Carbon-metal composite material and synthesis method thereof
A carbon-based material, metal source technology, applied in the direction of hydrocarbons, hydrocarbons, carbon compound catalysts, etc., can solve the problem that the selectivity and conversion rate are difficult to improve at the same time, and achieve the effect of improving selectivity and conversion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
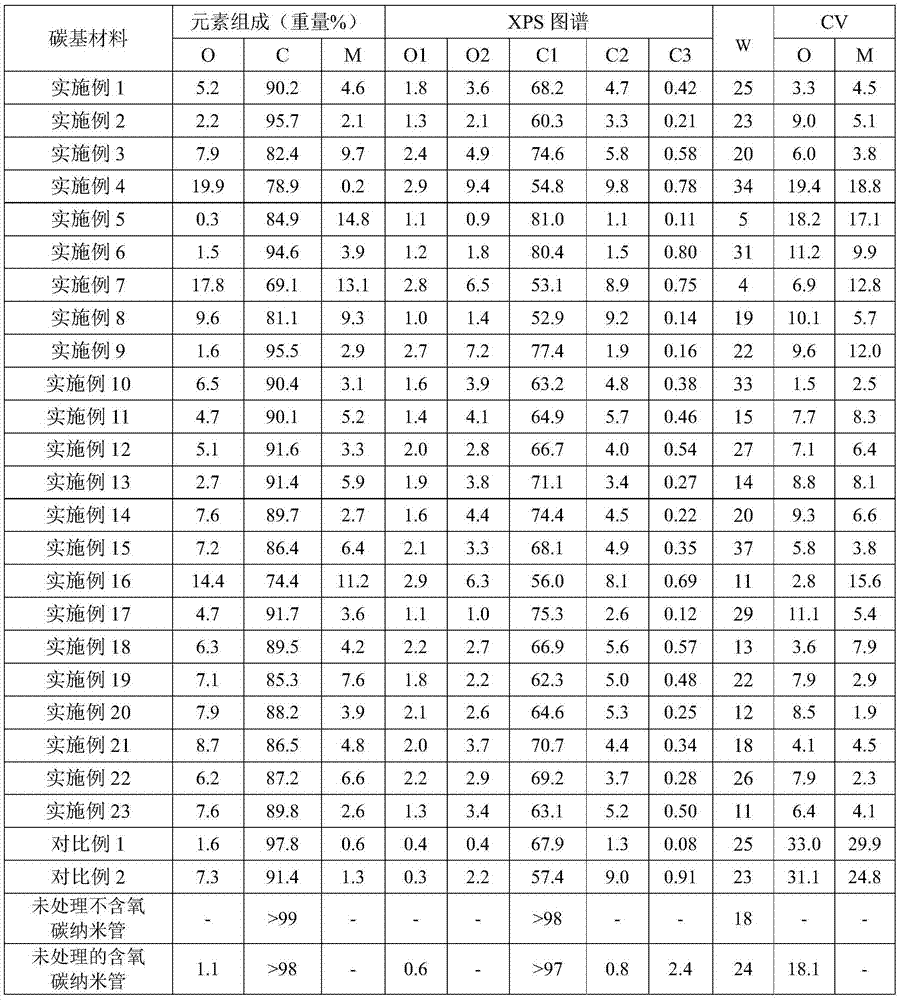
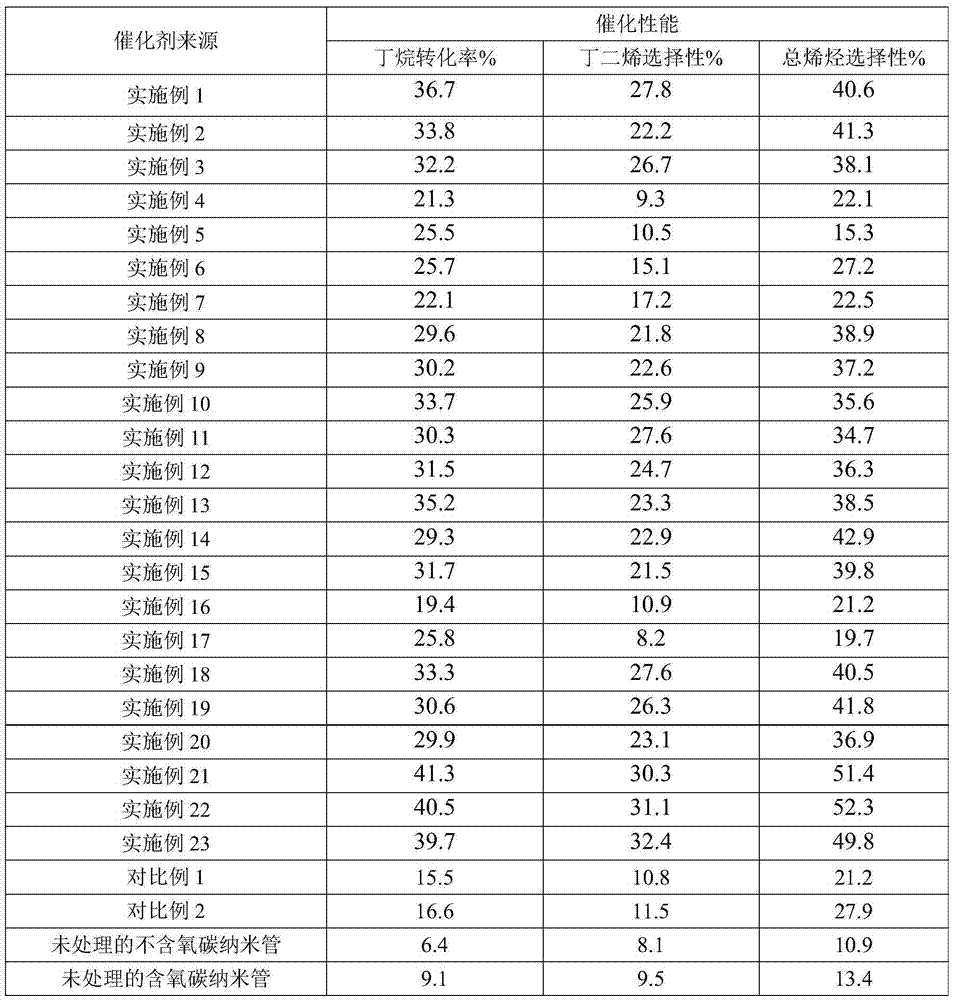
[0074] At room temperature (25°C), stir and mix the solid carbon source (carbon nanotubes not containing oxygen), the precursor (iron oxalate) and water for 2 hours to obtain a mixed material, wherein the solid carbon source and hydrogen The molar ratio of iron is 1:0.3, and the weight ratio of the solid carbon source to water is 1:20; the mixed material obtained above is placed in a sealed autoclave with a polytetrafluoroethylene liner, and Hydrothermal treatment at 140°C for 24 hours under autogenous pressure, the solid in the hydrothermally treated material was separated by filtration and dried, the drying temperature was 120°C, until the solid obtained by filtration and separation maintained a constant weight (drying time was 6h), The dried material was obtained, and then the obtained dried material was calcined in air at a calcination temperature of 330° C. for 2 h, and then calcined in air at a calcination temperature of 430° C. for 2 h to obtain the carbon-based Materia...
Embodiment 2
