DMPA in chromatographic pure acetonitrile to prepare a DMPA acetonitrile solution with a concentration of 1M; (2) Dilute imidazole with water to prepare a concentration of 2.5mM, pH=6 Imidazole buffer; (3) EDC is dissolved in water to prepare an EDC solution with a concentration of 500 mM; (4) A 3 mL solid phase extraction cartridge is filled with 200 mg of amino silica gel; (5) The volume fraction of ammonia is 0.25%, acetonitrile The volume fraction of solvent S is 80%, and the volume fraction of pure water is 19.75%.
[0037] 2. In addition to protein: take a certain amount of biological sample into a 3mL homogenization tube, and add a methanol aqueous solution pre-cooled to -80°C (methanol: water = 4:1, v / v). Place the homogenization tube in a mixture of ice and water to grind the tissue for 10 minutes, transfer the homogenized mixture to a 5 mL centrifuge tube, and add 1.5 mL of methanol aqueous ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2: Analysis of Nucleotides in Urine Samples
[0043] Urine samples were centrifuged twice at 5000×g at 4°C for 10 minutes each time to remove insoluble matter. The supernatant after centrifugation was passed through a nylon filter membrane (13mm×0.22μM, Shanghai Anpu Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd.) to remove protein. After protein removal, the urine sample is enriched with amino silica gel cartridges, then chemically labeled with DMPA, and then liquid-liquid extraction is used to remove excess labeling reagents, and finally Strata X cartridges are used to remove excess activation After adding EDC, it was dried with nitrogen at 37°C, re-dissolved in 100μL of water, injected 70μL, and analyzed by LC-MS.
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3: Analysis of Nucleotides in Human Renal Cancer Tissues and Paracancerous Tissues
[0045] A certain amount of kidney cancer and adjacent tissues were added to a 3 mL homogenization tube, and a methanol aqueous solution (methanol: water = 4:1, v / v) pre-cooled to -80°C was added. Place the homogenization tube in a mixture of ice and water to grind the tissue for 10 minutes, transfer the homogenized mixture to a 5 mL centrifuge tube, and add 1.5 mL of methanol aqueous solution pre-cooled to -80°C (methanol: water = 4 :1, v / v) After cleaning the homogenization tube, it is combined with the extraction solution. The combined extracts were centrifuged at a speed of 14000×g at 4°C for 10 min, the supernatant was taken out, and dried under nitrogen at 37°C.
[0046] After protein removal, the sample is enriched with amino silica gel cartridges, then chemically labeled with DMPA, and then liquid-liquid extraction is used to remove excess labeling reagents, and finally Strat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com