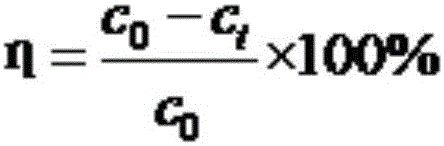Method for degrading residual polyacrylamide in slime water through composite bacteria
A technology of polyacrylamide and compound strains, which is applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., and can solve the problems that polyacrylamide research has not been reported.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0035] 1) Get the Erlenmeyer flask containing 100ml degradation medium, wherein the concentration of polyacrylamide is 100mg / L, with 2% Phanerochaete chrysosporium spore suspension and 2% Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides suspension Added together to the degradation medium;
[0036] 2) Use a pen-type pH meter to adjust the pH value of the medium to 5, and place it in a shaking incubator at 30°C and 130r / min for continuous cultivation for 6 days;
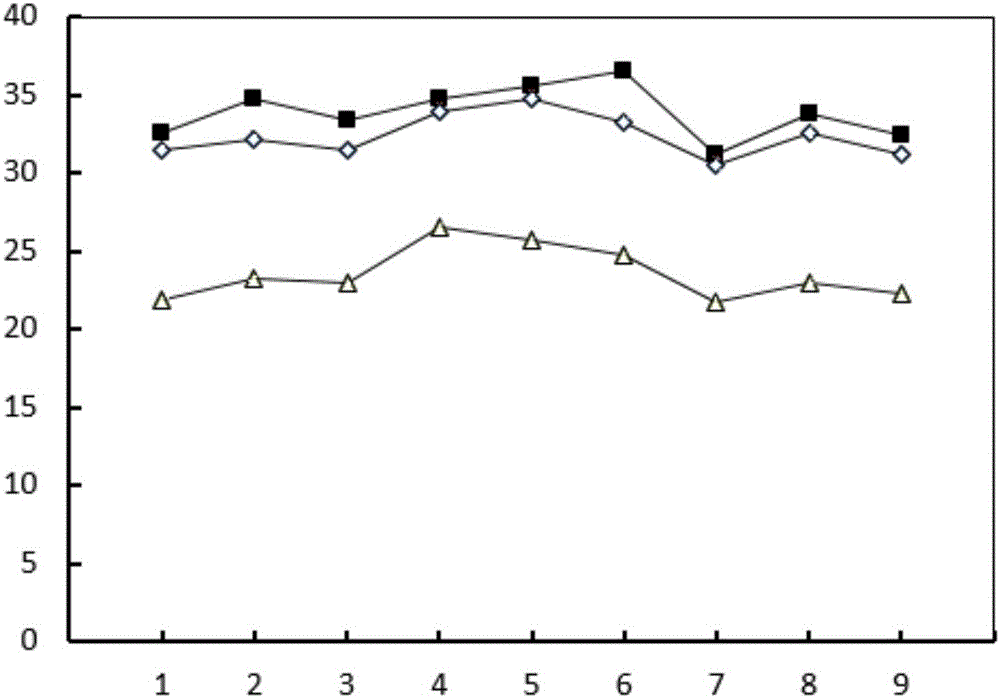
[0037] 3) Measure the absorbance of the degradation medium at 660 nm with a UV-5100 ultraviolet spectrophotometer every day during the culture period, and compare with the standard to obtain the corresponding polymer concentration, and the degradation rate is 32.5%. Under other conditions unchanged, the polyacrylamide biodegradation bacteria were replaced with 2ml of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides suspension, the degradation rate was 21.9%, and the polyacrylamide biodegradation bacteria were replaced with 2ml of Chrysosporium Phaneroderma ...
example 2
[0039] 1) Get the Erlenmeyer flask containing 100ml degradation medium, wherein the concentration of polyacrylamide is 100mg / L, with 3% Phanerochaete chrysosporium spore suspension and 3% Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides suspension Added together to the degradation medium;
[0040] 2) Use a pen-type pH meter to adjust the pH value of the medium to 6, and place it in a shaking incubator at 30°C and 140r / min for continuous cultivation for 6 days;
[0041] 3) During the culture period, the absorbance of the degradation medium was measured at 660nm with a UV-5100 ultraviolet spectrophotometer every day, and the corresponding polymer concentration could be obtained by comparing with the standard, and the degradation rate was 34.7%. Under other conditions unchanged, the polyacrylamide biodegradation bacteria were replaced with 3ml of Rhodopseudomonas globosa suspension, the degradation rate was 23.2%, and the polyacrylamide biodegradation bacteria were replaced with 3ml of Chrysosporium...
example 3
[0043] 1) Get the Erlenmeyer flask containing 100ml degradation medium, wherein the concentration of polyacrylamide is 100mg / L, with 4% Phanerochaete chrysosporium spore suspension and 4% Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides suspension Added together to the degradation medium;
[0044] 2) Use a pen-type pH meter to adjust the pH value of the medium to 7, and place it in a shaking incubator at 30°C and 150r / min for continuous cultivation for 6 days;
[0045] 3) Measure the absorbance of the degradation medium at 660 nm with a UV-5100 ultraviolet spectrophotometer every day during the culture period, compare with the standard to obtain the corresponding polymer concentration, and the degradation rate is 33.4%. Under other conditions unchanged, the polyacrylamide biodegradation bacteria were replaced with 4ml of Rhodopseudomonas globosa suspension, and the degradation rate was 22.9%. Phaneroderma spore suspension, the degradation rate was 31.4%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com