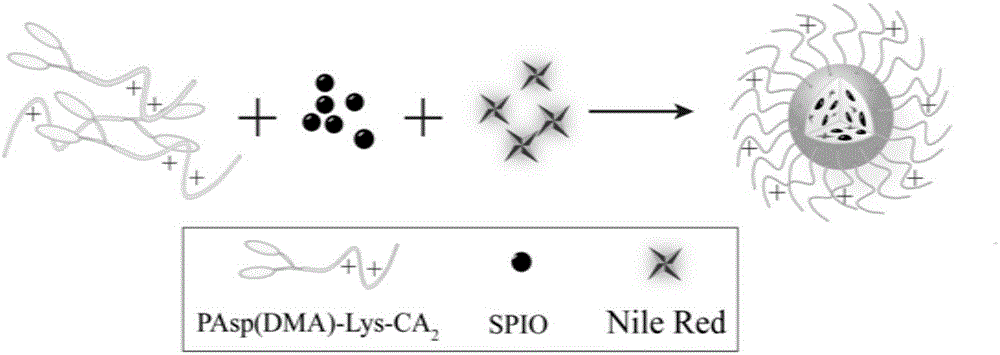
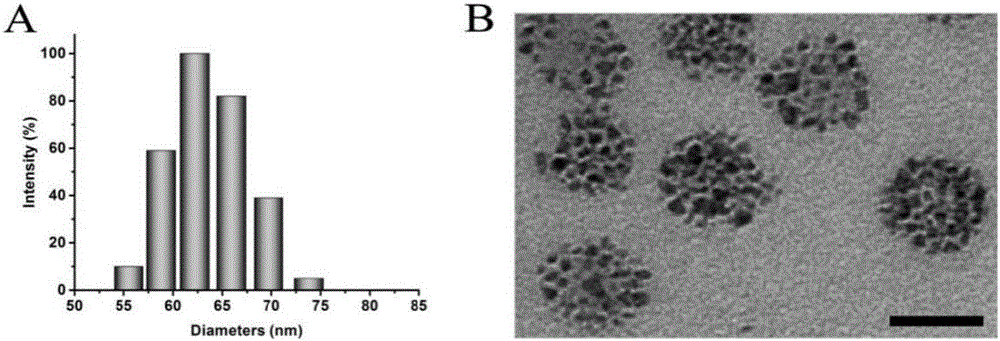
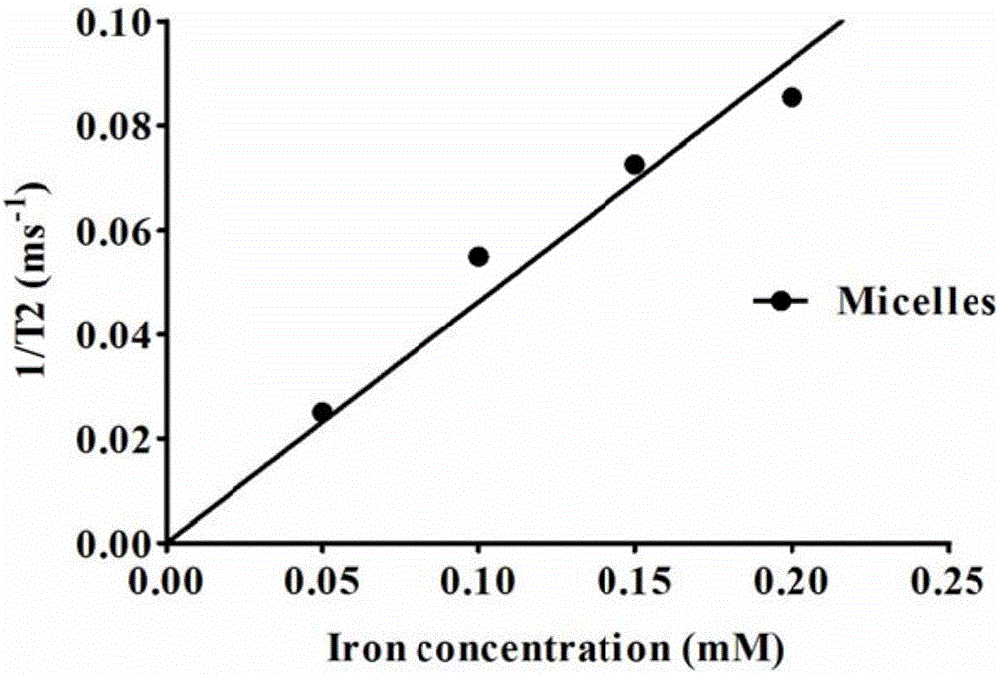
Degradable nano-micelle capable of performing MR-fluorescence bimodal imaging as well as preparation method and application of degradable nano-micelle
A nanomicelle and fluorescence technology, applied in the field of nanomedicine and biomedical engineering, can solve the problems of difficult to achieve effective labeling of stem cells, complex reporter gene operation, proliferation, differentiation and other abilities, and achieve real-time dynamic MR-fluorescence dual mode state localization monitoring, high-efficiency dual-modal labeling, and the effect of improving drug loading efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The synthesis of embodiment 1 amphiphilic block polymer
[0037] (1) Synthesis of benzyloxycarbonyl aspartic anhydride (BLA-NCA), the reaction mechanism and process are as follows:
[0038]
[0039] Benzyl alcohol and L-aspartic acid are used to synthesize β-aspartic acid benzyl ester; then bis(trichloromethyl) carbonate is added to synthesize benzyloxycarbonyl aspartic anhydride (BLA-NCA). Refer to the literature for specific steps 1 .
[0040] (2) Synthesis of n-butylamine-polybenzylaspartic acid (BA-PBLA), the reaction mechanism and process are as follows:
[0041]
[0042] Initiated by dodecanol, BLA-NCA was ring-opened and polymerized to n-butylamine-polybenzylaspartic acid (BA-PBLA). Weigh 73.14mg of n-butylamine (1.0nmol, 0.74g / mL) into a 50mL reaction flask, add 30mL of anhydrous CH 2 Cl 2 Fully dissolve. After weighing 2.49g BLA-NCA (10mmol) and dissolving it in 20mL of anhydrous dimethylformamide, under the protection of nitrogen, it was added into...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Synthesis of embodiment 2 amphiphilic block polymer
