Novel symmetric key algorithm for high speed encryption
A technology of symmetric key and encryption algorithm, which is applied in the direction of encryption device with shift register/memory, digital transmission system, electrical components, etc. The effects of key repetition, improved security, and fast encryption speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] A kind of encryption algorithm specific process of the novel symmetric key algorithm that is used for high-speed encryption of the present invention is as follows:
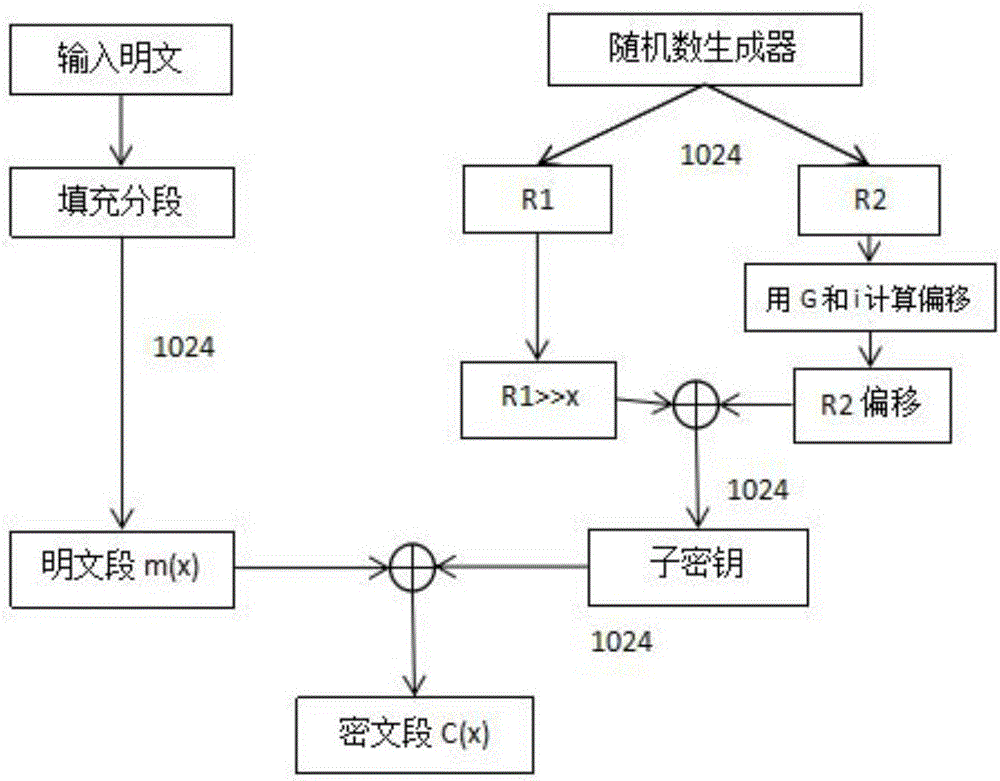
[0060] A1: Let the plaintext population be M, group the plaintext population M to get M i ,M i The packet length is 1024bit (or an integer multiple of 1024bit), so there are M i ∈{M 0 , M 1 ,···,M n-1};
[0061] A2: Use a random number generator to generate two strings of 1024-bit binary sequence random numbers R 1 and R 2 , R 1 and R 2 as the base key, R 1 ∈{0,1} 1024 , R 2 ∈{0,1} 1024 ;
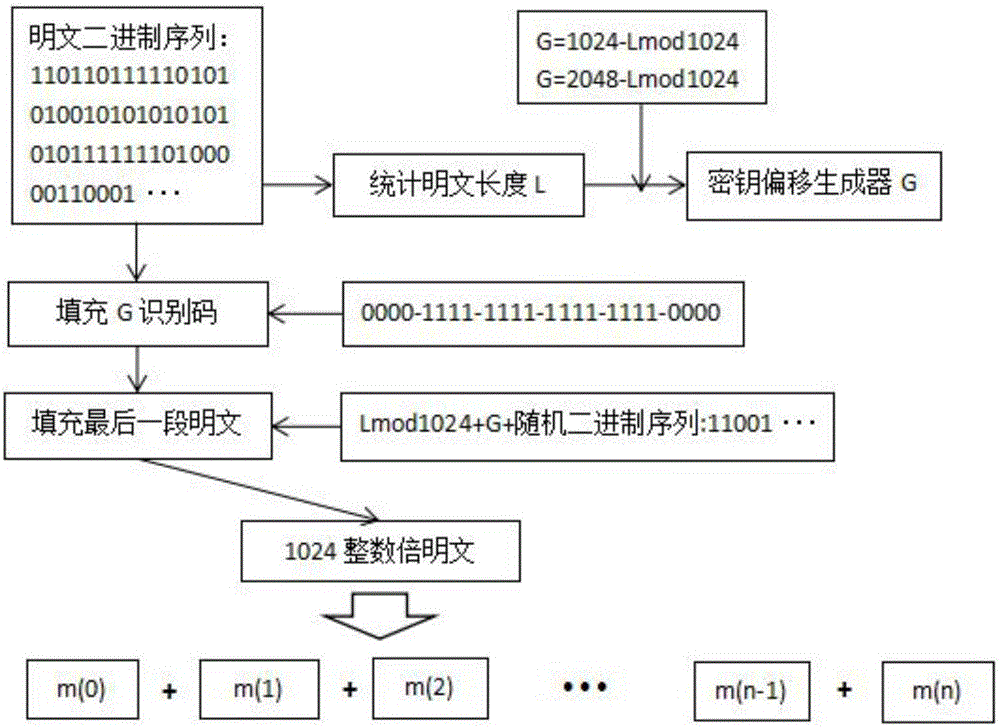
[0062] A3: If figure 1 As shown, the plaintext M is converted into a binary sequence Mess, and the plaintext length L is counted, and the calculation formula is (1); the last group M n-1 It may be less than 1024 bits, so it is necessary to M n-1 for padding; if M n-1 When ∈(0,1000), first fill in the binary key generator identification code after the plaintext, the identification code is 24 bits, the ide...
