Encapsulation of oral care active agents
A technology for oral care and active agents, which is applied in the field of encapsulating water-soluble oral care active agents, and can solve problems such as uncomfortable oral care active agents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
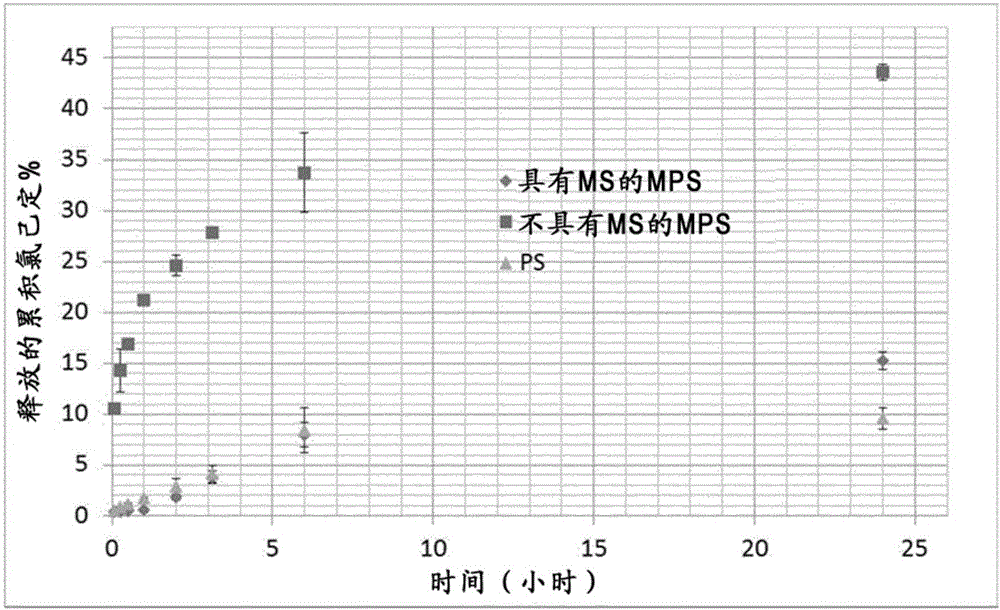
[0049] A polymer solution was prepared by dissolving 6 g of cellulose acetate in 40 ml of ethyl formate overnight (14 hours) at room temperature in a glass sealed container. Chlorhexidine diacetate (1.5 g) was then dispersed into the pre-cooled polymer solution, placed on ice while stirring with a magnetic stirrer at 300 rpm for 10 minutes, and then the suspension was poured into a circulating water bath connected to in a jacketed reactor to control the temperature at 5 °C. On a weight basis, the active / polymer ratio is 1 / 4. A mixture containing magnesium stearate (anti-aggregation and release rate controlling agent (MS, 1 g) prepared by blending at 8000 rpm for 2 minutes with a high shear rotor stator mixer (Silverson L4RT) while cooling the system with an ice bath. ) and polyglycerol polyricinoleate emulsifier (PGPR, 0.5g) anti-solvent liquid paraffin (200mL) was pumped (6mL / min) into the previously prepared active-polymer suspension while using The pitched blade impeller ...
Embodiment 2
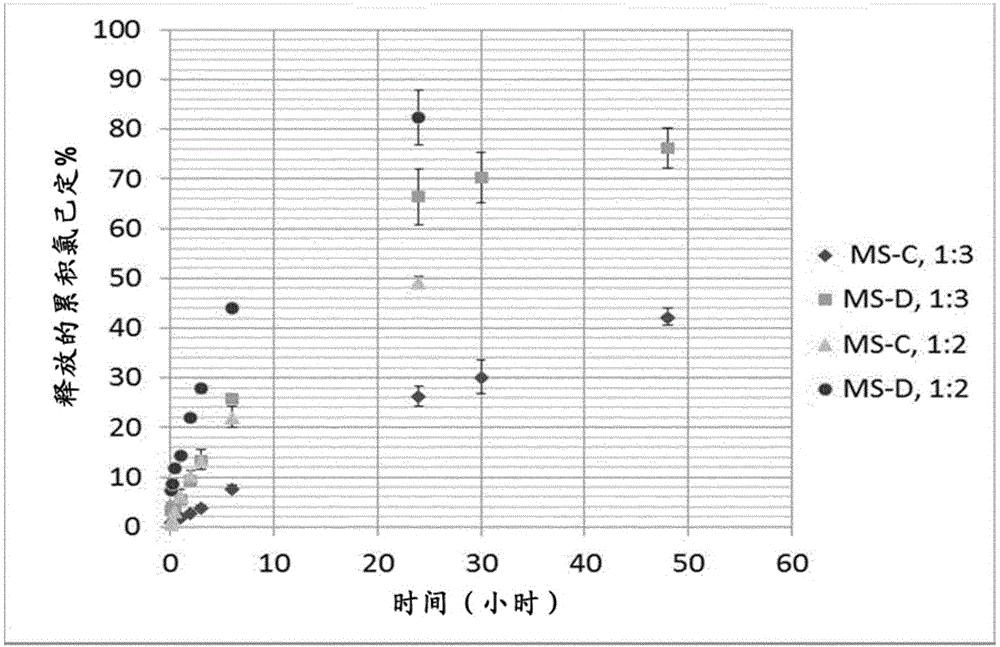
[0060] Dissolve 4 g of cellulose acetate in 20 ml of ethyl formate. The continuous phase was prepared by adding 0.85 g MS to 70 ml liquid paraffin containing 0.35 g PGPR emulsifier and mixing with a high shear rotor stator mixer (Silverson L4RT) at 8000 rpm for 2 minutes while cooling the system with an ice bath. A given amount of chlorhexidine was then