TDR-based anti-interference cable fault testing system and testing method
A cable fault and testing system technology, applied in the fault location, detecting faults by conductor type, and using pulse reflection method to detect faults, etc., can solve the problems of limited cable length, difficult measurement time, complex reflected wave waveform, etc. The effect of measurement accuracy, accurate measurement position, and fast and accurate echo filtering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] The principles and features of the present invention are described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, and the examples given are only used to explain the present invention, and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
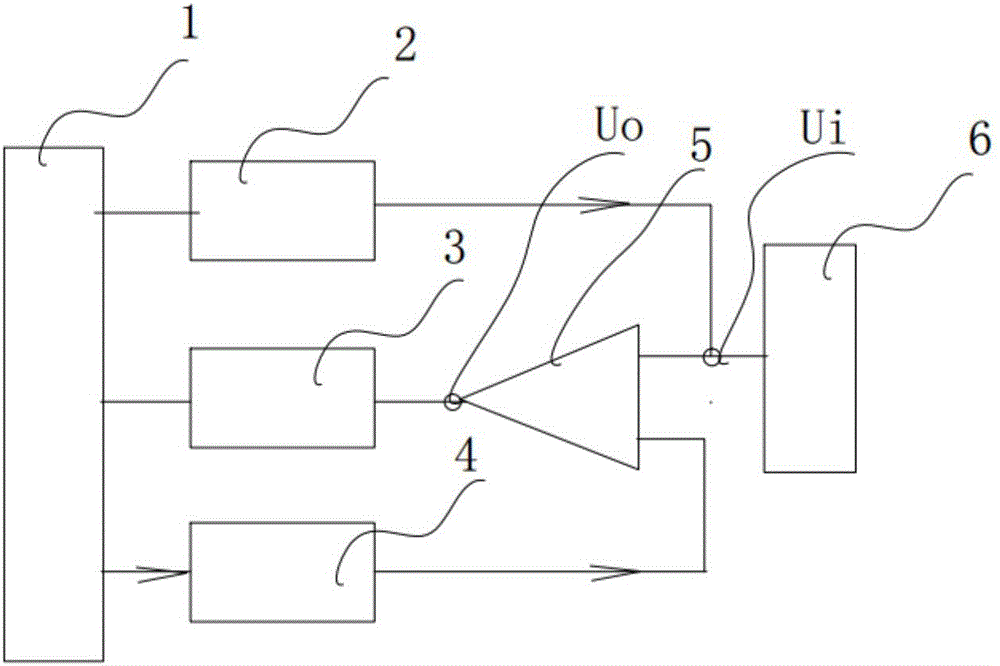
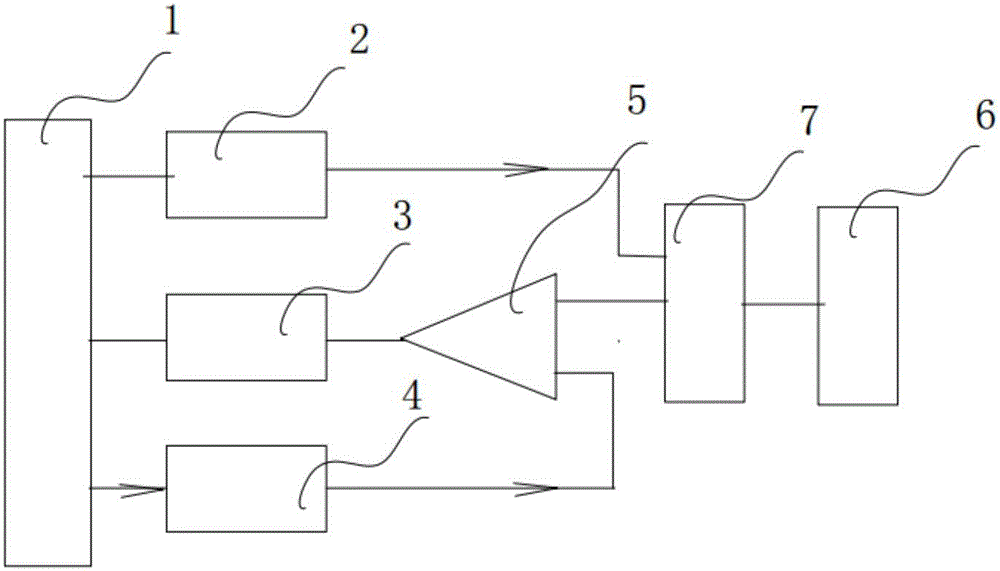
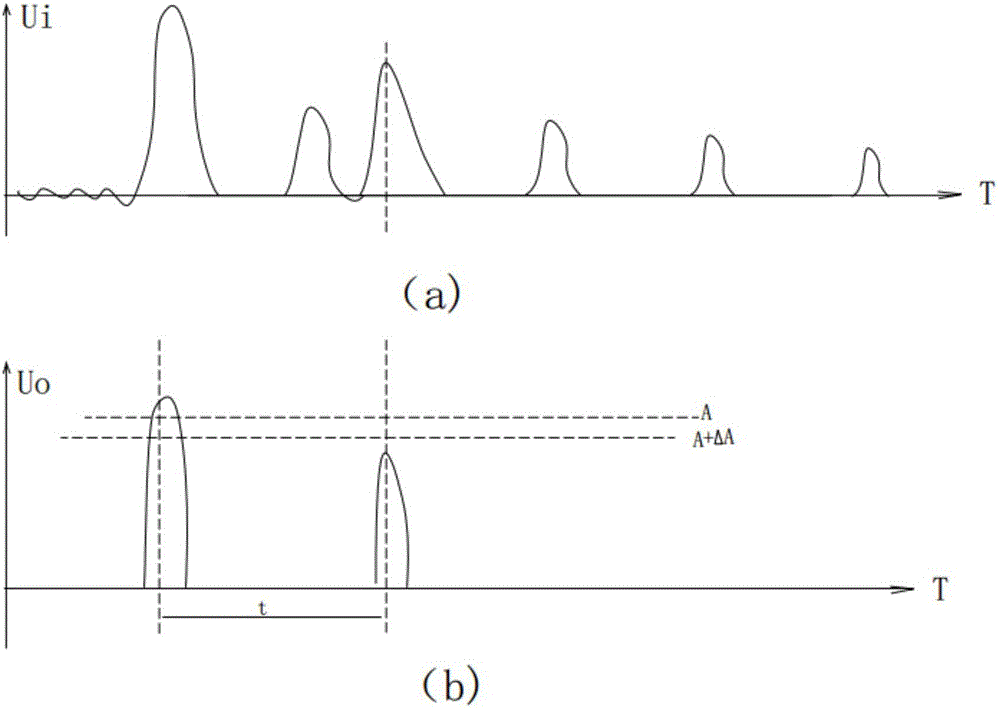
[0044] Such asfigure 1 As shown, a TDR-based anti-interference cable fault test system includes a main control module 1, a pulse generation module 2, a pulse time interval measurement module 3, a D / A converter 4 and a comparator 5; here the main control module can be SCM and other components.
[0045] The pulse generating module 2 is electrically connected with the main control module 1 and the cable under test 6; the comparator 5 includes a reference terminal, a signal input terminal and a comparison output terminal, and the digital terminal of the D / A converter 4 and The analog end is electrically connected with the reference end of the main control module 1 and the comparator 5 respectively, and the pulse time in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com