Catalyst for producing low-carbon olefins from syngas and preparation method thereof
A low-carbon olefin and catalyst technology, applied in the field of catalysts and their preparation, can solve the problems of easy flying temperature, low weight selectivity of low-carbon olefins, difficult reaction heat removal and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
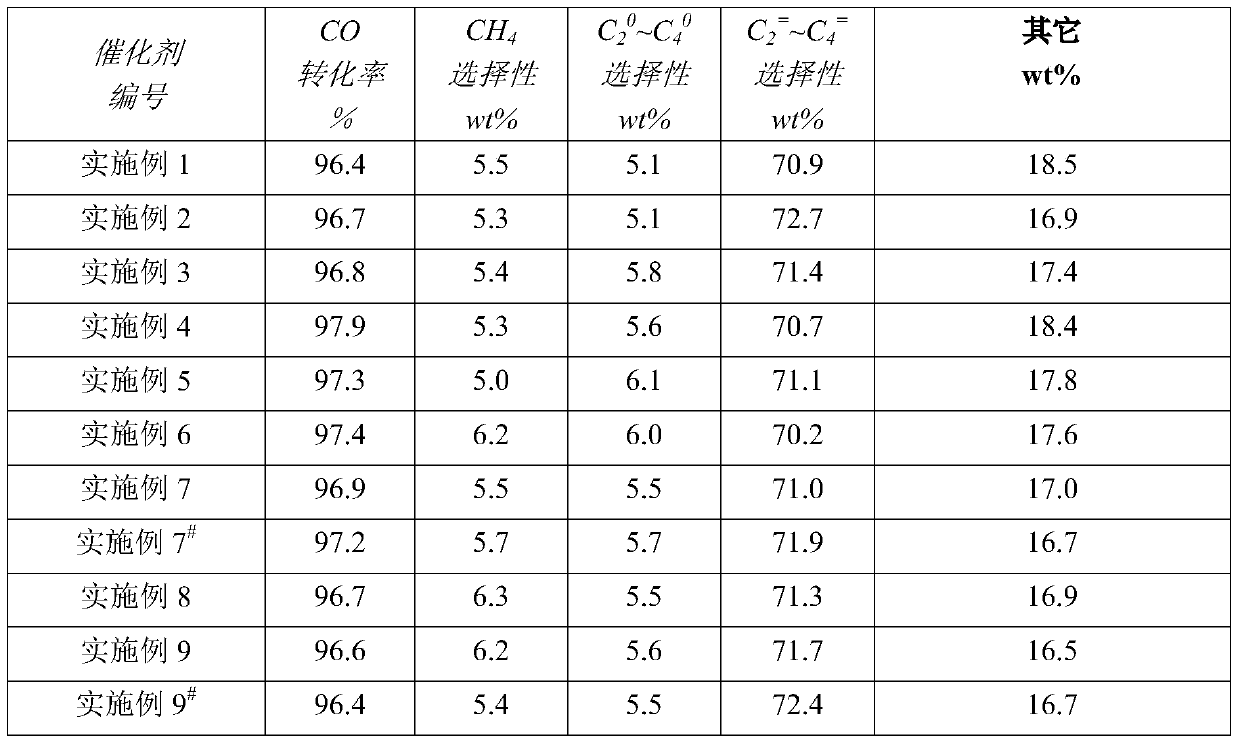
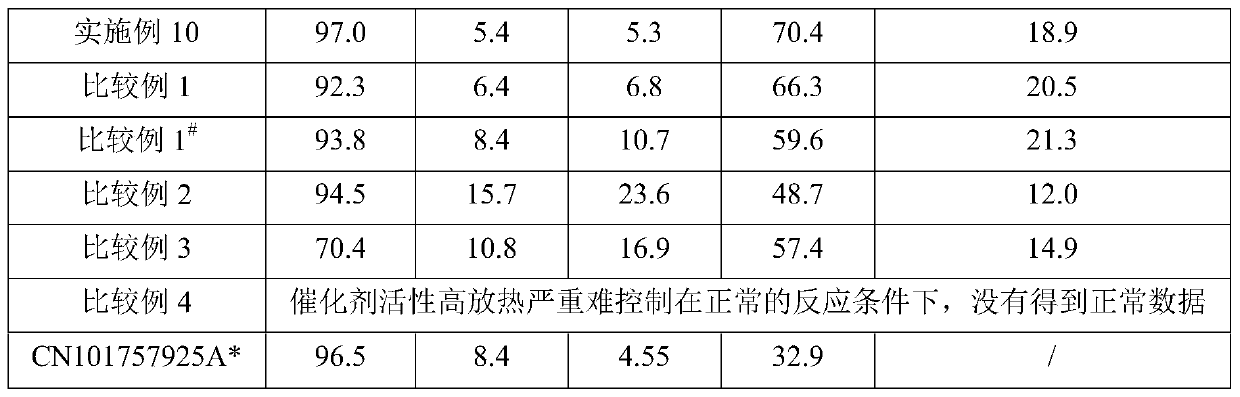
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] 1) Dissolve 606.03g of ferric nitrate nonahydrate and 0.314g of rhodium trichloride in water to form a solution, then centrifuge the solution and 400g of 25% by weight of concentrated ammonia water and wash it three times with deionized water to obtain Mixed precipitation Ⅰ of fresh ferric hydroxide and rhodium oxide;
[0026] 2) 134.5g of 50% by weight of manganese nitrate and 3.13g of gallium nitrate nonahydrate were dissolved in water to make solution II;
[0027] 3) mixing and beating the solution II and the mixed sediment I to obtain a colloidal slurry III;
[0028] 4) Dissolve 0.042g of potassium hydroxide in water and add it to slurry III, mix and beat, adjust the pH value of the slurry to 5 with ammonia water, and obtain a uniform slurry that is uniformly dispersed in a sol state and will not be layered after a long period of storage Material IV (45% solid content);
[0029] 5) The slurry IV is spray-dried and molded. The inlet temperature of the sprayer is 38...
Embodiment 2
[0033] 1) Get 606.03g of ferric nitrate nonahydrate and 44.79g of iridium trichloride to be dissolved in water to form a solution, then the solution is centrifuged with 400g of 25% by weight concentrated ammonia water and washed three times with deionized water to obtain Mixed precipitation of fresh ferric hydroxide and iridium oxide I;
