Method for recovering and purifying nickel cobalt from manganese-containing waste material
A waste, nickel-cobalt technology, applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, manganese sulfate, nickel compounds, etc., can solve the problems of environmental safety hazards, large removal costs, waste of resources, etc., to reduce environmental safety hazards, reduce costs, The effect of improving the utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0021] The specific implementation mode of above-mentioned technical scheme of the present invention is as follows:
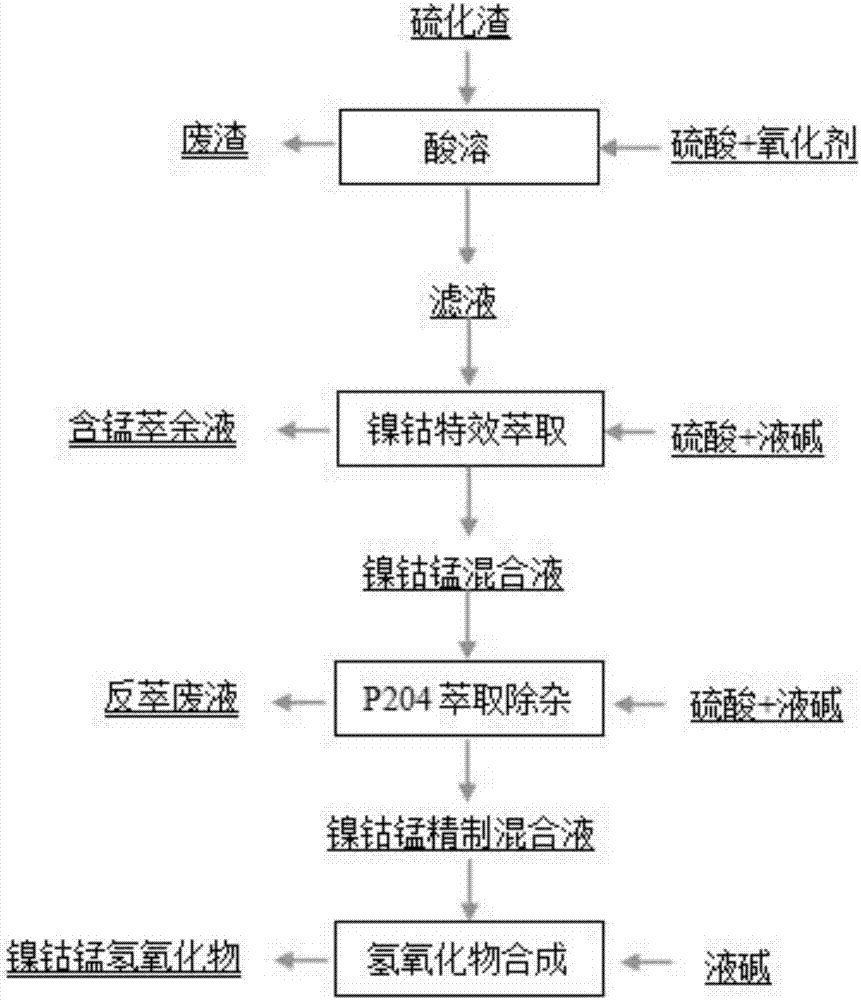
[0022] a kind of like figure 1 Shown is the method for recovering and purifying nickel and cobalt from manganese-containing waste, specifically comprising the following steps:
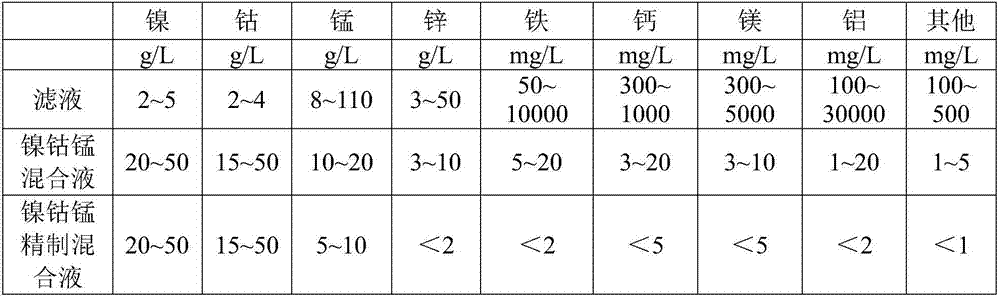
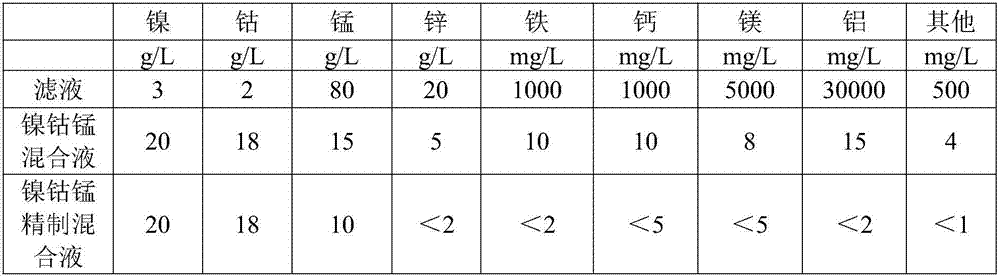
[0023] (1) Acid soluble: use the vulcanized slag produced in the production process of manganese sulfate as raw material, the content of nickel in the solid waste of the vulcanized slag is 0.5% to 1.5%, the content of cobalt is 0.5% to 1%, and the content of manganese is 9% to 20%. , the iron content is 2% to 5%, and it also contains 10% to 20% of barium sulfate, 10% to 30% of silicon dioxide, and the content of some metal impurities is 1% to 5%. Slurry the above-mentioned sulfide slag with water according to the liquid-solid ratio of 1-0.5, add oxidant according to 1-2 times the molar number of sulfur radicals, add sulfuric acid during the process to stabilize the pH in the kettle in ...
Embodiment 1
