Modular multi-level converter inter-phase power unbalance control method
A modular multi-level, power unbalanced technology, applied in the direction of reducing the asymmetry of the multi-phase network, eliminating/reducing the asymmetry of the multi-phase network, converting the AC power input to the DC power output, etc., can solve the three-phase power imbalance. Problems such as balance, unbalanced three-phase power of battery panels, unbalanced output power of AC grid, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0119] The preferred modes of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
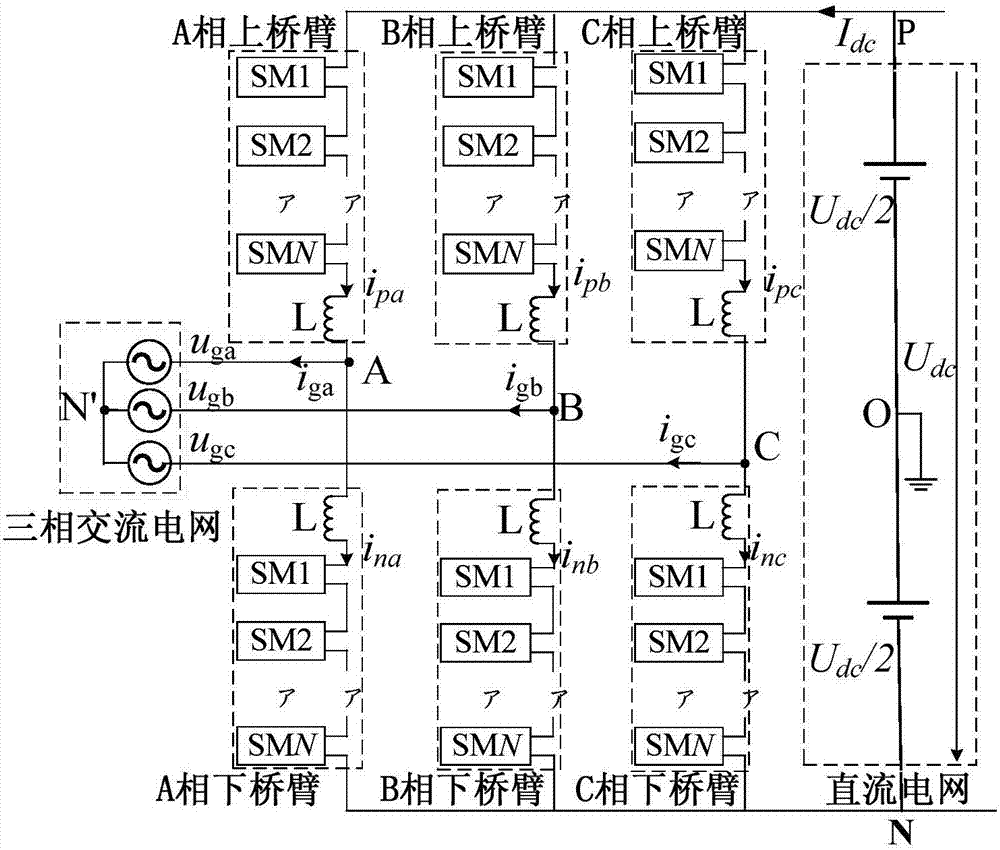
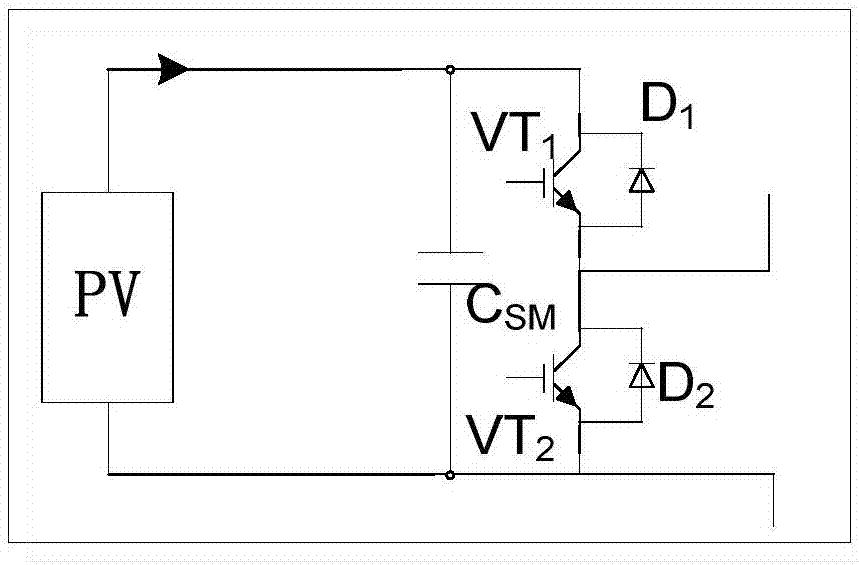
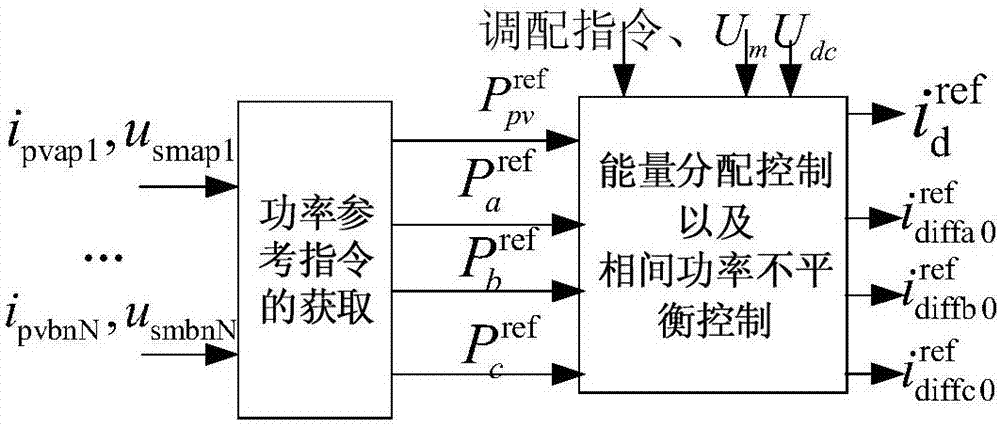
[0120] A method for controlling power imbalance between phases of a modular multilevel converter. The modular multilevel converter of the present invention includes ABC three-phases, each phase is divided into an upper bridge arm and a lower bridge arm, and each bridge The arm is composed of N sub-modules with photovoltaic cells and an inductor L, the i-th sub-module of the bridge arm is denoted as SMi, i=1, 2, 3···N, where N>1, that is, the Each phase of the modular multilevel converter contains 2N sub-modules; the modular multi-level converter system contains a common DC bus, connected to the DC grid; each sub-module consists of a half-bridge sub-module, a supporting capacitor C SM and a group of photovoltaic cells in parallel; the output voltage of each sub-module is 0V or the voltage of the photovoltaic cell; the half-bridge sub-mod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com