added to the polymer solution, placed on ice, to achieve a specific active / polymer ratio (1 / 2; 1 / 3) with stirring. The mixture was further stirred at 300 rpm for 10 min with a magnetic stirrer, then it was added to the reactor containing the previously prepared continuous phase, saturated with 30% (v / v) ethyl formate (i.e., 21 mL) and cooled to 5°C. The mixture was magnetically stirred at 400 rpm for 2 hours using a six pitched blade Rushton impeller to create an emulsion. The oil-in-oil emulsion was gradually heated to 20°C and stirred at this temperature for 16 hours to allow the diffusion of ethyl formate into the liquid p...
Embodiment 3
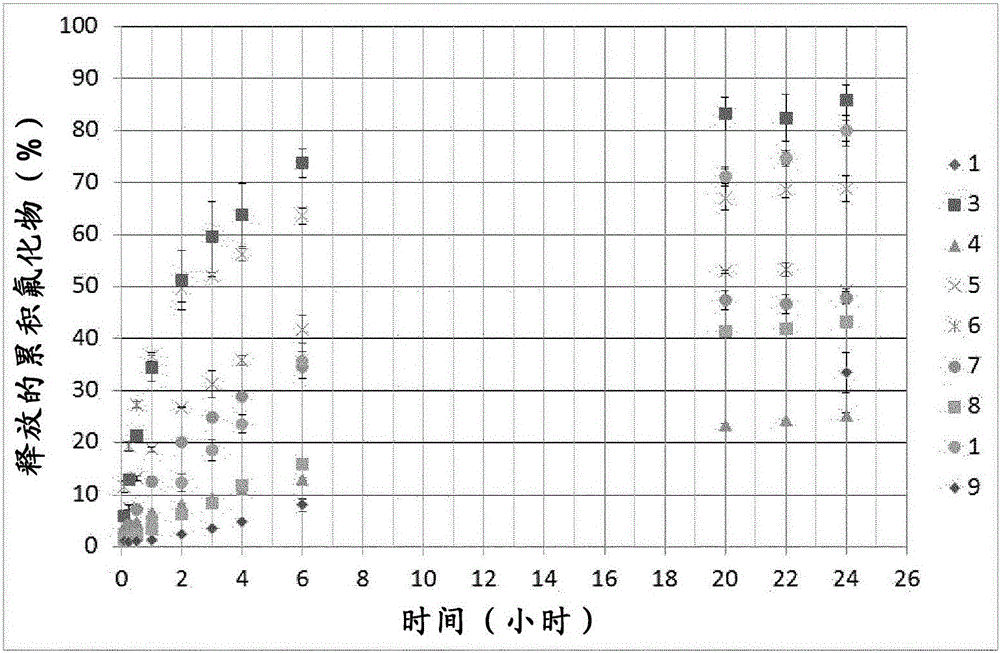
[0063] NaF-loaded microparticles were prepared by emulsion solvent evaporation according to a two-level factorial design (Table 4) with three factors: polymer concentration (10% and 20%, weight / volume), solvent evaporation temperature (10°C and 20°C) and solvent concentration in the continuous phase (ie, the amount of ethyl formate in liquid paraffin at the start of emulsification, 15% (10.5 mL) and 30% (21 mL), v / v). Samples were prepared according to the procedure described in Example 2 with MS in the dispersed phase. To the CAB solution containing 1 g or 0.5 g NaF was added 0.85 g magnesium stearate dispersed in 5 mL ethyl formate with an ice-containing ultrasonic bath for 30 minutes to achieve an active polymer ratio of 1:4. Polymer solutions containing 10% and 20% polymer in total ethyl formate were prepared by dissolving 2 g and 4 g of polymer, respectively, in 15 mL of ethyl formate. NaF was dispersed into the polymer solution for 7 minutes before MS was added and the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com