[0076] At room temperature (25°C), stir and mix the solid carbon source (carbon nanotubes without oxygen), the precursor (iron acetate) and water for 1 hour to obtain a mixed material, wherein the solid carbon source and iron acetate The molar ratio is 1:0.02, and the weight ratio of the solid carbon source to water is 1:40. The mixed material obtained above is placed in a sealed autoclave with a polytetrafluoroethylene liner, and is heated at 180 ℃ under autogenous pressure for 24 hours, the solid in the material after the hydrothermal treatment is filtered and separated and dried, the drying temperature is 120 ℃, until the solid obtained by filtration and separation basically maintains a constant weight (the drying time is 6 hours), and the obtained The dried material is then calcined in air at a calcination temperature of 300° C. for 2 h, and then calcined in air at a calcination temperature of 400° C. for 2 h to obtain the carbon-based material of this embodiment .
Embodiment 3
[0078] At room temperature (25° C.), the solid carbon source (carbon nanotubes without oxygen), the precursor (zinc naphthenate) and water were stirred and mixed for 3 hours to obtain a mixed material, wherein the solid carbon source and The molar ratio of zinc naphthenate is 1:0.5, and the weight ratio of the solid carbon source to water is 1:8; the mixed material obtained above is placed in a sealed autoclave with a polytetrafluoroethylene liner In the process, hydrothermal treatment was carried out at 110°C for 48h under autogenous pressure, and the solids in the hydrothermally treated material were separated by filtration and dried. The drying temperature was 120°C until the mixed material basically maintained a constant weight (drying time was 6h ) to obtain the dried material, then the obtained dried material was calcined in the air for 2 h at a calcination temperature of 350 ° C, and then calcined in the air for 2 h at a calcination temperature of 450 ° C to obtain the p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com