Method for domestication and modular planting of sedum lineare for roof greening and special-purpose structural frame
A technology of roof greening and planting structure, applied in botany equipment and methods, roof decoration, application, etc., can solve the problems of high construction and maintenance costs, heavy planting soil, uneven greening surface, etc., and achieve good drainage effect and fertilizer efficiency Long, beautifully laid out effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
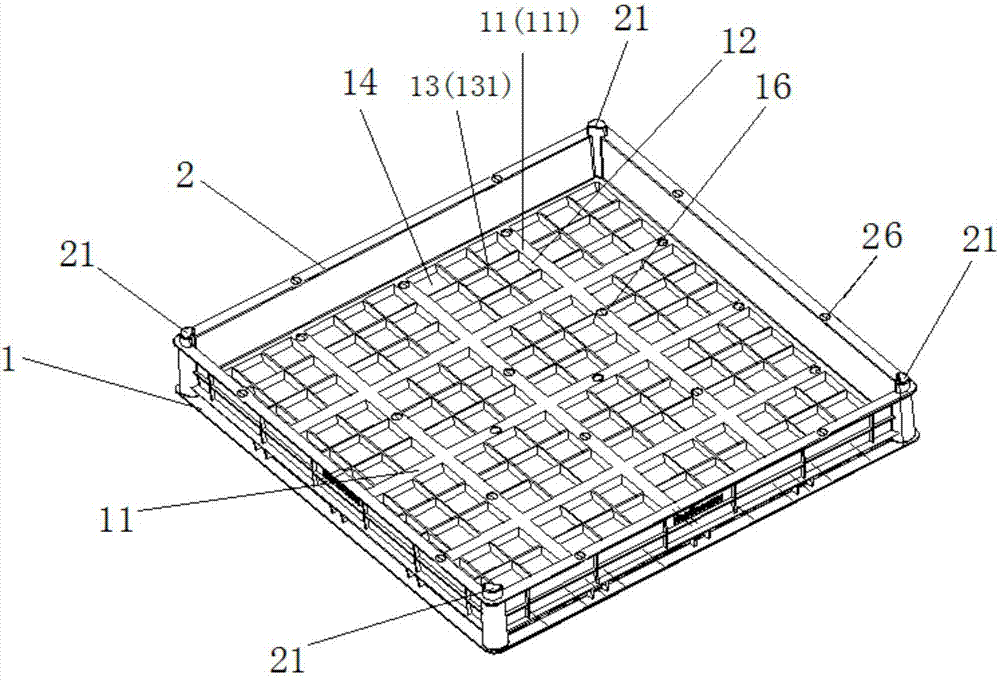
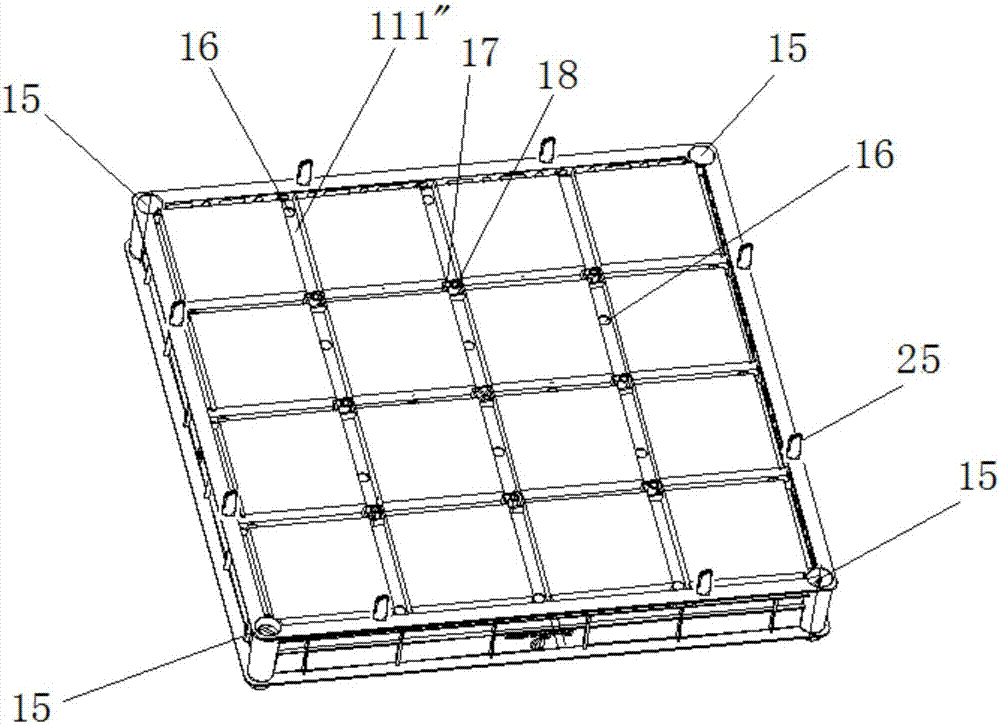
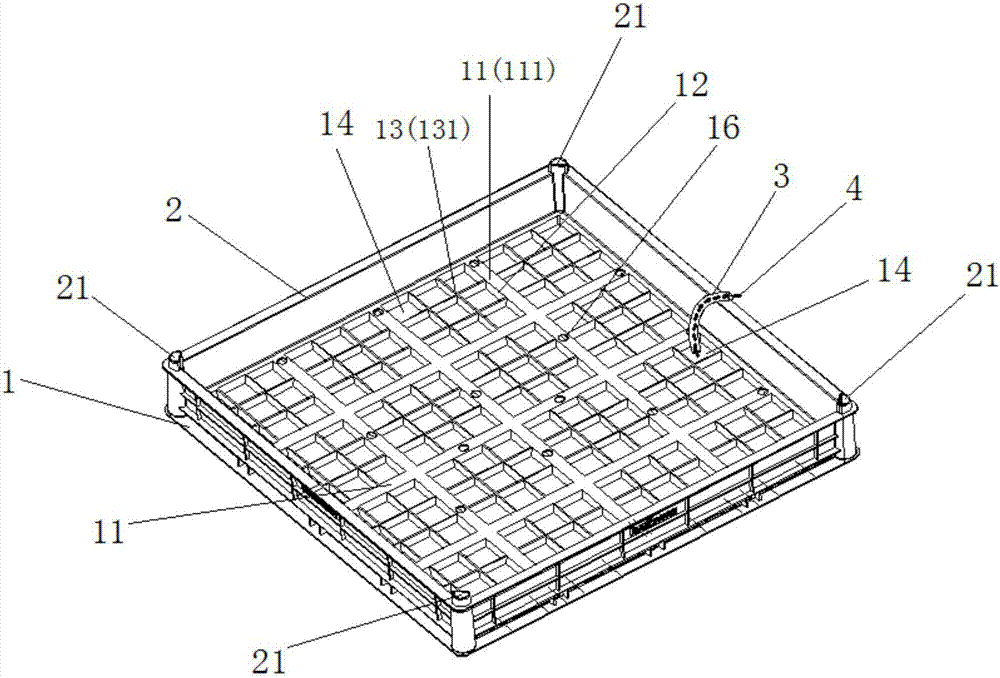
[0035] See figure 1 and figure 2 , the present embodiment provides a method for domesticating and modular planting of S. argentina for roof greening, comprising the following steps:
[0036] (1) Carry out S. japonica domestication in the cultivation base to obtain high-quality finished grass;
[0037] (2) Prefabricating several planting structure frames, which are composed of a frame bottom 1 and frame borders 2 arranged around the frame bottom 1;
[0038] (3) Lay a filter layer in each planting structure frame, and lay a 2-5cm thick lightweight organic matrix on the filter layer;
[0039] (4) Transplanting or planting domesticated Sageria on a light organic substrate;
[0040] (5) After the transplantation or planting of the domesticated S. chinensis is completed, a number of planting structure frames are assembled up and down, loaded and transported, and then the planting structure frames are transported to the roof, and the carpet is laid out. Through the transportation ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The main difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is: the configuration method of the lightweight organic matrix in the step (3) is:
[0054] (3.1) Prepare the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40 parts of pine bark; 80 parts of peat; 50 parts of organic fertilizer; 20 parts of vermiculite; 30 parts of perlite; 30 parts of sand;
[0055] (3.2) Stir pine bark, peat, organic fertilizer, vermiculite, perlite and sandy materials evenly to obtain a mixture, pile it up, and sprinkle water on it to make the water content of the mixture 70%, then sprinkle on the mixture Gymboree substrate nutrient soil starter, and stir evenly, ferment until the temperature reaches 70°C, and turn it over 3 times, the fermentation is completed, and the resulting pH is 7.0, and the bulk density is 1.0g / cm 3 lightweight organic substrate.
[0056] Other steps are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
Embodiment 3
[0058] The main difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is: the configuration method of the lightweight organic matrix in the step (3) is:
[0059] (3.1) Prepare the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30 parts of pine bark; 70 parts of peat; 40 parts of organic fertilizer; 15 parts of vermiculite; 20 parts of perlite; 25 parts of sand;
[0060] (3.2) Stir pine bark, peat, organic fertilizer, vermiculite, perlite and sandy raw materials evenly to obtain a mixture, pile it up, and sprinkle water on it to make the water content of the mixture 65%, and then sprinkle on the mixture Gymboree substrate nutrient soil starter, and stir evenly, ferment until the temperature reaches 60°C, and turn it twice, and the fermentation is completed, forming a pH of 6 and a bulk density of 0.5g / cm 3 lightweight organic substrate.
[0061] Other steps are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com