[0033] a kind of like figure 1 Shown is the method for recovering and purifying nickel and cobalt from manganese-containing waste, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0034] (1) Acid soluble: take the vulcanized slag produced in the manganese sulfate production process as raw material, the nickel content is 0.5%, the cobalt content is 0.5%, the manganese content is 9%, the iron content is at 2%, and also contains 10% barium sulfate, 10% silicon dioxide, and 1% of some metal impurities. Slurry 100kg of the aforementioned sulfide slag with 50kg of tap water at a liquid-solid ratio of 0.5, add manganese dioxide as an oxidant according to 1 times the molar number of sulfur radicals, add sulfuric acid during the process to stabilize the pH in the kettle at 1.0, and the temperature of the reaction kettle during the acid dissolution process. 60°C, the stirring speed is 200-350r / min, and after the pH is stable, the stirring is continued for 2 hours, filtered to obtain the ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] a kind of like figure 1 Shown is the method for recovering and purifying nickel and cobalt from manganese-containing waste, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0043] (1) acid soluble: take the vulcanized slag produced in the manganese sulfate production process as raw material, the nickel content is 1.5%, the cobalt content is 1%, the manganese content is 20%, the iron content is at 5%, and also contains 20% of barium sulfate, 30% of silicon dioxide, and 2% of some metal impurities. Add 100kg of the aforementioned sulfide slag to slurry according to the liquid-solid ratio of 1, add 100kg of tap water, add the oxidant sodium chlorate according to 1.2 times the molar number of sulfur radicals, add sulfuric acid during the process to stabilize the pH in the kettle at 1.0, and the temperature of the reaction kettle during the acid dissolution process. 60°C, the stirring speed is 200-350r / min, and after the pH is stable, continue to stir for 2 hours, filter to o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com