A kind of modification method of proton exchange membrane for all-vanadium redox flow battery
An all-vanadium redox flow battery and proton exchange membrane technology, applied in fuel cells, regenerative fuel cells, circuits, etc., can solve the problems affecting the electrochemical performance of all-vanadium redox flow batteries, poor vanadium resistance performance, etc., and achieve vanadium ion permeation. The effect of reduced rate, good bonding, uniform cross-section
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
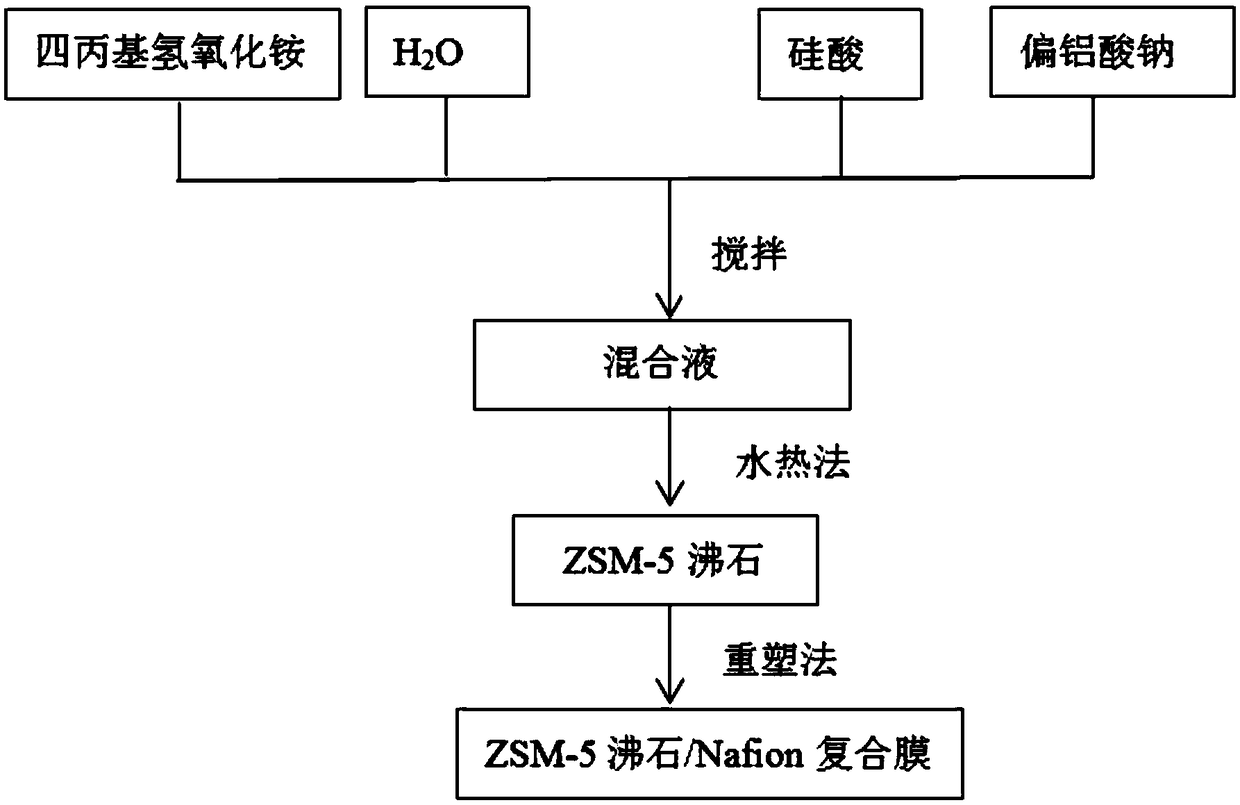
[0041] Such as figure 1 As shown, embodiment 1 provides a kind of modification method for the proton exchange membrane of all-vanadium redox flow battery, and it comprises the following steps:
[0042] S1. Preparation of submicron ZSM-5 zeolite: first weigh 2.185g of deionized water, add it to 5.463g (the mass ratio of deionized water to tetrapropylammonium hydroxide is 1:2.5) and the concentration is 1.0 mol / L tetrapropylammonium hydroxide (TPAOH) aqueous solution, stirring to form a uniform solution; then weigh 1.093g of silicic acid (that is, the mass ratio of silicic acid to TPAOH is 1:5), and add silicic acid to the above uniform solution; then add 0.044g of sodium metaaluminate (that is, the mass ratio of sodium metaaluminate to silicic acid is 1:25) powder into the above solution, and stir evenly to obtain a milky white solution; then the obtained milky white The solution was stirred for 24 hours to obtain a homogeneous solution, which was transferred to a 100mL Teflon...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The difference between the modification method of a proton exchange membrane used in an all-vanadium redox flow battery provided in Example 2 and the modification method described in Example 1 is that the quality of TPAOH in Step S1 of Example 1 is 5.463 g is replaced by: the mass of TPAOH is 6.555g, that is to say, the mass ratio of deionized water to TPAOH is 1:3, and at the same time, according to the mass ratio of silicic acid to TPAOH is 1:5, sodium metaaluminate and silicic acid The mass ratio is 1:25, add 1.311g silicic acid and 0.052g sodium metaaluminate, other content is all the same as embodiment 1, repeats no more here. The composite proton exchange membrane prepared in Example 2 is numbered A2.