Embodiment 2
[0081] A kind of decryption algorithm specific process of the novel symmetric key algorithm that is used for high-speed encryption of the present invention is as follows:
[0082] B1: received ciphertext key C R , decrypt it with the RSA-OAEP scheme, and obtain the basic key R 1 and R 2 ;
[0083] B2: First intercept the last 2048-bit binary sequence of the ciphertext, and use the basic key R obtained by decryption 1 and R 2 Perform an XOR operation after offsetting n bits in the same direction as the encryption, and get 2048 bits containing M n-1 the binary sequence;
[0084] B3: contains M for 2048 bits n-1 Search the binary sequence and identify the 24-bit key generator identification code generated when filling, and get the key offset generator G, then discard the random number sequence to get M n-1 Plaintext group, the calculation formula is (13);
[0085]
[0086] B4: From C 0 Starting in the forward direction, one operation is performed according to the numb...
Embodiment 3
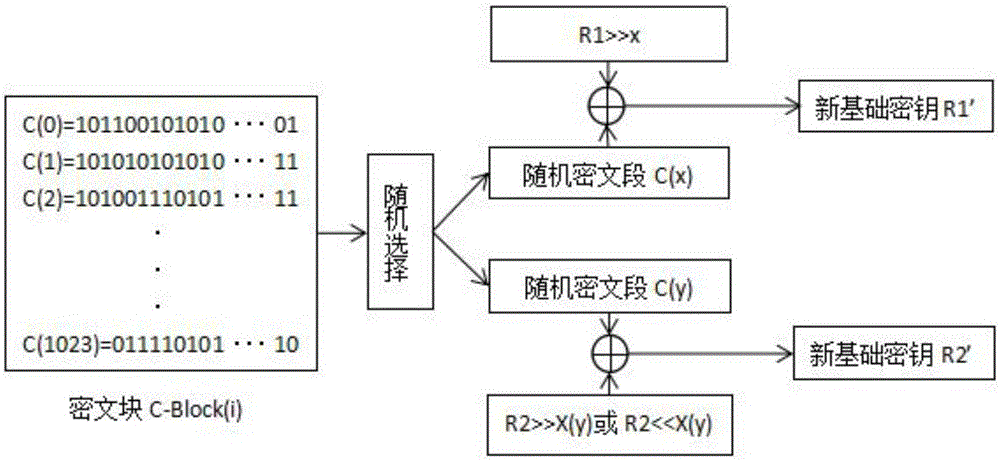
[0089] In order to perform encryption more securely, the basic key of a novel symmetric key algorithm for high-speed encryption of the present invention will be reconstructed.
[0090] A set of two strings of random number sequences R generated by initial encryption 1 and R 2 , first for M n-1 After encryption, and then sequentially from M 0 Start the corresponding offset encryption, for the base key R 1 , each plaintext group encryption is equivalent to shifting one bit to the right, so when encrypting to M 1023 when R 1 Duplication occurs, so when M i When i mod 1024-1=0, the basic key needs to be reconstructed.
[0091] like image 3 As shown, the basic key reconstruction process is as follows:
[0092] C1: a set of base keys R 1 and R 2 , the encrypted plaintext space is 1024×1024 bits, and the encrypted equivalent space is the ciphertext block (C-Block);
[0093] C2: When the basic key needs to be reconstructed, the new basic key is selected from the previous c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com