Preparation method and application of oxygen-potential-deficiency magnetic copper ferrite catalyst
A technology of copper ferrite and catalyst is applied in the field of preparation of oxygen-deficient copper ferrite catalyst, which can solve the problems of inability to widely use carcinogenesis, loss of activity, and unsatisfactory catalytic effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] (1) Add copper nitrate and ferric nitrate to deionized water, and then add citric acid after dissolving. The molar ratio of the above-mentioned copper nitrate, ferric nitrate, and citric acid is 1:2:3.5; the total volume is 200ml, and the molar ratio of copper nitrate The concentration is 0.025mol / L.
[0032] (2) The solution obtained in step (1) was magnetically stirred in an oil bath at 60°C for 4 hours, and when about 100 mL of the solution remained, the solution was dried in an oven at 70°C until a gel was formed;
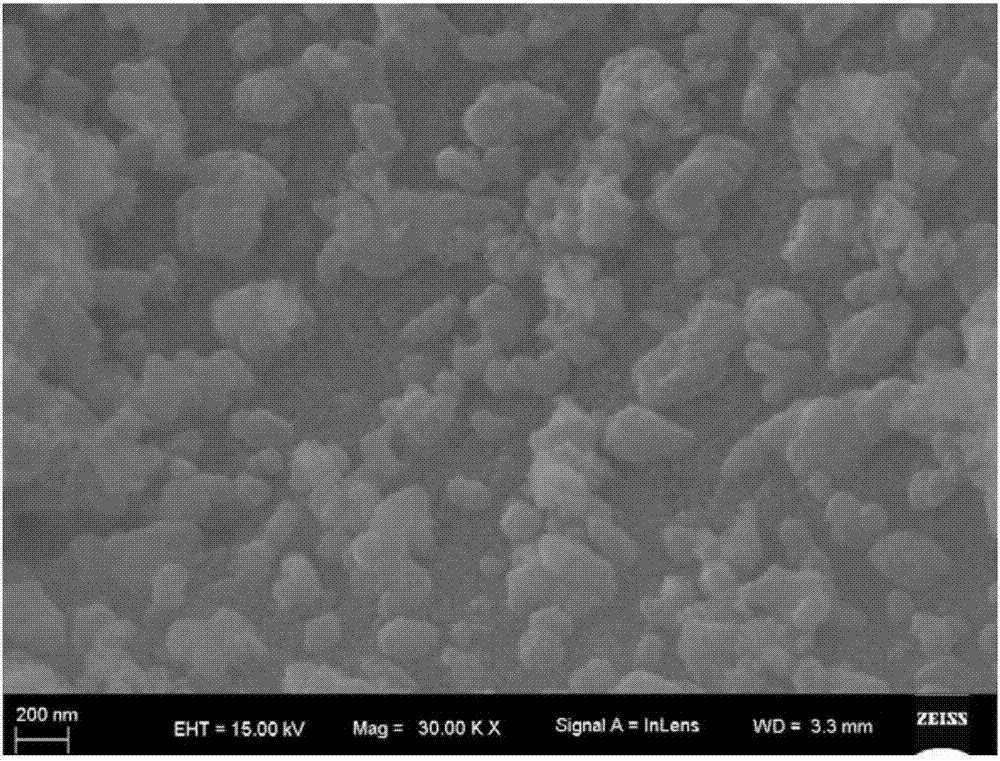
[0033] (3) The gel obtained in step (2) was calcined at 300°C for 2 hours to degumming, and after natural cooling and grinding, the following figure 1 the first component shown;
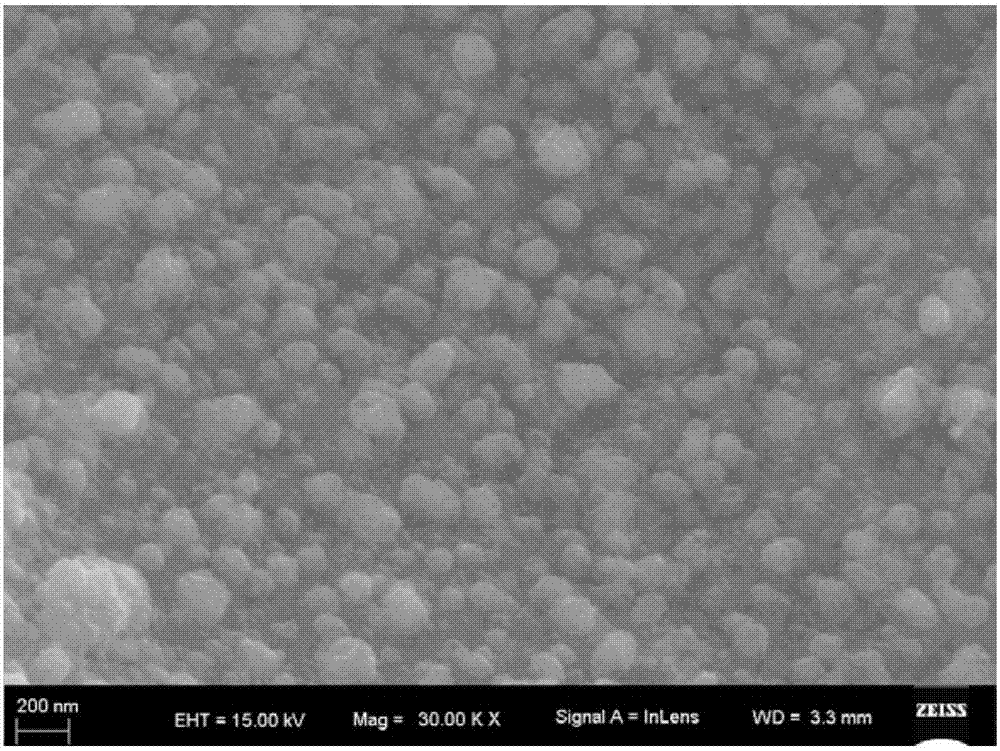
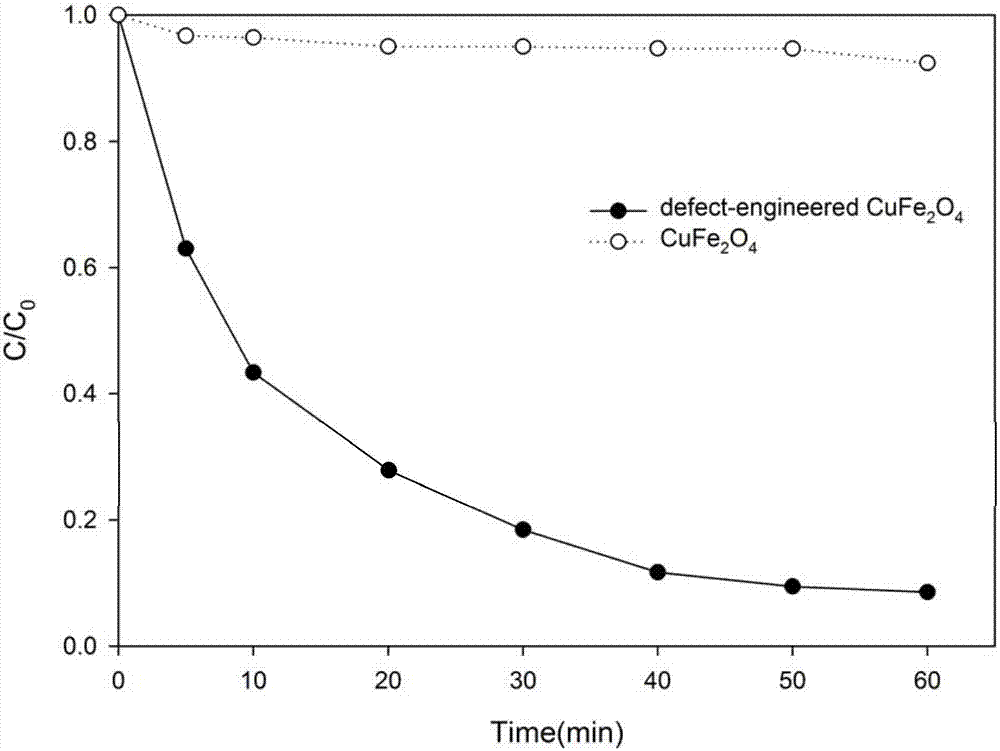
[0034] (4) Place the first component in a hydrogen atmosphere at 300°C for 3 hours, and take it out after natural cooling to obtain the following figure 2 The oxygen-deficient copper ferrite catalyst shown is stored in a nitrogen atmosphere;
[0035] 100 mL of paracetamol s...
Embodiment 2
[0037] (1) Add copper nitrate and ferric nitrate to deionized water, and then add citric acid after dissolving. The molar ratio of the above-mentioned copper nitrate, ferric nitrate, and citric acid is 1:2:4; the total volume is 200ml, and the molar ratio of copper nitrate The concentration is 0.025mol / L.