Embodiment 3
[0053] The difference between the modification method of a proton exchange membrane used in an all-vanadium redox flow battery provided in Example 3 and the modification method described in Example 1 is that the quality of TPAOH in step S1 of Example 1 is 5.463 g is replaced by: the mass of TPAOH is 7.648g, that is to say, the mass ratio of deionized water to TPAOH is 1:3.5, and at the same time, according to the mass ratio of silicic acid to TPAOH is 1:5, sodium metaaluminate and silicic acid The mass ratio is 1:25, add 1.530g silicic acid and 0.061g sodium metaaluminate, other content is all the same as embodiment 1, repeats no more here. The composite proton exchange membrane prepared in Example 3 is numbered A3.
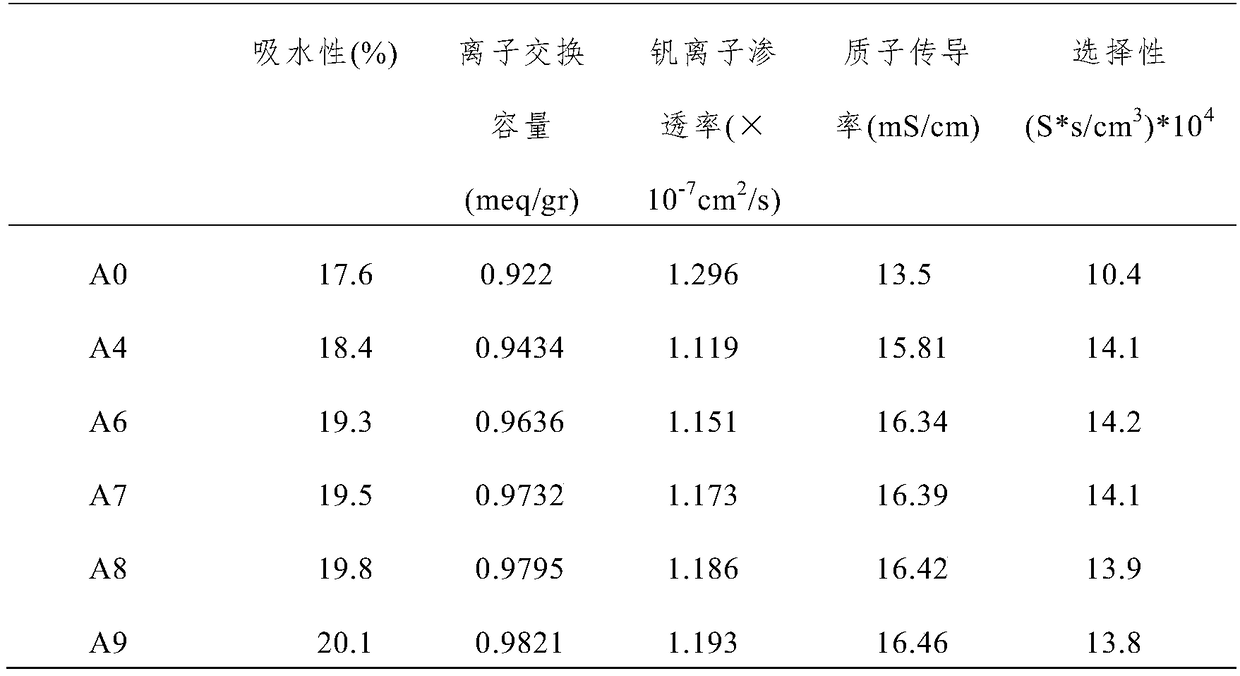
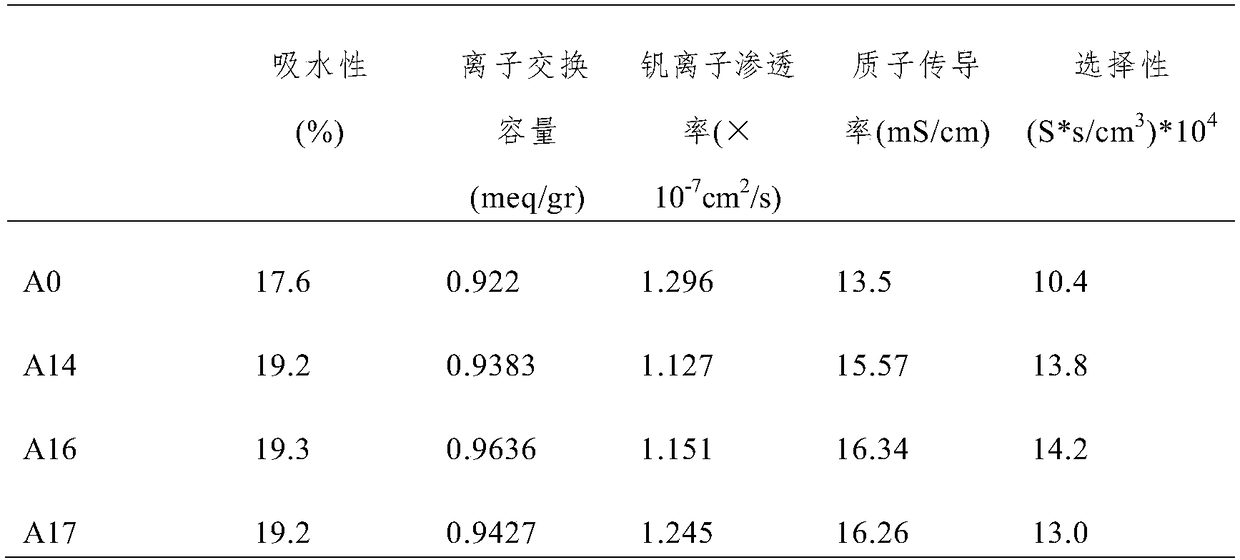
[0054] Comparing the properties of the composite proton exchange membranes prepared in Examples 1-3, it was found that the performance of the composite proton exchange membrane prepared in Example 2 was the best. In other words, the performance of the composite ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com