Catalyst for preparing low-carbon olefins from synthesis gas and preparation method thereof
A technology of low-carbon olefins and catalysts, applied in the field of catalysts and their preparation, can solve the problems of easy deactivation of catalysts, easy overheating, and difficulty in removing heat from reactions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
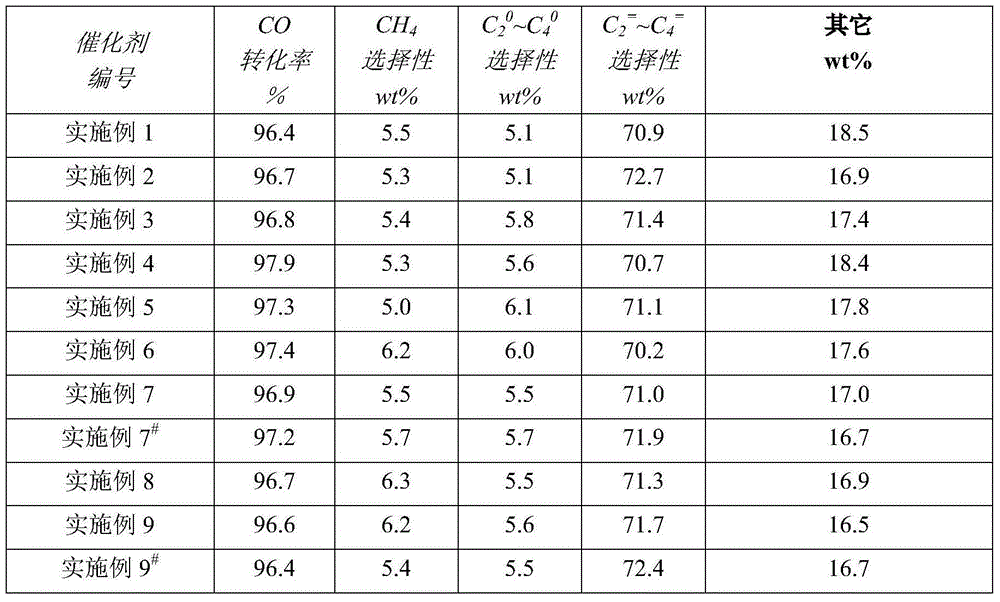
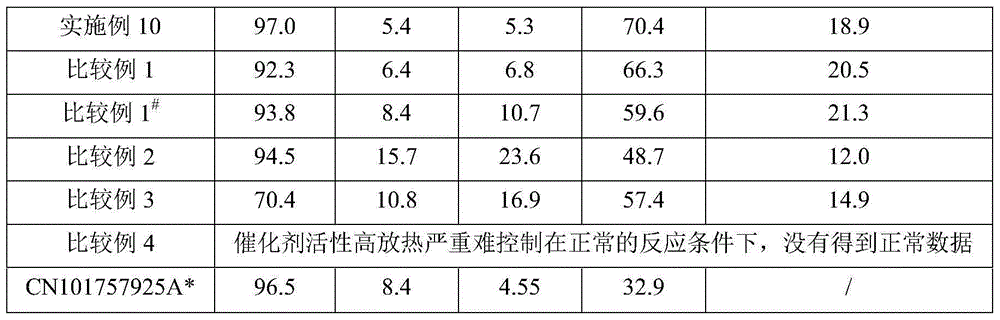
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] 1) Dissolve 606.03g of ferric nitrate nonahydrate and 0.314g of rhodium trichloride in water to form a solution, then centrifuge the solution and 400g of 25% by weight of concentrated ammonia water and wash it three times with deionized water to obtain Mixed precipitation Ⅰ of fresh ferric hydroxide and rhodium oxide;
[0026] 2) 134.5g of 50% by weight of manganese nitrate and 3.13g of gallium nitrate nonahydrate were dissolved in water to make solution II;
[0027] 3) mixing and beating the solution II and the mixed sediment I to obtain a colloidal slurry III;
[0028] 4) Dissolve 0.042g of potassium hydroxide in water and add it to slurry III, mix and beat, adjust the pH value of the slurry to 5 with ammonia water, and obtain a uniform slurry that is uniformly dispersed in a sol state and will not be layered after a long period of storage Material IV (45% solid content);
[0029] 5) The slurry IV is spray-dried and molded. The inlet temperature of the sprayer is 38...
Embodiment 2
[0033] 1) Get 606.03g of ferric nitrate nonahydrate and 44.79g of iridium trichloride to be dissolved in water to form a solution, then the solution is centrifuged with 400g of 25% by weight concentrated ammonia water and washed three times with deionized water to obtain Mixed precipitation of fresh ferric hydroxide and iridium oxide I;
[0034]2) 1345g of 50% by weight manganese nitrate and 117.3g of indium nitrate pentahydrate were dissolved in water to make solution II;
[0035] 3) mixing and beating the solution II and the mixed sediment I to obtain a colloidal slurry III;
[0036] 4) Dissolve 4.20g of potassium hydroxide in water and add it to the slurry III, mix and beat, adjust the pH value of the slurry to 1 with dilute nitric acid, and obtain a uniform slurry that is uniformly dispersed in the form of a sol and will not be stratified after a long period of storage Material IV (15% solid content);
[0037] 5) Slurry IV is spray-dried and molded. The inlet temperature...
Embodiment 3
[0041] 1) get 367.43g ferric citrate and 1.57g rhodium trichloride to be dissolved in water and make solution, then this solution and the strong ammonia water of 400g 25% by weight co-flow and centrifuge, obtain fresh after washing three times with deionized water Mixed precipitation of iron hydroxide and rhodium oxide Ⅰ;
[0042] 2) 269.0g of 50% by weight of manganese nitrate and 125.2g of gallium nitrate nonahydrate were dissolved in water to make solution II;
[0043] 3) mixing and beating the solution II and the mixed sediment I to obtain a colloidal slurry III;
[0044] 4) Dissolve 1.05g of sodium hydroxide in water and add it to slurry III, mix and beat, and at the same time adjust the pH of the slurry to 3 with dilute ammonia water to obtain a sol-like dispersion that is uniform and will not be layered after long-term storage. Slurry IV (solid content 35%);
[0045] 5) Slurry slurry IV is spray-dried and formed, the inlet temperature of the sprayer is 230°C, the outl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com