[0038] (2) Magnetically stir the solution obtained in step (1) in an oil bath at 70°C for 4 hours. When about 50 mL of the solution remains, dry the solution in an oven at 60°C until a gel is formed;
[0039] (3) The gel obtained in step (2) is calcined at 500° C. for 3 hours to degumming, and the first component is obtained after natural cooling and grinding;
[0040] (4) Place the first component in a hydrogen atmosphere at 400°C for 1 hour for reduction, take it out after natural cooling to obtain an oxygen-deficient copper ferrite catalyst, and store it in a nitrogen atmosphere;
Embodiment 3
[0042] (1) Add copper nitrate and ferric nitrate to deionized water, and then add citric acid after dissolving. The molar ratio of the above-mentioned copper nitrate, ferric nitrate, and citric acid is 1:2:3.5; the total volume is 200ml, and the molar ratio of copper nitrate The concentration is 0.025mol / L.
[0043] (2) The solution obtained in step (1) was magnetically stirred in an oil bath at 50°C for 6 hours, and when about 75mL of the solution remained, the solution was dried in an oven at 80°C until a gel was formed;
[0044] (3) The gel obtained in step (2) is calcined at 200° C. for 5 hours to degumming, and the first component is obtained after natural cooling and grinding;
[0045] (4) Place the first component in a hydrogen atmosphere at 200°C for 8 hours, take it out after natural cooling to obtain an oxygen-deficient copper ferrite catalyst, and store it in a nitrogen atmosphere;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com