[0034]2) 1345g of 50% by weight manganese nitrate and 117.3g of indium nitrate pentahydrate were dissolved in water to make solution II;
[0035] 3) mixing and beating the solution II and the mixed sediment I to obtain a colloidal slurry III;
[0036] 4) Dissolve 4.20g of potassium hydroxide in water and add it to the slurry III, mix and beat, adjust the pH value of the slurry to 1 with dilute nitric acid, and obtain a uniform slurry that is uniformly dispersed in the form of a sol and will not be stratified after a long period of storage Material IV (15% solid content);
[0037] 5) Slurry IV is spray-dried and molded. The inlet temperature...
Embodiment 3
[0041] 1) Dissolve 367.43g of iron citrate and 1.57g of rhodium trichloride in water to form a solution, and then centrifuge the solution and 400g of 25% by weight of strong ammonia in parallel flow, and wash with deionized water three times to obtain fresh hydrogen Mixed precipitation of iron oxide and rhodium oxide Ⅰ;
[0042] 2) 269.0g of 50% by weight of manganese nitrate and 125.2g of gallium nitrate nonahydrate were dissolved in water to make solution II;
[0043] 3) mixing and beating the solution II and the mixed sediment I to obtain a colloidal slurry III;
[0044] 4) Dissolve 1.05g of sodium hydroxide in water and add it to slurry III, mix and beat, and at the same time adjust the pH of the slurry to 3 with dilute ammonia water to obtain a sol-like dispersion that is uniform and will not be layered after long-term storage. Slurry IV (solid content 35%);
[0045] 5) Slurry slurry IV is spray-dried and formed, the inlet temperature of the sprayer is 230°C, the outlet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com