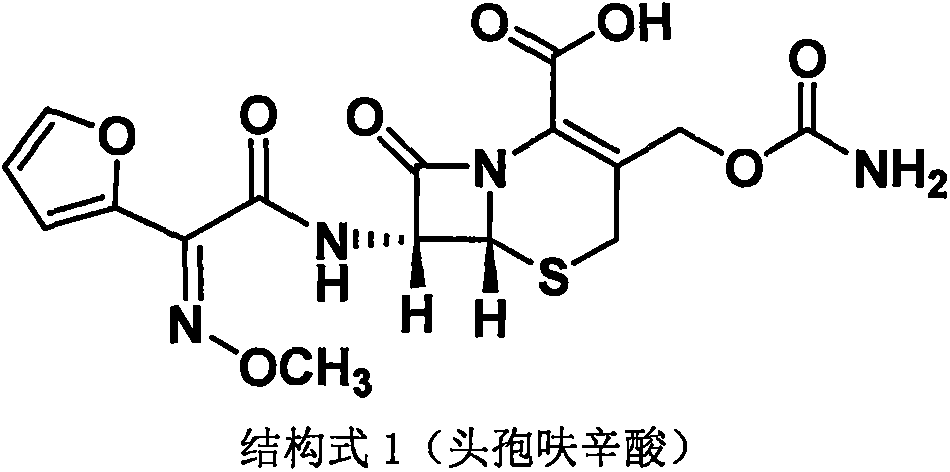
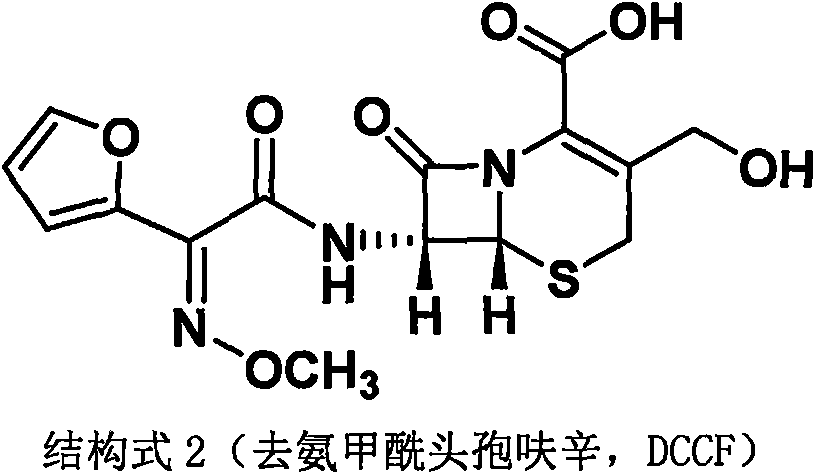
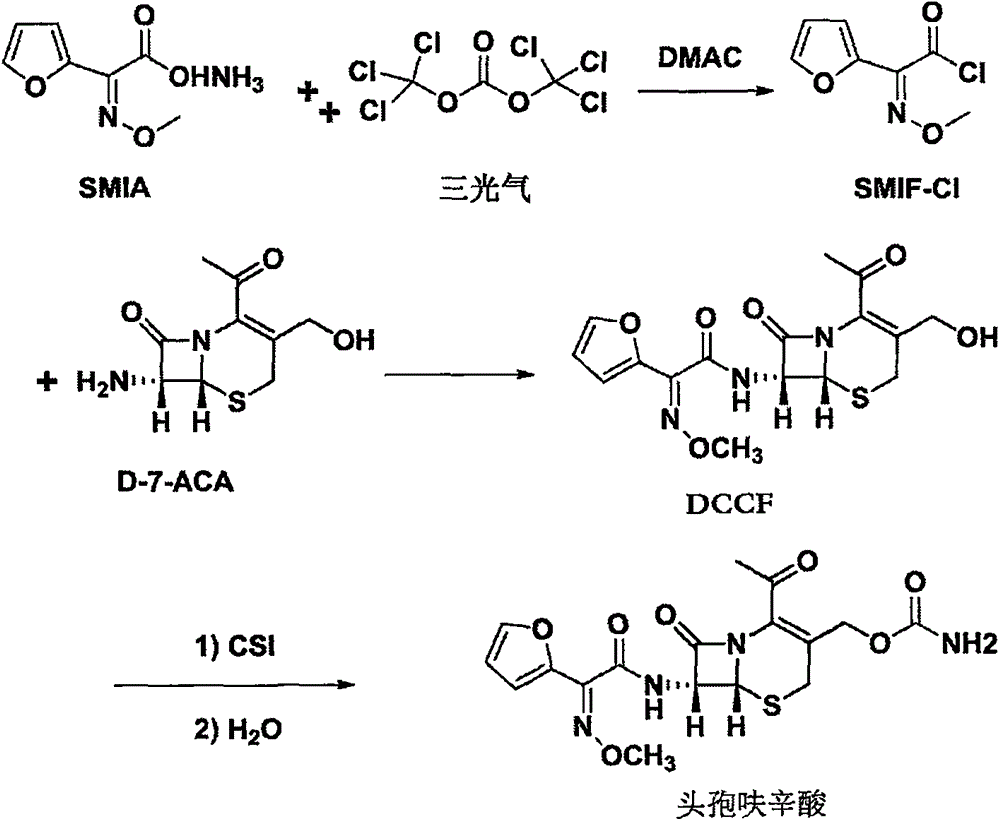
Method for preparing cefuroxime acid
A technology of cefuroxime acid and furoxine, which is applied in the field of drug synthesis, can solve the problems of large equipment damage, high recovery cost, harsh reaction conditions, etc., and achieve the effect of low cost and high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1 Preparation of decarbamoylcefuroxine (DCCF)
[0044] Experiment (1): The method of the present invention prepares decarbamylated cefuroxime (DCCF)
[0045] (a) Dissolve triphosgene (24.4g) in carbon dichloride (350ml), stir and cool down to -21°C, add DMAC (75ml), SMIA (41g,), and control the temperature to -10°C and stir to react;
[0046] (b) After the reaction is completed, control the temperature to about 0°C and add purified water, stir and stand still to separate the layers, remove the water layer, and store the organic layer at low temperature for later use.
[0047] (c) Add purified water (230ml) to D-7-ACA (42.3g), cool down to about 0°C, add 15% NaOH dropwise to control pH=8.0, and stir until completely dissolved.
[0048](d) Drop the organic layer solution prepared in step (b) into the D-7-ACA solution prepared in step (c), and simultaneously add 15% NaOH dropwise to control pH6.0. After the dropwise addition was completed, let stand to separate t...
Embodiment 2
[0055] The preparation of embodiment 2 cefuroxime acid
[0056] Experiment (3): the method of the present invention prepares cefuroxime acid
[0057] (1) Dissolve DCCF (40.0g) in methyl acetate (360ml), cool down to -39°C, add CSI (23.1g), and react at -25°C.
