Polyolefin graphene nanocomposite material, and preparation method thereof
A nanocomposite material and nanocomposite powder technology are applied in the field of polyolefin graphene nanocomposite materials and their preparation, which can solve the problems of difficulty in obtaining nanometer-level polymer graphene nanocomposite materials, poor dispersion effect, etc., and achieve a wide range of applications. Adaptability and industrial compatibility, effects of improved elongation at break, improved impact strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
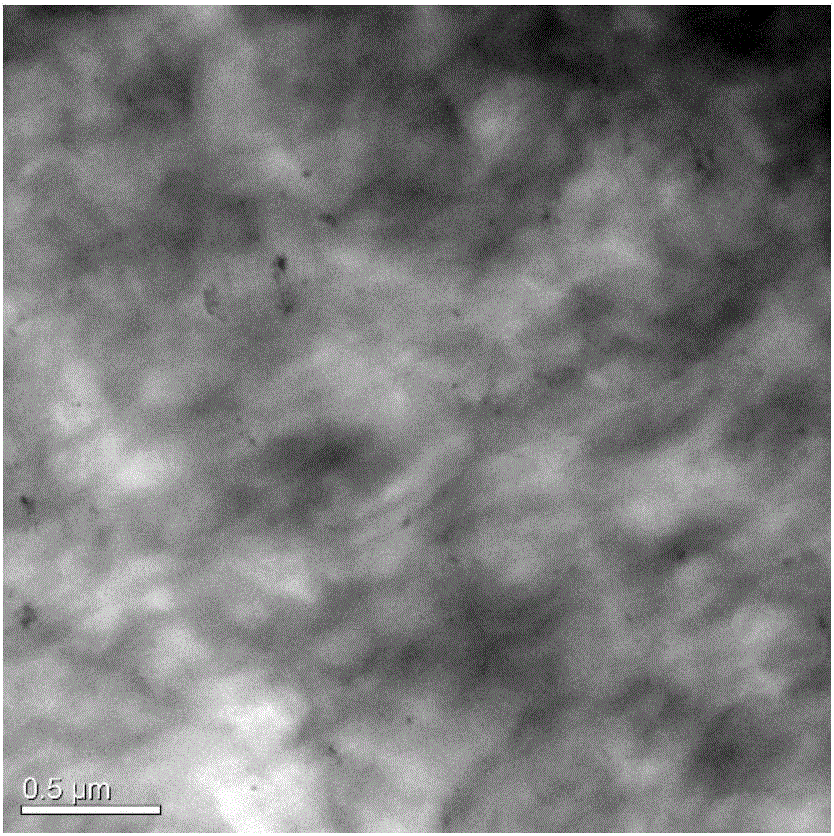
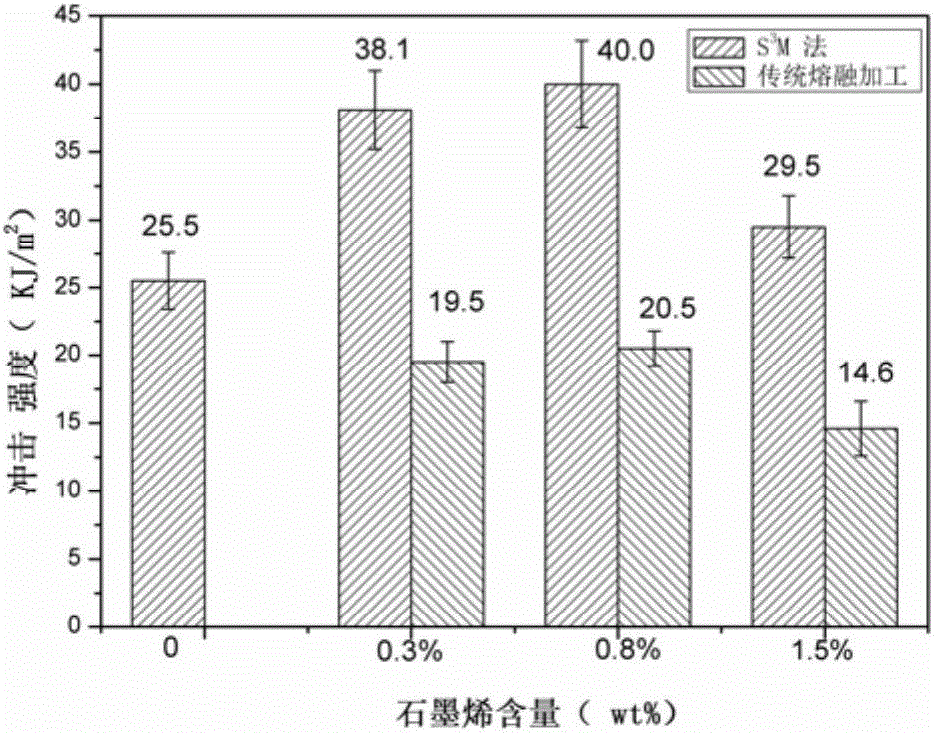
[0044] Put commercially available high-density polyethylene (HDPE) into the grinding disc type solid-phase force chemical reactor, pass cooling circulating water at room temperature during the grinding process, and control the temperature of the grinding disc surface at 20°C, the pressure at 10KN, and the rotation speed at 50 rpm / min, cyclic grinding 15 times to obtain ultrafine high-density polyethylene powder with an average volume particle size of about 300 μm. Mechanically mix 100 parts by weight of high-density polyethylene ultrafine powder with 3 parts by weight of reduced graphite oxide, add it to the disc type solid-phase mechanochemical reactor again, keep the parameters unchanged, and continue grinding for 15 times to obtain high-density Polyethylene / graphene composite powder, the average particle size is about 100μm.