[0054] Synthetic amphiphilic block polymer with reference to embodiment 1, change the molecular weight of n-butylamine-polybenzyl aspartic acid (BA-PBLA), design degree of polymerization is respectively 5 and 20 (embodiment 1 is 10), and the rest The reaction steps are all consistent with Example 1, and the block polymer PAsp(DMA)-Lys-CA with different lengths of positively charged blocks is obtained. 2 , The molecular weights of polyaspartame dimethyl ethylene diamine (PAsp (DMA)) are 900Da and 3600Da, respectively.
Embodiment 3
[0055] Synthesis of embodiment 3 amphiphilic block polymer
[0056] With reference to Example 1, the amphiphilic block polymer was synthesized to obtain polybenzylaspartic acid-lysine (PBLA-Lys), and its terminal two amino groups were combined with two (tert-butoxycarbonyl)-L-lysine After amino acid (Boc-Lys(Boc)-OH) coupling and deprotection, PBLA-Lys with four amino groups at the end can be obtained 3 , PBLA-Lys 3 One more Boc-Lys(Boc)-OH and deprotection can obtain PBLA-Lys with 8 amino groups at the end 7 . PBLA-Lys 3 and PBLA-Lys 7 According to the method of Example 1, cholic acid was grafted and ammolyzed to obtain amphiphilic polymers with different numbers of cholic acid grafted at the end, and the number of cholic acid grafted was 4 and 8 respectively.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com