[0058] (2) After the reaction is completed, add purified water and heat up to 20°C for hydrolysis.
[0059] (3) After the hydrolysis is complete, adjust the pH to 4.5 with sodium bicarbonate (48.0g), add methyl acetate (240ml), adjust the pH to 2.0 with 30% hydrochloric acid, let stand to separate the organic layer, and concentrate at temperature T=40°C to Viscous concentrated organic layer.
[0060] (4) Add purified water to the concentrated organic layer, lower the temperature to 10° C., filter after crystallization, wash the filter cake with purified water, and dry to obtain 41.2 g of cefuroxime acid with a molar yield of 92.6% and an HPLC purity of 99.5%.
[0061] Experiment (4): Prepare cefuroxime acid according...
Embodiment 3
[0067] (1) Dissolve DCCF (40.0g) in ethyl acetate (360ml), the feed ratio of DCCF and ethyl acetate is 1:9 (w / v), cool down to -35°C, add CSI (23.1g), control Reaction at -20°C.
[0068] (2) After the reaction is completed, add purified water and heat up to 25°C for hydrolysis.
[0069] (3) After the hydrolysis is complete, adjust the pH to 4.9 with sodium bicarbonate (48.0 g), add ethyl acetate (240 ml), adjust the pH to 2.0 with 30% hydrochloric acid, let stand to separate the organic layer, and concentrate at temperature T=40°C to Viscous concentrated organic layer.
[0070] (4) Add purified water to the concentrated organic layer, lower the temperature to 5° C., filter after crystallization, wash the filter cake with purified water, and dry to obtain 41.1 g of cefuroxime acid with a molar yield of 92.3% and an HPLC purity of 99.3%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com