[0045] Add high-density polyethylene / graphene composite powder to high-density polyethylene pure material and dilute it to a graphene mass fraction ...
Embodiment 2
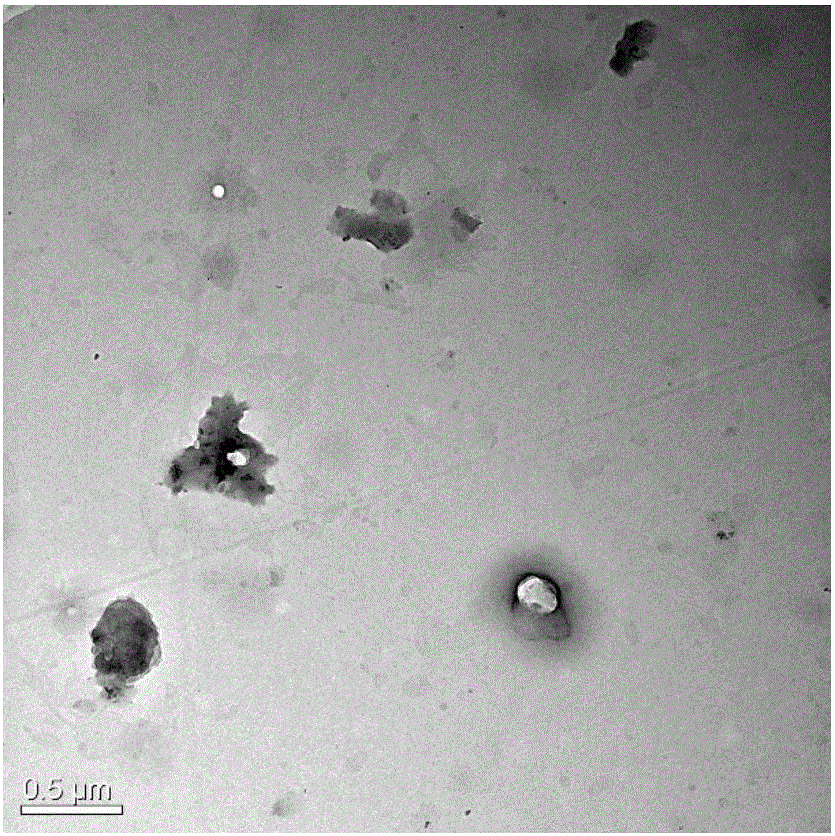
[0048] Put commercially available high-density polyethylene (HDPE) into the disc-type solid-phase mechanochemical reactor, pass cooling circulating water at room temperature during the milling process, and control the temperature of the disc surface at 20°C, the pressure at 15KN, and the speed at 50 rpm / min, and circularly grind 20 times to obtain ultrafine high-density polyethylene powder with an average volume particle size of about 150 μm. Mechanically mix 100 parts by weight of low-density polyethylene ultra-fine powder with 1.5 parts by weight of reduced graphite oxide, add it to a disc-type solid-phase mechanochemical reactor again, keep the parameters constant, and continue to grind for 20 times to obtain high-density polyethylene powder. Ethylene / graphene composite powder, the average particle size is about 80μm.
[0049] The high-density polyethylene / graphene composite powder is added to the high-density polyethylene pure material and diluted to a graphene mass fract...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Put commercially available high-density polyethylene (HDPE) into the disc-type solid-phase mechanochemical reactor, pass cooling circulating water at room temperature during the milling process, and control the temperature of the disc surface at 10°C, the pressure at 15KN, and the speed at 100 rpm / min, cyclic grinding 10 times to obtain ultrafine high-density polyethylene powder with an average volume particle size of about 300 μm. 100 parts by weight of high-density polyethylene ultrafine powder is mechanically mixed with 10 parts by weight of ball milling mechanically exfoliated graphene, and then added to the disc type solid-phase mechanochemical reactor, keeping the parameters constant, and continuing to grind 20 times to obtain a low Density polyethylene / graphene composite powder, the average particle size is about 100μm.
[0053] The high-density polyethylene / graphene composite powder is added to the high-density polyethylene pure material and diluted to a graphe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com